|
Coverage Data
A coverage is the digital representation of some spatio-temporal phenomenon. ISO 19123 provides the definition: * '' feature that acts as a function to return values from its range for any direct position within its spatial, temporal or spatiotemporal domain'' Coverages play an important role in geographic information systems (GIS), geospatial content and services, GIS data processing, and data sharing. A coverage is represented by its "domain" (the universe of extent) and a collection representing the coverage's values at each defined location within its range. For example, a satellite image derived from remote sensing might record varying degrees of light pollution. Aerial photography, land cover data, and digital elevation models all provide coverage data. Generally, a coverage can be multi-dimensional, such as 1-D sensor timeseries, 2-D satellite images, 3-D x/y/t image time series or x/y/z geo tomograms, or 4-D x/y/z/t climate and ocean data. However, coverages ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ArcInfo
ArcInfo (formerly ARC/INFO) is a full-featured geographic information system produced by Esri, and is the highest level of licensing (and therefore functionality) in the ArcGIS Desktop product line. It was originally a command line interface, command-line based system. The command-line processing abilities are now available through the GUI of the ArcGIS Desktop product. History ARC/INFO ESRI launched the first version of ARC/INFO - which it claims as "the very first modern GIS" - in 1982 on minicomputers. The name refers to its architecture as a geographic information system composed of: # geographic input, processing, and output tools ("ARC") with # a complementary, but separate database ("INFO")INFO, a single-user, relational database product developed by Henco, Inc., now supported by Doric. Inc. Retrieved frodoric.co.uk/ref> The early releases of ARC/INFO comprised a set of FORTRAN programs linked together and accessed through a command-line interface built with the scripti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Web Coverage Processing Service
The Web Coverage Processing Service (WCPS) defines a language for filtering and processing of multi-dimensional raster coverages, such as sensor, simulation, image, and statistics data. The Web Coverage Processing Service is maintained by the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC). This raster query language allows clients to obtain original coverage data, or derived information, in a platform-neutral manner over the Web. Overview WCPS allows to generate pictures suitable for displaying to humans and information concise enough for further consumption by programs. In particular, the formally defined syntax and semantics make WCPS amenable to program-generated queries and automatic service chaining. As the WCPS language is not tied to any particular transmission protocol, the query paradigm can be embedded into any service framework, such as OGC Web Coverage Service (WCS) and OGC Web Processing Service (WPS). The current WCPS version is 1.0. The standards document, available from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Web Feature Service
In computing, the Open Geospatial Consortium Web Feature Service (WFS) Interface Standard provides an interface allowing requests for geographical features across the web using platform-independent calls. One can think of geographical features as the "source code" behind a map, whereas the WMS interface or online tiled mapping portals like Google Maps return only an image, which end-users cannot edit or spatially analyze. The XML-based Geography Markup Language (GML) furnishes the default payload-encoding for transporting geographic features, but other formats like shapefiles can also serve for transport. In early 2006 the OGC members approved the OpenGIS GML Simple Features Profile. This profile is designed both to increase interoperability between WFS servers and to improve the ease of implementation of the WFS standard. The OGC membership defined and maintains the WFS specification. Numerous commercial and open-source implementations of the WFS interface standard exist, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
MIME
A mime artist, or simply mime (from Greek language, Greek , , "imitator, actor"), is a person who uses ''mime'' (also called ''pantomime'' outside of Britain), the acting out of a story through body motions without the use of speech, as a theatrical medium or as a performance art. In earlier times, in English, such a performer would typically be referred to as a mummer. Miming is distinguished from silent comedy, in which the artist is a character in a film or skit without sound. Jacques Copeau, strongly influenced by Commedia dell'arte and Japanese Noh theatre, used masks in the training of his actors. His pupil Étienne Decroux was highly influenced by this, started exploring and developing the possibilities of mime, and developed corporeal mime into a highly sculptural form, taking it outside the realms of naturalism. Jacques Lecoq contributed significantly to the development of mime and physical theatre with his training methods. As a result of this, the practice of mime h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
National Imagery Transmission Format
The National Imagery Transmission Format Standard (NITFS) is a U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) and Federal Intelligence Community (IC) suite of standards for the exchange, storage, and transmission of ''digital-imagery'' products and ''image-related'' products. DoD policy is that other image formats can be used internally within a single system; however, NITFS is the default format for interchange between systems. NITFS provides a package containing information about the image, the image itself, and optional overlay graphics. (i.e. a "package" containing an image(s), subimages, symbols, labels, and text as well as other information related to the image(s)) NITFS supports the dissemination of secondary digital imagery from overhead collection platforms. Guidance on applying the suite of standards composing NITFS can be found in MIL-HDBK-1300A, National Imagery Transmission Format Standard (NITFS), 12 October 1994. The NITFS allows for Support Data Extensions (SDEs), which are a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
HDF-EOS
Hierarchical Data Format (HDF) is a set of file formats (HDF4, HDF5) designed to store and organize large amounts of data. Originally developed at the U.S. National Center for Supercomputing Applications, it is supported by The HDF Group, a non-profit corporation whose mission is to ensure continued development of HDF5 technologies and the continued accessibility of data stored in HDF. In keeping with this goal, the HDF libraries and associated tools are available under a liberal, BSD-like license for general use. HDF is supported by many commercial and non-commercial software platforms and programming languages. The freely available HDF distribution consists of the library, command-line utilities, test suite source, Java interface, and the Java-based HDF Viewer (HDFView). The current version, HDF5, differs significantly in design and API from the major legacy version HDF4. Early history The quest for a portable scientific data format, originally dubbed AEHOO (All Encompassin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
NetCDF
NetCDF (Network Common Data Form) is a set of software libraries and self-describing, machine-independent data formats that support the creation, access, and sharing of array-oriented scientific data. The project homepage is hosted by the Unidata program at the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR). They are also the chief source of netCDF software, standards development, updates, etc. The format is an open standard. NetCDF Classic and 64-bit Offset Format are an international standard of the Open Geospatial Consortium. History The project started in 1988 and is still actively supported by UCAR. The original netCDF binary format (released in 1990, now known as "netCDF classic format") is still widely used across the world and continues to be fully supported in all netCDF releases. Version 4.0 (released in 2008) allowed the use of the HDF5 data file format. Version 4.1 (2010) added support for C and Fortran client access to specified subsets of remote data via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
GeoTIFF
GeoTIFF is a public domain metadata standard which allows georeferencing information to be embedded within a TIFF file. The potential additional information includes map projection, coordinate systems, ellipsoids, datums, and everything else necessary to establish the exact spatial reference for the file. The GeoTIFF format is fully compliant with TIFF 6.0, so software incapable of reading and interpreting the specialized metadata will still be able to open a GeoTIFF format file. An alternative to the "inlined" TIFF geospatial metadata is the *.tfw World File sidecar file format which may sit in the same folder as the regular TIFF file to provide a subset of the functionality of the standard GeoTIFF described here. History The GeoTIFF format was originally created by Dr. Niles Ritter while he was working at the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The reference implementation code was released mostly as public domain software with some parts under a permissive X license. On S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
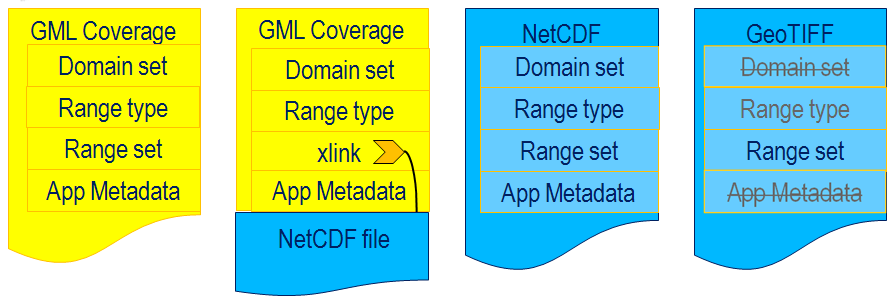
Coverage Encoding Variants
Coverage may refer to: Filmmaking * Coverage (lens), the size of the image a lens can produce * Camera coverage, the amount of footage shot and different camera setups used in filming a scene * Script coverage, a short summary of a script, written by script readers to recommend whether a film should be made Media and journalism * Broadcasting, radio, television, etc. * News ("press coverage", "media coverage"), the communication of selected information on current events Music * Coverage, a Descendents/ALL cover band from Calgary, Alberta, Canada * ''Coverage'' (album), a 2003 album by Mandy Moore Science and technology * Code coverage measure used in software testing * Coverage (telecommunication), a measure of cell phone or radio connectivity * Coverage (information systems), a measure for the quality/completeness of an information service * Coverage (shot peening), a criterion for quality of shot peening introduced by J.O. Almen in the 1940s * Coverage data, the mappin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ISO 19109
ISO/TC 211 is a standard technical committee formed within ISO, tasked with covering the areas of digital geographic information (such as used by geographic information systems) and geomatics. It is responsible for preparation of a series of International Standards and Technical Specifications numbered in the number range starting at ISO-19101. The Chair of the committee was 1994-2016: Olaf Østensen; during 2017-2018: Christina Wasström; and from 2019 Agneta Gren Engberg. Scope ISO/TC 211 is concerned with the standardization in the field of digital geographic information. This work aims to establish a structured set of standards for information concerning objects or phenomena that are directly or indirectly associated with a location relative to the Earth. Project specification areas within the ISO/TC 211 technical committee include: * Simple Features access * Reference models * Spatial and temporal schemas * Location-based services * Metadata * Web feature and map se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Feature Data
In geographic information systems, a feature is an object that can have a geographic location and other properties. Common types of geometries include points, arcs, and polygons. Carriageways and cadastre A cadastre or cadaster ( ) is a comprehensive recording of the real estate or real property's metes-and-bounds of a country.Jo Henssen, ''Basic Principles of the Main Cadastral Systems in the World,'/ref> Often it is represented graphically in ...s are examples of feature data. Features can be labeled when displayed on a map. Feature types The definition of features that share membership of a common theme is a ''feature type'', though there are a number of terms for this characteristic, including ''category'', ''feature class'', ''group'', ''layer'', ''level'', ''object'', and ''theme''. ''Layer'' served as the traditional term of choice, but use of this word has declined, as data has become more object-oriented and less concerned with cartographic layering. Data modeler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thiessen Polygon
In mathematics, a Voronoi diagram is a partition of a plane into regions close to each of a given set of objects. It can be classified also as a tessellation. In the simplest case, these objects are just finitely many points in the plane (called seeds, sites, or generators). For each seed there is a corresponding region, called a Voronoi cell, consisting of all points of the plane closer to that seed than to any other. The Voronoi diagram of a set of points is dual to that set's Delaunay triangulation. The Voronoi diagram is named after mathematician Georgy Voronoy, and is also called a Voronoi tessellation, a Voronoi decomposition, a Voronoi partition, or a Dirichlet tessellation (after Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet). Voronoi cells are also known as Thiessen polygons, after Alfred H. Thiessen. Voronoi diagrams have practical and theoretical applications in many fields, mainly in science and technology, but also in visual art. Simplest case In the simplest case, shown in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |