|
Crailsheim Station
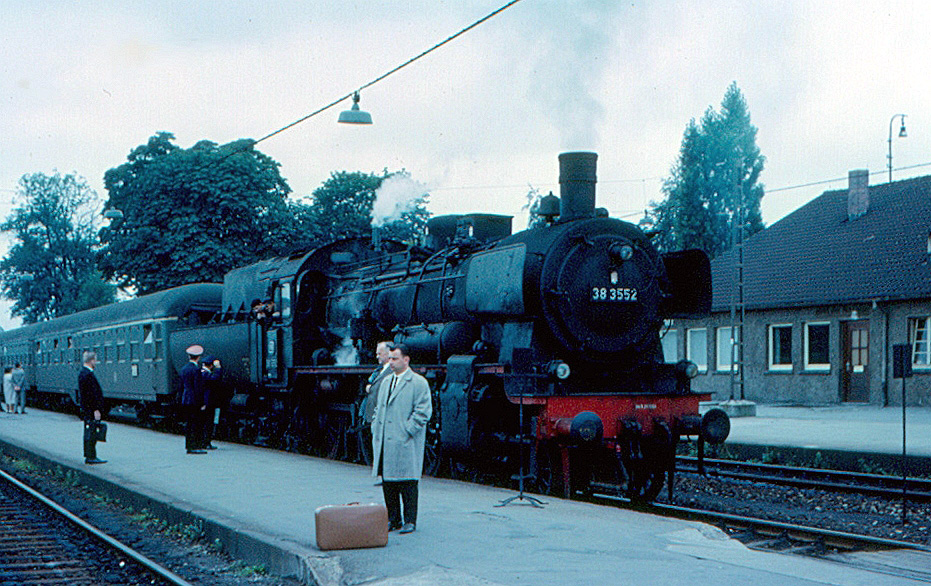
Crailsheim station is a junction station in the German state of Baden-Württemberg where four railway lines converge. It lies at the 30.4 km point (from Goldshöfe) on the Upper Jagst Railway, with the chainage continuing on the Hohenlohe Railway. The chainage on the Tauber Valley Railway and the line to Nuremberg starts at the station. With its four platform tracks and numerous passing tracks and sidings, it is the largest station in the district of Schwäbisch Hall. It is by served by Intercity and regional trains. History The construction of a railway line from Heilbronn via Schwäbisch Hall to Wasseralfingen (near Aalen) was authorised in a resolution of the parliament of the Kingdom of Württemberg on 17 November 1858. The proponents planned a route along the Jagst to connect the cities of Crailsheim and Ellwangen. The route was in competition with a proposed line from Gaildorf and the upper Kocher valley, which was a much shorter route. Crailsheim mayor Nagel a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crailsheim
Crailsheim is a town in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. Incorporated in 1338, it lies east of Schwäbisch Hall and southwest of Ansbach in the Schwäbisch Hall district. The city's main attractions include two Evangelical churches, a Catholic church, and the 67 metre tower of its town hall. History Crailsheim is famed for withstanding a siege by forces of three imperial cities - Schwäbisch Hall, Dinkelsbühl, and Rothenburg ob der Tauber - lasting from 1379 until 1380, a feat which it celebrates annually. Crailsheim became a possession of the Burgrave of Nuremberg following the siege. In 1791 it became part of the Prussian administrative region, before returning to Bavaria in 1806 and becoming a part of Württemberg in 1810. Crailsheim's railroad and airfield were heavily defended by the Waffen-SS during World War II. Following an American assault in mid-April 1945, the town was occupied briefly by US forces before being lost to a German counter-offensive. Intense U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch''). The three administrative regions of Lower, Middle and Upper Franconia (largest cities, respectively: Würzburg, Nuremberg and Bamberg) in the State of Bavaria are part of the cultural region of Franconia, as are the adjacent Franconian-speaking South Thuringia, south of the Rennsteig ridge (largest city: Suhl), Heilbronn-Franconia (largest city: Schwäbisch Hall) in the state of Baden-Württemberg, and small parts of the state of Hesse. Those parts of the Vogtland lying in the state of Saxony (largest city: Plauen) are sometimes regarded as Franconian as well, because the Vogtlandian dialects are mostly East Franconian. The inhabitants of Saxon Vogtland, however, mostly do not consider themselves as Franconian. On the other hand, the inhabitants of the Hessian-speaking parts of Lower Franconia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
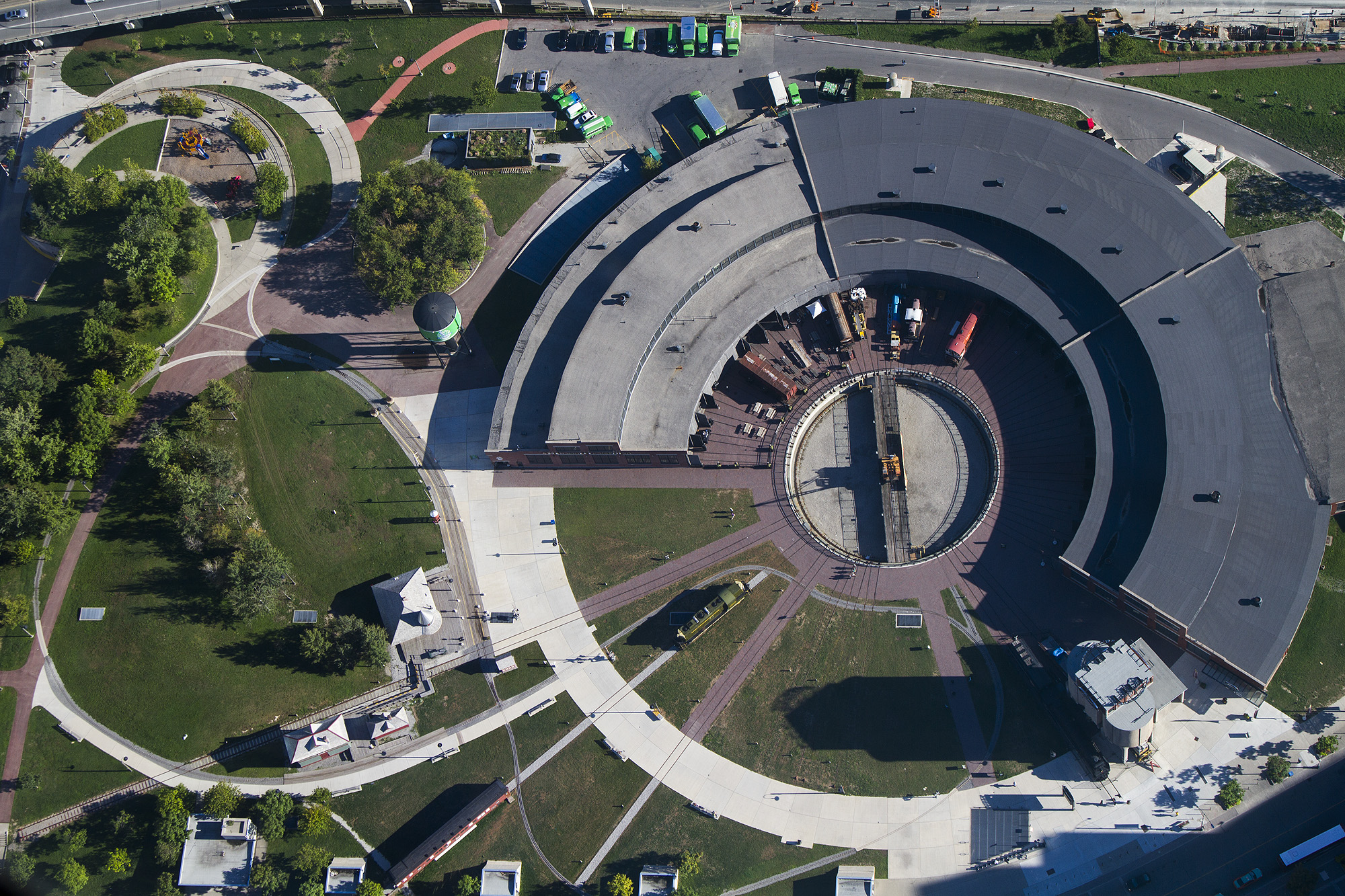
Railway Roundhouse
A railway roundhouse is a building with a circular or semicircular shape used by railways for servicing and storing locomotives. Traditionally, though not always the case today, these buildings surrounded or were adjacent to a turntable. Overview Early steam locomotives normally traveled forwards only. Although reverse operations capabilities were soon built into locomotive mechanisms, the controls were normally optimized for forward travel, and the locomotives often could not operate as well in reverse. Some passenger cars, such as observation cars, were also designed as late as the 1960s for operations in a particular direction. Turntables allowed locomotives or other rolling stock to be turned around for the return journey, and roundhouses, designed to radiate around the turntables, were built to service and store these locomotives. Most modern diesel and electric locomotives can run equally well in either direction, and many are push-pull trains with control cabs at ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Bavarian State Railways
The Royal Bavarian State Railways (''Königliche Bayerische Staats-Eisenbahnen'' or ''K.Bay.Sts.B.'') was the state railway company for the Kingdom of Bavaria. It was founded in 1844. The organisation grew into the second largest of the German state railways (after that of the Prussian state railways) with a railway network of 8,526 kilometres (including the Palatinate Railway or ''Pfalzbahn'') by the end of the First World War. Following the abdication of the Bavarian monarchy at the end of the First World War, the 'Royal' title was dropped and on 24 April 1920 the Bavarian State Railway (''Bayerische Staatseisenbahn''), as it was now called, was merged into the newly formed German Reich Railways Authority or Deutsche Reichseisenbahnen as the Bavarian Group Administration (''Gruppenverwaltung Bayern''). The management of the Bavarian railway network was divided into four Reichsbahn divisions: Augsburg, Munich, Nuremberg and Regensburg. The former Palatinate Railway formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dombühl
Dombühl is a municipality in the district of Ansbach in Bavaria in Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe .... Division of the municipality Dombühl has eight districts: References External links * Ansbach (district) {{Ansbachdistrict-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Württemberg State Railways
The Royal Württemberg State Railways (''Königlich Württembergische Staats-Eisenbahnen'' or ''K.W.St.E.'') were the state railways of the Kingdom of Württemberg (from 1918 the ''People's State of Württemberg'') between 1843 and 1920. Please see also the main article History of the railway in Württemberg. Early history As in many other states of the German Empire, there was increasing debate about how to improve transport communications across the country from about 1825. Private interest groups were formed and, from 1834, the state also worked on the question, giving experts the task of finding suitable solutions. After years of preparatory work, it was decided to set up a railway network, the main lines of which would be built by the state. The Railway Bill of 18 April 1843, established the legal foundation for the construction of the railway network; this date is seen as the birthday for the ''K.W.St.E.''. The law expressly envisaged that the construction of branch r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest city in Germany. On the Pegnitz River (from its confluence with the Rednitz in Fürth onwards: Regnitz, a tributary of the River Main) and the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal, it lies in the Bavarian administrative region of Middle Franconia, and is the largest city and the unofficial capital of Franconia. Nuremberg forms with the neighbouring cities of Fürth, Erlangen and Schwabach a continuous conurbation with a total population of 800,376 (2019), which is the heart of the urban area region with around 1.4 million inhabitants, while the larger Nuremberg Metropolitan Region has approximately 3.6 million inhabitants. The city lies about north of Munich. It is the largest city in the East Franconian dialect area (colloquially: "F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Würzburg
Würzburg (; Main-Franconian: ) is a city in the region of Franconia in the north of the German state of Bavaria. Würzburg is the administrative seat of the ''Regierungsbezirk'' Lower Franconia. It spans the banks of the Main River. Würzburg is situated approximately east-southeast of Frankfurt am Main and approximately west-northwest of Nuremberg (). The population (as of 2019) is approximately 130,000 residents. The administration of the ''Landkreis Würzburg'' ( district of Würzburg) is also located in the town. The regional dialect is East Franconian. History Early and medieval history A Bronze Age (Urnfield culture) refuge castle, the Celtic Segodunum,Koch, John T. (2020)CELTO-GERMANIC Later Prehistory and Post-Proto-Indo-European vocabulary in the North and West p. 131 and later a Roman fort, stood on the hill known as the Leistenberg, the site of the present Fortress Marienberg. The former Celtic territory was settled by the Alamanni in the 4th or 5th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kocher
The Kocher () is a -longincluding its source river Schwarzer Kocher right tributary of the Neckar in the north-eastern part of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The name "Kocher" originates from its Celtic name "cochan" and probably means winding, meandering river. Its total drainage area is . The Kocher rises in the eastern foothills of the Swabian Alb from two karst springs, the Schwarzer (black) Kocher and the Weißer (white) Kocher, that join in Unterkochen near Aalen. The Schwarzer Kocher is approximately long. Its source discharge varies between 50 L/s and 4,000 L/s with an average of 680 L/s. The long Weißer Kocher has an average discharge of 400 L/s. Course The Schwarzer Kocher rises south of Oberkochen. The second source, the Weißer Kocher rises west of Unterkochen from many small sources. The name Weißer Kocher comes from the white foam on the water when it quickly rushes over the stones. In contrast, the Schwarzer Kocher flows rather slowly and the covered ground ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaildorf
Gaildorf is a town in the district of Schwäbisch Hall, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is located on the river Kocher, 13 km south of Schwäbisch Hall. Gaildorf is the approximate center of the Limpurger Land district, formerly a county of the Holy Roman Empire ruled by the counts Schenk von Limpurg until their extinction in 1713, thereafter inherited by a number of female heirs, and mediatized to the Kingdom of Württemberg in 1806. Notable people * (1806–1883), member of Landtag * (1700-1783), organ-maker * (1807–1857), Württembergian city councilman * (1817–1907), doctor and poet (son of Justinus Kerner) * (1824–1895), merchant and member of landtag * (1835–1914), prime minister of Württemberg * (1839–1892), Schultheiß and politician * (1847–1928), pharmacist and fossil-collector in Crailsheim * (born 1926), agriculturalist * (1936–2009), writer * (born 1959), composer * (born 1969), politician (CDU) *Hermann Frasch Herman Frasch r Hermann Fras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellwangen
Ellwangen an der Jagst, officially Ellwangen (Jagst), in common use simply Ellwangen () is a town in the district of Ostalbkreis in the east of Baden-Württemberg in Germany. It is situated about north of Aalen. Ellwangen has 25,000 inhabitants. Geography Ellwangen is situated in the valley of the river Jagst, between the foothills of the Swabian Alb and Virngrund (ancient Virgundia) forest, the latter being part of the Swabian-Franconian Forest. The Jagst runs through Ellwangen from south to north. History The town developed in the 7th century as an Alemannic settlement in the Virgunna forest next to the Franconian-Swabian border. In 764 the Frankish noble Hariolf, Bishop of Langres, founded a Benedictine monastery, Ellwangen Abbey, on a hill next to the settlement. The monastery was mentioned in a document of Louis the Pious as ''Elehenuuwang'' in 814. It became a ''Reichsabtei'' in 817. From 870 to 873 the Byzantine Greek "Apostle of the Slavs" Saint Methodius was imprison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |