|
Courland (other)
Courland is one of the historical and cultural regions of Latvia. Courland may also refer to: ; Political entities * Bishopric of Courland, an ecclesiastical state in the Livonian Confederation 1254-1562 * Duchy of Courland and Semigallia, 1561–1795 (including a list of dukes) ** Duchess of Courland, a list * Courland Governorate, a Baltic governorate of the Russian Empire 1795–1915 * Provisional Land Council of Courland Provisional Land Council of Courland ( lv, Kurzemes Pagaidu zemes padome; russian: Временный земский совет Курляндской губернии) was created on 27 April 1917 in Tartu as the representative organ of Courlan ..., 1917 * Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (1918), a short-lived client state of the German Empire ; Other uses * Courland (Saeima constituency), constituency of the Saeima, the national legislature of Latvia * Courland Peninsula, the north-western part of Courland * Courland Pocket, the part of the Courland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courland
Courland (; lv, Kurzeme; liv, Kurāmō; German and Scandinavian languages: ''Kurland''; la, Curonia/; russian: Курляндия; Estonian: ''Kuramaa''; lt, Kuršas; pl, Kurlandia) is one of the Historical Latvian Lands in western Latvia. The largest city is Liepāja, the third largest city in Latvia. The regions of Semigallia and Selonia are sometimes considered as part of Courland as they were formerly held by the same duke. Geography and climate Situated in western Latvia, Courland roughly corresponds to the former Latvian districts of Kuldīga, Liepāja, Saldus, Talsi, Tukums and Ventspils. When combined with Semigallia and Selonia, Courland's northeastern boundary is the Daugava, which separates it from the regions of Latgale and Vidzeme. To the north, Courland's coast lies along the Gulf of Riga. On the west it is bordered by the Baltic Sea, and on the south by Lithuania. It lies between 55° 45′ and 57° 45′ North and 21° and 27° East. The name is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishopric Of Courland
The Bishopric of Courland ( la, Episcopatus Curoniensis, Low German: ''Bisdom Curland'') was the second smallest (4500 km2) ecclesiastical state in the Livonian Confederation founded in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade. During the Livonian War in 1559 the bishopric became a possession of Denmark, and in 1585 sold by Denmark to Poland–Lithuania. History In ancient times a Baltic tribe, the Curonians, inhabited Courland and had strong links with the maritime tribes in both sides of the Baltic sea. In 1230, Lamekinas, Duke of West Courland, signed an agreement with the vice-legat Baldwin of Alna (''Baudoin d’Aulne'') of the Pope Gregory IX about the voluntary conversion of his people to Christianity and receiving the same rights as the inhabitants of Gotland. In 1234 Dominican friar Engelbert was appointed to be the first bishop of Courland. In 1242 the area of Courland passed under the influence of the Teutonic Knights owing to the amalgamation of this ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Courland And Semigallia
The Duchy of Courland and Semigallia ( la, Ducatus Curlandiæ et Semigalliæ; german: Herzogtum Kurland und Semgallen; lv, Kurzemes un Zemgales hercogiste; lt, Kuršo ir Žiemgalos kunigaikštystė; pl, Księstwo Kurlandii i Semigalii) was a duchy in the Baltic region, then known as Livonia, that existed from 1561 to 1569 as a nominally vassal state of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and subsequently made part of the Crown of the Polish Kingdom from 1569 to 1726 and incorporated into the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1726. On March 28, 1795, it was annexed by the Russian Empire in the Third Partition of Poland. There was also a short-lived wartime state existing from March 8 to September 22, 1918, with the same name. Plans for it to become part of the United Baltic Duchy, subject to the German Empire, were thwarted by Germany's surrender of the Baltic region at the end of the First World War. The area became a part of Latvia at the end of World War I. History In 1561 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchess Of Courland
Duchess of Courland House of Kettler, 1561–1737 House of Biron, 1737–1740 * Council of the Duke, 1740–58 House of Wettin, 1758–1763 *None, although Charles of Saxony was morganatically married with the Polish countess Franciszka Korwin-Krasińska. House of Biron, 1763–1795 {, width=95% class="wikitable" !width = "8%" , Picture !width = "10%" , Name !width = "9%" , Father !width = "10%" , Birth !width = "9%" , Marriage !width = "9%" , Became Duchess !width = "9%" , Ceased to be Duchess !width = "9%" , Death !width = "6%" , Spouse , - , align="center", , align="center", Benigna Gottliebe von Trotha genannt Treyden , align="center", Wilhelm von Trohta Truiden , align="center", 15 October 1703 , align="center", 25 February 1723 , align="center", 1763''husband's restoration'' , align="center", 1769''husband abdication'' , align="center", 5 November 1782 , align="center", Ernst Johann von Biron , - , align="center", , align="center", Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courland Governorate
The Courland Governorate, also known as the Province of Courland, Governorate of Kurland (german: Kurländisches Gouvernement; russian: Курля́ндская губерния, translit=Kurljándskaja gubernija; lv, Kurzemes guberņa; lt, Kuršo gubernija; et, Kuramaa kubermang) and known from 1795 to 1796 as the Viceroyalty of Courland was one of the Baltic governorates of the Russian Empire, that is now part of the Republic of Latvia. The governorate was created in 1795 out of the territory of the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia that was incorporated into the Russian Empire as the province of Courland with its capital at Mitau (now Jelgava), following the third partition of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Courland and Livonia were united to form new state Republic of Latvia on 18 November 1918. Geography The governorate was bounded in the north by the Baltic Sea, the Gulf of Riga and the Governorate of Livonia; west by the Baltic Sea; south by the Vilna Governor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provisional Land Council Of Courland
Provisional Land Council of Courland ( lv, Kurzemes Pagaidu zemes padome; russian: Временный земский совет Курляндской губернии) was created on 27 April 1917 in Tartu as the representative organ of Courland Governorate. Because Courland was under German military occupation since the summer of 1915, the Council was created in Estonian city of Tartu, and following the German offensive, was evacuated to Russian city Kazan in October 1917.Stanley PagThe Formation of the Baltic States: A Study of the Effects of Great Power Politics Upon the Emergence of Lithuania, Latvia, and EstoniaHarvard University Press, 1959 - Baltic States - 193 pages Issue 39 of Harvard historical monographs, After the democratic February Revolution in the Russian Empire, approximately 170 000 war refugees and soldiers from Courland elected 313 representatives, who then proceeded to elect the Provisional Land Council with 60 members. Their leader was the future Presiden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Courland And Semigallia (1918)
The Duchy of Courland and Semigallia was the name for a proposed client state of the German Empire during World War I which did not come into existence. It was proclaimed on 8 March 1918, in the German-occupied Courland Governorate by a council composed of Baltic Germans, who offered the crown of the once-autonomous duchy to Kaiser Wilhelm II, despite the existence of a formerly sovereign reigning family in that duchy, the Biron descendants of Ernst Johann von Biron. Although the German Reichstag supported national self-determination for the peoples of the Baltic provinces (what is now Latvia and Estonia), the German High Command continued the policy of attaching these territories to the German Reich by relying on the local Baltic Germans.Kevin O'ConnorThe History of the Baltic States page 78, . In October 1918, the Chancellor of Germany, Prince Maximilian of Baden, proposed to have the military administration in the Baltic replaced by civilian authority. After the German Revolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courland (Saeima Constituency)
Courland ( lv, Kurzeme; russian: Курземе) is one of the five multi-member constituencies of the Saeima, the national legislature of Latvia. The constituency was established in 1922 when the Saeima was established following Latvia's independence from the Soviet Union. It consists of the cities of Liepāja and Ventspils and municipalities of Kuldīga, Saldus, South Kurzeme, Talsi and Ventspils in the region of Courland. The constituency currently elects 12 of the 100 members of the Saeima using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2022 parliamentary election it had 180,070 registered electors. Electoral system Courland currently elects 12 of the 100 members of the Saeima using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. Constituency seats are allocated using the Sainte-Laguë method. Only parties that reach the 5% national threshold compete for constituency seats (4% in 1993). Election results Summary Detailed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courland Peninsula
The Courland Peninsula (, German: ''Kurland'') is a historical and cultural region in western Latvia in the north-western part of Courland. Fourteen coastal villages on the peninsula make of the Livonian core area. It is bordered by the Baltic Sea in the West, the Irbe Strait in the North and the Gulf of Riga in the East. It covers northwestern Latvia. The Courland Peninsula was the site of the Courland Pocket of World War II. See also * Courland Pocket The Courland Pocket (Blockade of the Courland army group), (german: Kurland-Kessel)/german: Kurland-Brückenkopf (Courland Bridgehead), lv, Kurzemes katls (Courland Cauldron) or ''Kurzemes cietoksnis'' (Courland Fortress)., group=lower-alpha ... References {{coord, 57.2667, N, 22.2500, E, source:wikidata, display=title Peninsulas of Europe Courland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
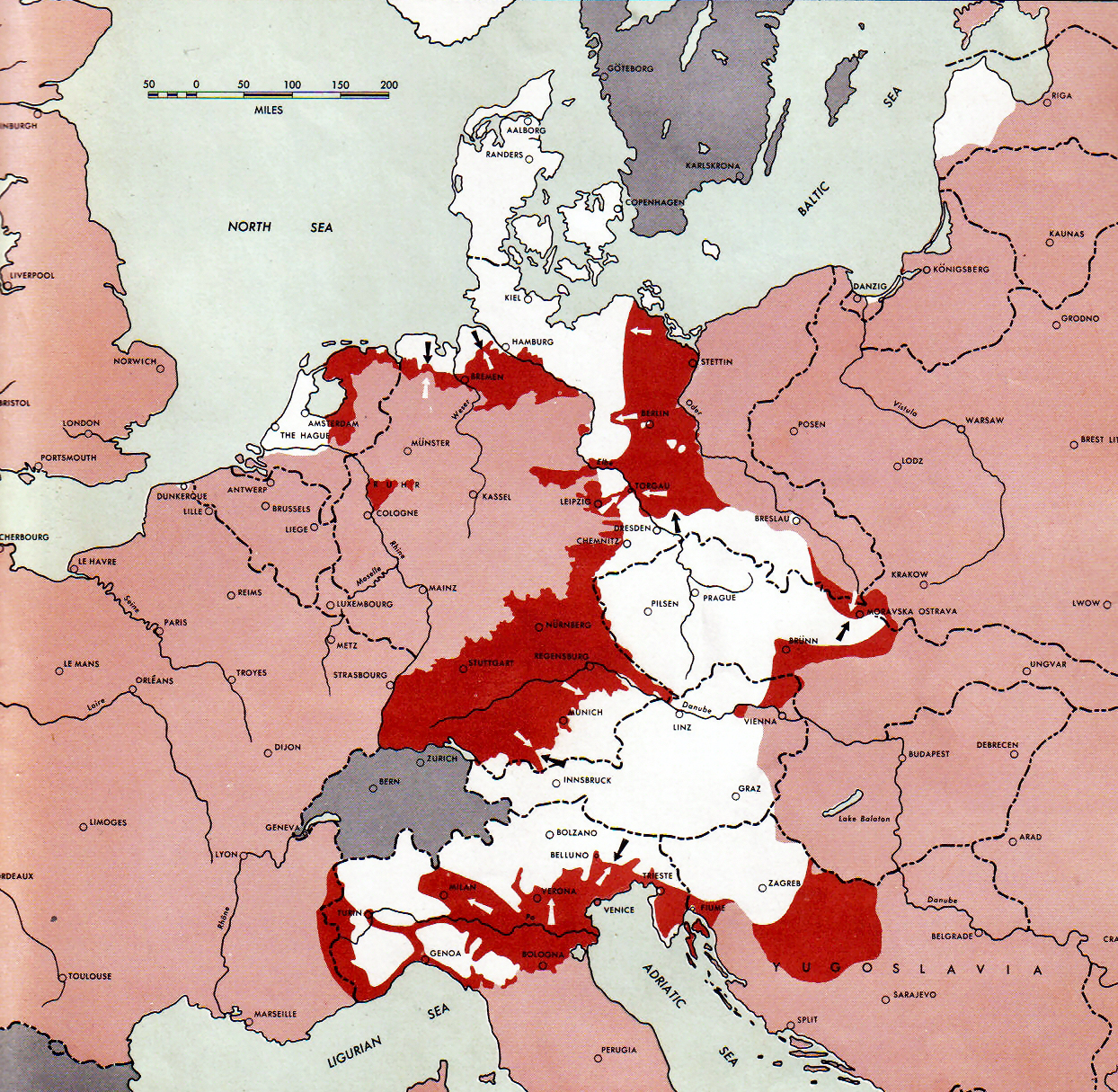
Courland Pocket
The Courland Pocket (Blockade of the Courland army group), (german: Kurland-Kessel)/german: Kurland-Brückenkopf (Courland Bridgehead), lv, Kurzemes katls (Courland Cauldron) or ''Kurzemes cietoksnis'' (Courland Fortress)., group=lower-alpha was an area of the Courland Peninsula where Army Group North of Nazi Germany and the Reichskommissariat Ostland were cut off and surrounded by the Red Army for almost a year, lasting from July 1944 until 10 May 1945. The pocket was created during the Red Army's Baltic Offensive, when forces of the 1st Baltic Front reached the Baltic Sea near Memel (Klaipėda) during its lesser Memel Offensive Operation phases. This action isolated the German Army Group North from the rest of the German forces, having been pushed from the south by the Red Army, standing in a front between Tukums and Libau in Latvia, with the Baltic Sea in the West, the Irbe Strait in the North and the Gulf of Riga in the East behind the Germans. Renamed Army Group Courl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group Courland
Army Group Courland (german: Heeresgruppe Kurland) was a German Army Group on the Eastern Front which was created from remnants of the Army Group North, isolated in the Courland Peninsula by the advancing Soviet Army forces during the 1944 Baltic Offensive of the Second World War. The army group remained isolated in the Courland Pocket until the end of World War II in Europe. All units of the Army Group were ordered to surrender by the capitulated Wehrmacht command on 8 May 1945. At the time agreed for all German armed forces to end hostilities (see the German Instrument of Surrender, 1945), the Sixteenth and Eighteenth armies of Army Group Courland, commanded by General (of Infantry) Carl Hilpert, ended hostilities at 23:00, on 8 May 1945, surrendering to Leonid Govorov, commander of the Leningrad Front. By the evening of 9 May 1945 189,000 German troops, including 42 officers in the rank of general, in the Courland Pocket had surrendered.60 anniversary of surrender project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurland (other)
Kurland may refer to: People *Abraham Kurland (1912-1999), Danish Olympic medalist in wrestling * Ben Kurland, American actor * Bob Kurland, American basketball center *Cys Kurland, South African footballer *Gilbert Kurland, American sound engineer and production manager *Justine Kurland, American fine art photographer *Lynn Kurland, American author *Michael Kurland, American author *Peter Kurland, American motion picture sound mixer *Sheldon Kurland, American violinist and musical arranger Places *Courland (German: ''Kurland''), a region of Latvia * Curland, a village and civil parish in Somerset, England *Duchy of Courland and Semigallia, a former duchy in the Baltic region *Kurland, Norway, village in Akershus, Norway See also *Courland (other) Courland is one of the historical and cultural regions of Latvia. Courland may also refer to: ; Political entities * Bishopric of Courland, an ecclesiastical state in the Livonian Confederation 1254-1562 * Duchy of Courland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |