|
County Of Cleves
The Duchy of Cleves (german: Herzogtum Kleve; nl, Hertogdom Kleef) was a State of the Holy Roman Empire which emerged from the medieval . It was situated in the northern Rhineland on both sides of the Lower Rhine, around its capital Cleves and the towns of Wesel, Kalkar, Xanten, Emmerich, Rees and Duisburg bordering the lands of the Prince-Bishopric of Münster in the east and the Duchy of Brabant in the west. Its history is closely related to that of its southern neighbours: the Duchies of Jülich and Berg, as well as Guelders and the Westphalian county of Mark. The Duchy was archaically known as ''Cleveland'' in English. The duchy's territory roughly covered the present-day German districts of Cleves (northern part), Wesel and the city of Duisburg, as well as adjacent parts of the Limburg, North Brabant and Gelderland provinces in the Netherlands. History In the early 11th century Emperor Henry II entrusted the administration of the ''Klever Reichswald'', a large forest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German ( ) is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and Official language, official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italy, Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also a co-official language of Luxembourg and German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium, as well as a national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France (Bas-Rhin), Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Poland (Upper Silesia), Slovakia (Bratislava Region), and Hungary (Sopron). German is most similar to other languages within the West Germanic language branch, including Afrikaans, Dutch language, Dutch, English language, English, the Frisian languages, Low German, Luxembourgish, Scots language, Scots, and Yiddish. It also contains close similarities in vocabulary to some languages in the North Germanic languages, North Germanic group, such as Danish lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleverlandish
South Guelderish ( nl, Zuid-Gelders , german: Südgeldersch, ''Kleverländisch'') refers to the easternmost group of Dutch dialects spoken along the lower Rhine (Dutch Nederrijn and German Niederrhein). In its narrower sense, the term refers strictly to the Rivierenlands ( nl), Nijmeegs, and Liemers sub-dialects; in its broader sense, the term encompasses also North Limburgish in the Netherlands and Kleverlander (around Cleves; Dutch ''Kleverlands'', German ''Kleverländisch'') in Germany. South Guelderish (in the narrow sense) — especially Rivierenlands — is sometimes included as part of Brabantic, a more widely spoken Dutch dialect and the closest relative of South Guelderish. Alternatively, it is considered to extend southward into Northern Limburg until the Uerdingen line. It is arguably more appropriate to group South Guelderish (narrow sense), North Limburgish and, Kleverlander into one dialect group—East Dutch. In the Netherlands, South Guelderish is spoken in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
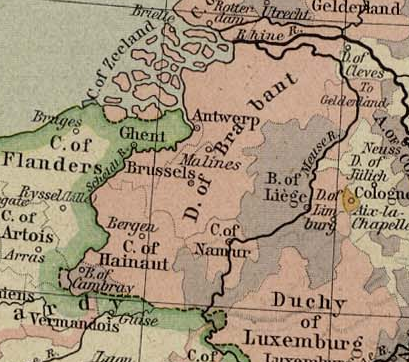
Duchy Of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1482, until it was partitioned after the Dutch revolt. Present-day North Brabant (''Noord-Brabant'') was ceded to the Generality Lands of the Dutch Republic according to the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, while the reduced duchy remained part of the Habsburg Netherlands until it was conquered by French Revolutionary forces in 1794, which was recognized by treaty in 1797. Today all the duchy's former territories, apart from exclaves, are in Belgium except for the Dutch province of North Brabant. Geography The Duchy of Brabant (adjective: ''Brabantian'' or '' Brabantine'') was historically divided into four parts, each with its own capital. The four capitals were Leuven, Brussels, Antwerp and 's-Hertogenbosch. Before 's-Hertogenb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince-Bishopric Of Münster
The Prince-Bishopric of Münster (german: Fürstbistum Münster; Bistum Münster, Hochstift Münster) was a large ecclesiastical principality in the Holy Roman Empire, located in the northern part of today's North Rhine-Westphalia and western Lower Saxony. From the sixteenth to the eighteenth centuries, it was often held in personal union with one or more of the nearby ecclesiastical principalities of Cologne, Paderborn, Osnabrück, Hildesheim, and Liège. Münster was bordered by the United Provinces to the west, by Cleves, Vest Recklinghausen, and Mark in the south, Paderborn and Osnabrück in the east. In the north and north-east it bordered East Frisia, Oldenburg and the Electorate of Hanover (est. 1692). As with all the other prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire, it is important to distinguish between the Prince-Bishopric of Münster and the Diocese of Münster although both entities were ruled by the same individual. The dioceses were generally larger than the cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duisburg
Duisburg () is a city in the Ruhr metropolitan area of the western German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Lying on the confluence of the Rhine and the Ruhr rivers in the center of the Rhine-Ruhr Region, Duisburg is the 5th largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia and the 15th-largest city in Germany. In the Middle Ages, it was a city-state and a member of the Hanseatic League, and later became a major centre of iron, steel, and chemicals industries. For this reason, it was heavily bombed in World War II. Today it boasts the world's largest inland port, with 21 docks and 40 kilometres of wharf. Status Duisburg is a city in Germany's Rhineland, the fifth-largest (after Cologne, Düsseldorf, Dortmund and Essen) of the nation's most populous federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Its 500,000 inhabitants make it Germany's 15th-largest city. Located at the confluence of the Rhine river and its tributary the Ruhr river, it lies in the west of the Ruhr urban area, Germany's larges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rees, Germany
Rees is a town in the district of Kleve in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located on the right bank of the Rhine, approximately 20 km east of Kleve. The population in 2005 was 22,559. Founded in 1228, Rees is the oldest town in the lower Rhine area. Geography Rees is administratively organized in eight communities: * Community of Bienen * Community of Empel * Community of Esserden * Community of Haffen * Community of Haldern * Community of Mehr * Community of Millingen * Community of Rees The neighbouring municipalities are Oude IJsselstreek (province of Gelderland, NL) and Isselburg (district of Borken) in the North, Hamminkeln and Wesel in the East, Xanten in the South (all district of Wesel), and Kalkar and Emmerich in the West. History The origin of the town is a Frankish settlement established between 500-800 AD. The name Rees most probably goes back to the Franconian term "Rys", which means "willow grove". The Lower Rhine area was Christiani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emmerich Am Rhein
Emmerich am Rhein ( Low Rhenish and nl, Emmerik) is a city and municipality in the northwest of the German federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The city has a harbour and a quay at the Rhine. In terms of local government organization, it is a medium-sized city belonging to the district of Kleve in the administrative region (''Regierungsbezirk'') of Düsseldorf. Geography Emmerich lies on the north bank of the Rhine, just within the German borders; it is only 4 km to the Netherlands to the north and 5 km to the west. Therefore, it is the last German town on the Rhine before the river flows into the Netherlands. Villages belonging to Emmerich am Rhein The populated places which comprise the municipality of Emmerich am Rhein are Emmerich, Borghees, Dornick, Elten, Hüthum, Klein-Netterden, Leegmeer, Praest, Speelberg and Vrasselt. Neighboring municipalities and cities To the north, the municipality of Emmerich borders the Dutch municipalities Montferland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanten
Xanten (, Low Rhenish: ''Santen'') is a town in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the district of Wesel. Xanten is known for the Archaeological Park, one of the largest archaeological open air museums in the world, built at the site of the Roman settlements ''Colonia Ulpia Traiana''. Other attractions include the medieval town centre with Xanten Cathedral, many museums and large man-made lakes for various watersport activities. Xanten is visited by approximately one million tourists a year. Geography Xanten, the only German town whose name begins with ''X'', is made up of three boroughs (''Ortsteile''): ''Hochbruch'', ''Niederbruch'', and the ''town centre''. Other localities (''Bezirke'') belonging to the town of Xanten include ''Birten'', ''Lüttingen'', ''Marienbaum'', ''Vynen'', ''Obermörmter'', ''Wardt'', ''Mörmter'', ''Willich'', ''Beek'' and ''Ursel''. Parts of a nature reserve called ''Bislicher Insel'' are located in the municipality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalkar
Kalkar ( is a municipality in the district of Kleve, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located near the Rhine, approx. 10 km south-east of Cleves. The catholic church St. Nicolai has preserved one of the most significant sacral inventories from the late Middle Ages in Germany. History Kalkar was founded by Dirk VI of Cleves in 1230 and received city rights in 1242. It was one of the seven "capitals" of Cleves (called Kleve), until the line of the Duchy of Cleves died out in 1609, whereupon the city went over to the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Marie of Burgundy, Duchess of Cleves retired to Monreberg castle in Kalkar, where she founded a Dominican convent in 1455. Under her influence the city bloomed and artists were attracted to the favorable climate for cultural investment. She died at Monreberg castle in 1463. Air base The USAF 470TH Air Base Squadron supports the NATO Joint Air Power Competence Center (JAPCC) in Kalkar and the NATO CAOC in Uedem. The 470th is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wesel
Wesel () is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the capital of the Wesel district. Geography Wesel is situated at the confluence of the Lippe River and the Rhine. Division of the city Suburbs of Wesel include Lackhausen, Obrighoven, Ginderich, Feldmark, Fusternberg, Büderich, Flüren and Blumenkamp. History Origin The city originated from a Franconian manor that was first recorded in the 8th century. In the 12th century, the Duke of Clèves took possession of Wesel. The city became a member of the Hanseatic League during the 15th century. Wesel was second only to Cologne in the lower Rhine region as an entrepôt. It was an important commercial centre: a clearing station for the transshipment and trading of goods. Early modern In 1590 the Spanish captured Wesel after a four-year siege. The city changed hands between the Dutch and Spanish several times during the Eighty Years War. In 1672 a French force under Louis II de Bourbon, Prince de Condé captured the ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleves
Kleve (; traditional en, Cleves ; nl, Kleef; french: Clèves; es, Cléveris; la, Clivia; Low Rhenish: ''Kleff'') is a town in the Lower Rhine region of northwestern Germany near the Dutch border and the River Rhine. From the 11th century onwards, Cleves was capital of a county and later a duchy. Today, Cleves is the capital of the district of Cleves in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The city is home to one of the campuses of the Rhine-Waal University of Applied Sciences. Territory of the municipality In addition to the inner city, the territory of Kleve comprises fourteen villages and populated places: Bimmen, Brienen, Donsbrüggen, Düffelward, Griethausen, Keeken, Kellen, Materborn, Reichswalde, Rindern, Salmorth, Schenkenschanz, Warbeyen and Wardhausen. History The name ''Kleff'' probably derives from Middle Dutch ''clef'', ''clif'' 'cliff, bluff', referring to the promontory on which the Schwanenburg castle was constructed. Since the city's coat of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Rhine
The Lower Rhine (german: Niederrhein; kilometres 660 to 1,033 of the river Rhine) flows from Bonn, Germany, to the North Sea at Hook of Holland, Netherlands (including the Nederrijn or "Nether Rhine" within the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta); alternatively, ''Lower Rhine'' may refer to the part upstream of Pannerdens Kop, excluding the Nederrijn. Almost immediately after entering the Netherlands, the Rhine splits into numerous branches. The main branch is called the Waal which flows from Nijmegen to meet the Meuse; after which it is called Merwede. Near Rotterdam the river is known as Nieuwe Maas, and becomes the Nieuwe Waterweg flowing into the North Sea at Hook of Holland. The downstream Lower Rhine is a low lying land. Up to the beginning of industrialization roughly one fifth of the land area could only be used as pasture: an endless meadow, which could not be farmed because of flooding and a high ground-water level. However, the remaining soils of the Lower Rhine were alwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_-_The_Water_Gate_in_Emmerich_am_Rhein.jpg)


.jpg)
