|
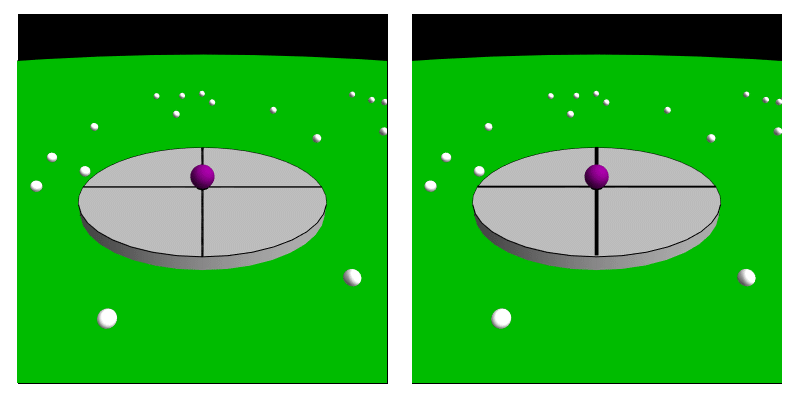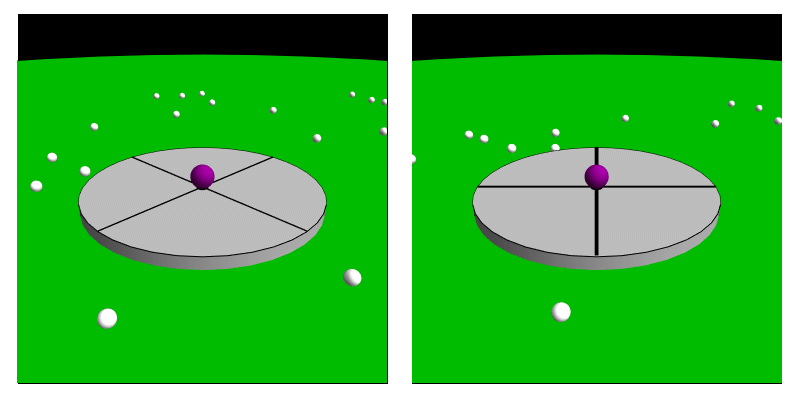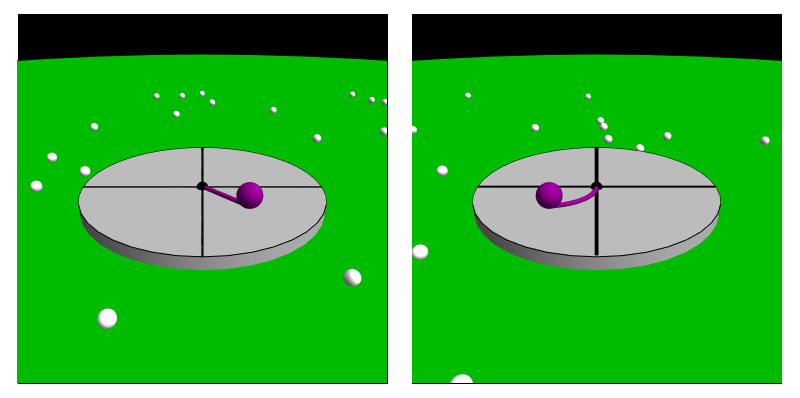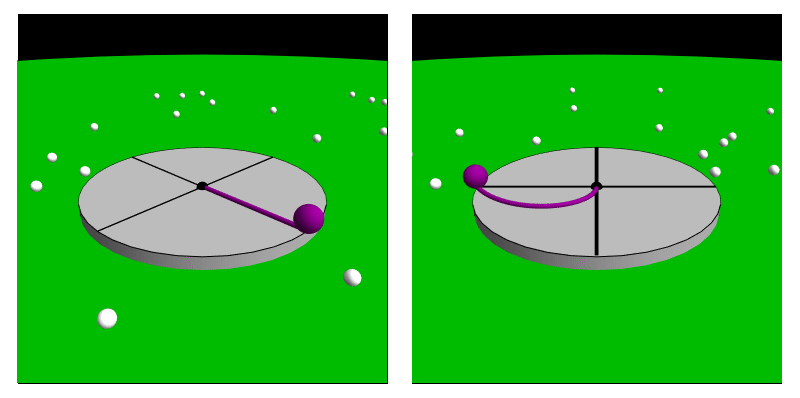
Coriolis Force (perception)
In Psychophysics, psychophysical perception, the Coriolis effect (also referred to as the Coriolis illusion or the vestibular Coriolis effect) is the misperception of body orientation due to head movement while under the effect of rotation, often inducing nausea. This effect comes about as the head is moved in contrary or similar motion with the body during the time of a spin. This goes on to affect the vestibular system, particularly the semicircular canals which are affected by the acceleration. This causes a sense of dizziness or nausea before equilibrium is restored after the head returns to a stabilized state. Crucially, this illusion is based entirely upon perception, and is largely due to conflicting signals between one's sight and one's perception of their body position or motion. Examples of situations where this can arise are circular acceleration and movement during a circular rotation. There is also the pseudo-Coriolis effect (also referred to as the optokinetic pseud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychophysics
Psychophysics is the field of psychology which quantitatively investigates the relationship between physical stimulus (physiology), stimuli and the sensation (psychology), sensations and perceptions they produce. Psychophysics has been described as "the scientific study of the relation between stimulus and Sensation (psychology), sensation" or, more completely, as "the analysis of perceptual processes by studying the effect on a subject's experience or behaviour of systematically varying the properties of a stimulus along one or more physical dimensions". ''Psychophysics'' also refers to a general class of methods that can be applied to study a perceptual system. Modern applications rely heavily on threshold measurement, ideal observer analysis, and Detection theory, signal detection theory. Psychophysics has widespread and important practical applications. For instance, in the realm of digital signal processing, insights from psychophysics have guided the development of models a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Acceleration In Semicircular Canals
Angular may refer to: Anatomy * Angular artery, the terminal part of the facial artery * Angular bone, a large bone in the lower jaw of amphibians and reptiles * Angular incisure, a small anatomical notch on the stomach * Angular gyrus, a region of the brain in the parietal lobe * Angular vein, formed by the junction of the frontal vein and supraorbital vein Other uses * Angular (web framework), an open-source web platform **AngularJS, the first incarnation of Angular * Angle, having an angle or angles * Angular diameter, describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view ** Angular diameter distance, used in astronomy * Angular Recording Corporation Angular Recording Corporation was an independent record label founded in New Cross, South East London. It was established in June 2003 by two ex-Goldsmiths College students, Joe Daniel and Joe Margetts, who reclaimed a local Ordnance Survey Tr ..., a British independent record label See also * Angle (dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Illusions In Aviation
Human senses are not naturally geared for the in-flight environment. Pilots may experience disorientation and loss of perspective, creating illusions that range from false horizons to sensory conflict with instrument readings or the misjudging of altitude over water. Vestibular system The vestibular system, which is responsible for the sense of balance in humans, consists of the otolith organs and the semicircular canals. Illusions in aviation are caused when the brain cannot reconcile inputs from the vestibular system and visual system. The three semicircular canals, which recognize accelerations in pitch, yaw, and roll, are stimulated by angular accelerations; while the otolith organs, the saccule and utricle, are stimulated by linear accelerations. Stimulation of the semicircular canals occurs when the movement of the endolymph inside the canals causes movement of the crista ampullaris and the hair cells within them. Stimulation of the otolith organs occurs when grav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equilibrioception
The sense of balance or equilibrioception is the perception of balance and spatial orientation. It helps prevent humans and nonhuman animals from falling over when standing or moving. Equilibrioception is the result of a number of sensory systems working together; the eyes (visual system), the inner ears ( vestibular system), and the body's sense of where it is in space (proprioception) ideally need to be intact. The vestibular system, the region of the inner ear where three semicircular canals converge, works with the visual system to keep objects in focus when the head is moving. This is called the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). The balance system works with the visual and skeletal systems (the muscles and joints and their sensors) to maintain orientation or balance. Visual signals sent to the brain about the body's position in relation to its surroundings are processed by the brain and compared to information from the vestibular and skeletal systems. Vestibular system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dizziness
Dizziness is an imprecise term that can refer to a sense of disorientation in space, vertigo, or lightheadedness. It can also refer to Balance disorder, disequilibrium or a non-specific feeling, such as giddiness or foolishness. Dizziness is a common medical complaint, affecting 20–30% of persons. Dizziness is broken down into four main subtypes: vertigo (~25–50%), equilibrioception#Dysfunction, disequilibrium (less than ~15%), presyncope (less than ~15%), and nonspecific dizziness (~10%). * Vertigo is the sensation of spinning or having one's surroundings spin about them. Many people find vertigo very disturbing and often report associated nausea and vomiting. * Presyncope describes lightheadedness or feeling faint; the name relates to Syncope (medicine), syncope, which is actually fainting. * equilibrioception#Dysfunction, Disequilibrium is the sensation of being off balance and is most often characterized by frequent falls in a specific direction. This condition is not of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fictitious Force
A fictitious force, also known as an inertial force or pseudo-force, is a force that appears to act on an object when its motion is described or experienced from a non-inertial reference frame, non-inertial frame of reference. Unlike real forces, which result from physical interactions between objects, fictitious forces occur due to the acceleration of the observer’s frame of reference rather than any actual force acting on a body. These forces are necessary for describing motion correctly within an accelerating frame, ensuring that Newton's laws of motion#Second, Newton's second law of motion remains applicable. Common examples of fictitious forces include the centrifugal force, which appears to push objects outward in a rotating system; the Coriolis force, which affects moving objects in a rotating frame such as the Earth; and the Euler force, which arises when a rotating system changes its angular velocity. While these forces are not real in the sense of being caused by ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaspard-Gustave De Coriolis
Gaspard-Gustave de Coriolis (; 21 May 1792 – 19 September 1843) was a French mathematician, mechanical engineer and scientist. He is best known for his work on the supplementary forces that are detected in a rotating frame of reference, leading to the Coriolis effect. He was the first to apply the term ''travail'' (translated as " work") for the transfer of energy by a force acting through a distance, and he prefixed the factor ½ to Leibniz's concept of '' vis viva'', thus specifying today's ''kinetic energy In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion. In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a non-rotating object of mass ''m'' traveling at a speed ''v'' is \fracmv^2.Resnick, Rober ...''. Biography Coriolis was born in Paris in 1792. In 1808 he sat the entrance exam and was placed second of all the students entering that year, and in 1816, he became a tutor at the École Polytechnique, where he d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compton Generator
A Compton generator or Compton tube is an apparatus for experiment to demonstrate the Earth's rotation, similar to the Foucault pendulum and to gyroscope devices. Arthur Compton (Nobel Prize in Physics in 1927) published it during his fourth year at the College of Wooster in 1913. Explanation of apparatus A Compton generator is a circular hollow glass ring tube shaped like a doughnut, the inside of which is filled with water. If the ring lies flat on the table, the water in the ring is stationary, and it is then turned over by rotating itself 180 degree around a diameter, such that it again lies flat on the table surface, which is horizontal. The result of the experiment is that the water moves with a certain constant drift velocity around the tube after the doughnut has been rotated. If there were no friction with the walls, the water would continue to circulate indefinitely. The ring used in the initial experiment was made of one inch brass tubing bent into a circle eighteen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coriolis Illusion Vertigo 3
Coriolis may refer to: * Gaspard-Gustave de Coriolis (1792–1843), French mathematician, mechanical engineer and scientist * Coriolis force, the apparent deflection of moving objects from a straight path when viewed from a rotating frame of reference * Coriolis (crater), a lunar crater * Coriolis (project), a French operational oceanographic project * Coriolis (satellite) The Coriolis satellite is a Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) and Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) Earth and space observation satellite launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base, on January 6, 2003, at 14:19 GMT. Instruments WINDSAT ''WI ..., an American Earth and space observation satellite launched in 2003 * Coriolis effect (perception) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibular System
The vestibular system, in vertebrates, is a sensory system that creates the sense of balance and spatial orientation for the purpose of coordinating motor coordination, movement with balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory system, it constitutes the labyrinth of the inner ear in most Mammal, mammals. As movements consist of rotations and translations, the vestibular system comprises two components: the semicircular canals, which indicate Angular acceleration, rotational movements; and the otoliths, which indicate Acceleration, linear accelerations. The vestibular system sends signals primarily to the neural structures that control eye movement; these provide the anatomical basis of the vestibulo-ocular reflex, which is required for clear vision. Signals are also sent to the muscles that keep an animal upright and in general control Neutral spine, posture; these provide the anatomical means required to enable an animal to maintain its desired position in space. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bárány Chair
The Barany chair or Bárány chair is a device used for aerospace physiology training, particularly for student pilots. Test The subject is placed in the swivel chair, blindfolded, then spun about the vertical axis while keeping their head upright or tilted forward or to the side. The subject is then asked to perform tasks such as determine their direction of rotation while blindfolded, or rapidly change the orientation of their head, or attempt to point at a stationary object without blindfold after the chair is stopped. The chair is used to demonstrate spatial disorientation effects, proving that the vestibular system is not to be trusted in flight. Pilots are taught that they should instead rely on their flight instruments. Uses The device is also used in motion sickness therapy. Nobel Prize The chair was named for Hungarian physiologist Robert Bárány, who used this device in his research into the role of the inner ear in the sense of balance. He won the 1914 Nobel Prize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disorientation Of False Motion
Illusions of self-motion (or "vection") occur when one perceives bodily motion despite no movement taking place. One can experience illusory movements of the whole body or of individual body parts, such as arms or legs. Vestibular illusions The vestibular system is one of the major sources of information about one's own motion. Disorders of the visual system can lead to dizziness, vertigo, and feelings of instability. Vertigo is not associated with illusory self-motion as it does not typically make one feel as though they are moving; however, in a subclass of vertigo known as subjective vertigo one does experience their own motion. People experience themselves being pulled heavily in one direction. There are also specific self-motion illusions that can occur through abnormal stimulation of various parts of the vestibular system, often encountered in aviation. This includes an illusion of inversion, in which one feels like they're tumbling backwards. Through various stimuli, people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |