|
Coup D'état (other)
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'; plural coups d'état), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, military, or a dictator. Many scholars consider a coup successful when the usurpers seize and hold power for at least seven days. Etymology The term comes from French ''coup d'État'', literally meaning a 'stroke of state' or 'blow of state'. In French, the word ''État'' () is capitalized when it denotes a sovereign political entity. Although the concept of a coup d'état has featured in politics since antiquity, the phrase is of relatively recent coinage.Julius Caesar's civil war, 5 January 49 BC. It did not appear within an English text before the 19th century except when used in the translation of a French source, there being no simple phrase in English to convey the contextualized idea of a 'knockout blow to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excerpt
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapters, 11th century BC), the '' Bamboo Annals'' (c. 296 BC) and the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (c. 91 BC) describe a Xia dynasty before the Shang, but no writing is known from the period, and Shang writings do not indicate the existence of the Xia. The Shang ruled in the Yellow River valley, which is commonly held to be the cradle of Chinese civilization. However, Neolithic civilizations originated at various cultural centers along both the Yellow River and Yangtze River. These Yellow River and Yangtze civilizations arose millennia before the Shang. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is among the world's oldest civilizations and is regarded as one of the cradles of civilization. The Zhou dynasty (1046–256 BC) supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beer Hall Putsch
The Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch,Dan Moorhouse, ed schoolshistory.org.uk, accessed 2008-05-31.Known in German as the or was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party ( or NSDAP) leader Adolf Hitler, Erich Ludendorff and other leaders in Munich, Bavaria, on 8– 9 November 1923, during the Weimar Republic. Approximately two thousand Nazis marched on the , in the city centre, but were confronted by a police cordon, which resulted in the deaths of 16 Nazi Party members and four police officers. Hitler escaped immediate arrest and was spirited off to safety in the countryside. After two days, he was arrested and charged with treason. The putsch brought Hitler to the attention of the German nation for the first time and generated front-page headlines in newspapers around the world. His arrest was followed by a 24-day trial, which was widely publicised and gave him a platform to express his nationalist sentiments to the nation. Hitler was found guilty of treason ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Küstrin Putsch
The Küstrin Putsch of 1 October 1923, also known as the Buchrucker Putsch after its leader, was a minimally planned coup attempt against the Weimar Republic by units of the paramilitary Black Reichswehr under Bruno Ernst Buchrucker. It was in large part an attempt by Buchrucker to halt the order to disband the units under his command and to have an arrest warrant against him lifted. It failed in the eastern German town of Küstrin when the colonel in charge of the Küstrin Fortress detained Buchrucker and called in the Reichswehr. Buchrucker was convicted of treason and sentenced to prison but was amnestied after serving four years of the ten-year sentence. Background Groups from the Black Reichswehr called labor commandos (German: ) led by Bruno Ernst Buchrucker wanted to bring down the Reich government of Chancellor Gustav Stresemann and replace the parliamentary democratic republic with a national dictatorship. The putsch was prompted when on 26 September 1923 the government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapp Putsch
The Kapp Putsch (), also known as the Kapp–Lüttwitz Putsch (), was an attempted coup against the German national government in Berlin on 13 March 1920. Named after its leaders Wolfgang Kapp and Walther von Lüttwitz, its goal was to undo the German Revolution of 1918–1919, overthrow the Weimar Republic, and establish an autocratic government in its place. It was supported by parts of the ''Reichswehr'', as well as nationalist and monarchist factions. Although the legitimate German government was forced to flee the city, the coup failed after a few days, when large sections of the German population joined a general strike called by the government. Most civil servants refused to cooperate with Kapp and his allies. Despite its failure, the Putsch had significant consequences for the future of the Weimar Republic. It was also one of the direct causes of the Ruhr uprising a few weeks later, which the government suppressed by military force, after having dealt leniently with lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclaimed itself, as the German Republic (german: Deutsche Republik, link=no, label=none). The state's informal name is derived from the city of Weimar, which hosted the constituent assembly that established its government. In English, the republic was usually simply called "Germany", with "Weimar Republic" (a term introduced by Adolf Hitler in 1929) not commonly used until the 1930s. Following the devastation of the First World War (1914–1918), Germany was exhausted and sued for peace in desperate circumstances. Awareness of imminent defeat sparked a revolution, the abdication of Kaiser Wilhelm II, formal surrender to the Allies, and the proclamation of the Weimar Republic on 9 November 1918. In its i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
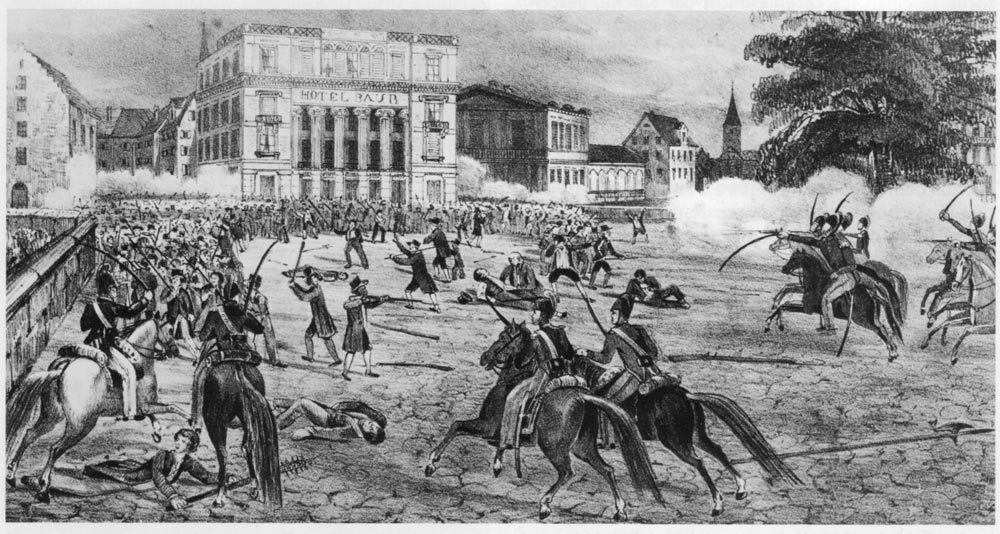
Züriputsch
The Züriputsch of 6 September 1839 was a putsch of the rural conservative population against the liberal rule of the city of Zürich on the eve of the formation of the Swiss federal state. The reason for the putsch was the appointment of the controversial German theologian David Strauss to the theological faculty of the University of Zürich by the liberal government. The rural population saw the old religious order in danger. Events Led by Bernhard Hirzel, pastor of Pfäffikon, several thousand putschists stormed the city from the west, and fought the cantonal troops in the alleys between Paradeplatz and Fraumünster. Botanist and councillor Johannes Jacob Hegetschweiler was shot in the head as he was acting as a mediator between the city's council and the insurgents. He died three days later. The Swiss German term ''putsch'', originally referring to any sort of hit, stroke or collision, entered the German language as a political term, popularized by Gottfried Keller. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akademie Verlag
:''There also were unrelated publishing houses in Stuttgart and in (East-)Berlin, and there is the (JAVG).'' Akademie Verlag (AV) is a German scientific and academic publishing company, founded in 1946 in the Soviet-occupied eastern part of divided Berlin to facilitate the publication of works by and for the German Academy of Sciences Berlin. Under the communist German Democratic Republic, from 1949 to 1990, it remained closely connected to the academy; unlike other publishing houses, it was not subject to direct control by the GDR ministry of culture. Still, it was regarded with suspicion in the West due to communist influence. Most of the output was sold in East Germany and the Eastern Bloc. Since 1957, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, the founder of the Prussian Academy of Sciences in 1700, and „theoria cum praxi“ are used as symbols. Since the 1970s, several volumes of the Nicolaus Copernicus Gesamtausgabe (complete edition) have been published by Akademie Verlag, cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss German
Swiss German (Standard German: , gsw, Schwiizerdütsch, Schwyzerdütsch, Schwiizertüütsch, Schwizertitsch Mundart,Because of the many different dialects, and because there is no defined orthography for any of them, many different spellings can be found. and others) is any of the Alemannic dialects spoken in the German-speaking part of Switzerland and in some Alpine communities in Northern Italy bordering Switzerland. Occasionally, the Alemannic dialects spoken in other countries are grouped together with Swiss German as well, especially the dialects of Liechtenstein and Austrian Vorarlberg, which are closely associated to Switzerland's. Linguistically, Alemannic is divided into Low, High and Highest Alemannic, varieties all of which are spoken both inside and outside Switzerland. The only exception within German-speaking Switzerland is the municipality of Samnaun, where a Bavarian dialect is spoken. The reason Swiss German dialects constitute a special group is their a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Russian Monarchs
This is a list of all reigning monarchs in the history of Russia. It includes the princes of medieval Rus′ state (both centralised, known as Kievan Rus′ and feudal, when the political center moved northeast to Vladimir and finally to Moscow), tsars, and emperors of Russia. The list begins with the semi-legendary prince Rurik of Novgorod, sometime in the mid 9th century ( 862) and ends with emperor Nicholas II who abdicated in 1917, and was executed with his family in 1918. The vast territory known today as Russia covers an area that has been ruled by various polities, including Kievan Rus', the Grand Duchy of Moscow, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, and the sovereigns of these many nations and throughout their histories have used likewise as wide a range of titles in their positions as chief magistrates of a country. Some of the earliest titles include ''kniaz'' and ''velikiy kniaz'', which mean "prince" and "grand prince" respectively but are often rend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island which it shares with the Dominican Republic. To its south-west lies the small Navassa Island, which is claimed by Haiti but is disputed as a United States territory under federal administration."Haiti" ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Haiti is in size, the third largest country in the Caribbean by area, and has an estimated population of 11.4 million, making it the most populous country in the Caribb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |