|
Copper (64Cu) Oxodotreotide
Copper (64Cu) oxodotreotide or Copper Cu 64 dotatate, sold under the brand name Detectnet, is a radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for use with positron emission tomography (PET) for localization of somatostatin receptor positive neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) in adults. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting and flushing. It was approved for medical use in the United States in September 2020. History The U.S. Food and Drug Administration The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ... (FDA) approved copper 64Cu dotatate based on data from two trials that evaluated 175 adults. Trial 1 evaluated adults, some of whom had known or suspected NETs and some of whom were healthy volunteers. The trial was conducted at one site in the United States (Houston, TX). Bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consumpti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PET Radiotracer
PET radiotracer is a type of radioligand that is used for the diagnostic purposes via positron emission tomography imaging technique. Mechanism PET is a functional imaging technique that produces a three-dimensional image of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide (tracer), which is introduced into the body on a biologically active molecule. Pharmacology In ''in vivo'' systems it is often used to quantify the binding of a test molecule to the binding site of radioligand. The higher the affinity of the molecule the more radioligand is displaced from the binding site and the increasing radioactive decay can be measured by scintillography. This assay is commonly used to calculate binding constant of molecules to receptors. Due to the probable injuries of PET-radiotracers, they could not be administrated in the normal doses of the medications. Therefore, the binding affinity (PKD) of the PET-tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in Metabolism, metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example, 18F-FDG, -FDG is commonly used to detect cancer, Sodium fluoride#Medical imaging, NaF is widely used for detecting bone formation, and Isotopes of oxygen#Oxygen-15, oxygen-15 is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common medical imaging, imaging technique, a Scintigraphy#Process, medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical, radiopharmaceutical — a radioisotope attached to a drug — is injected into the body as a radioactive tracer, tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
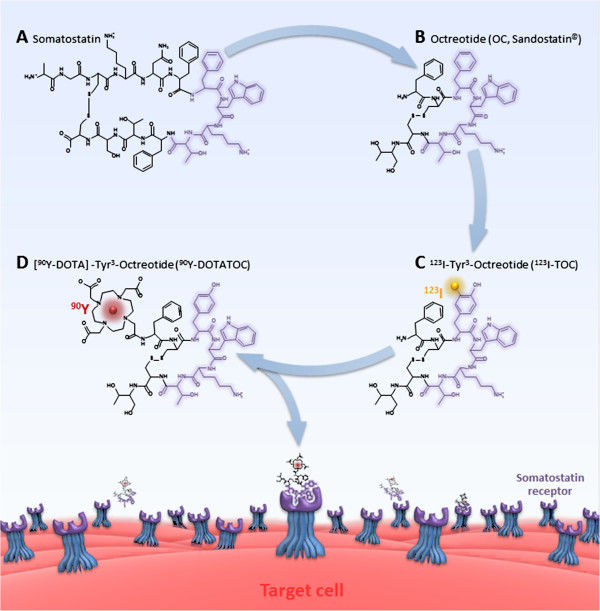
Somatostatin Receptor
Somatostatin receptors are receptors for the ligand somatostatin, a small neuropeptide associated with neural signaling, particularly in the post-synaptic response to NMDA receptor co-stimulation/activation. Somatostatin is encoded by a CRE and is very susceptible to gene promoter region activation by transcription factor CREB. There are five known somatostatin receptors: * SST1 () * SST2 () * SST3 () * SST4 () * SST5 () All are G protein-coupled seven transmembrane receptor G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of protein family, evolution ...s. References External links * G protein-coupled receptors {{transmembranereceptor-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroendocrine Tumors
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung, and the rest of the body. Although there are many kinds of NETs, they are treated as a group of tissue because the cells of these neoplasms share common features, such as looking similar, having special secretory granules, and often producing biogenic amines and polypeptide hormones. Classification WHO The World Health Organization (WHO) classification scheme places neuroendocrine tumors into three main categories, which emphasize the tumor grade rather than the anatomical origin: * well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumours, further subdivided into tumors with benign and those with uncertain behavior * well-differentiated (low grade) neuroendocrine carcinomas with low-grade malignant behavior * poorly differentiated (high grade) ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper-64
Copper-64 (64Cu) is a positron and beta emitting isotope of copper, with applications for molecular radiotherapy and positron emission tomography. Its unusually long half-life (12.7-hours) for a positron-emitting isotope makes it increasingly useful when attached to various ligands, for PET and PET-CT scanning. Properties 64Cu has a half-life of 12.7 hours and decays 17.9% by positron emission to 64Ni, 39.0% by beta decay to 64Zn, 43.1% by electron capture to 64Ni, and 0.475% gamma radiation/internal conversion. These emissions are 0.579 MeV, 0.653 MeV and 1.35 MeV for beta minus, positron, and gamma respectively. The oxidation states of copper in biology are I and II since Cu3+ is too powerful to exist in biochemical systems. Furthermore, copper(I) exists as a strong complex in aqueous solution and is not often seen. Copper(II) forms mononuclear complexes that are paramagnetic and prefers ligands of sulfur and nitrogen. Copper is essential in the human body as both a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
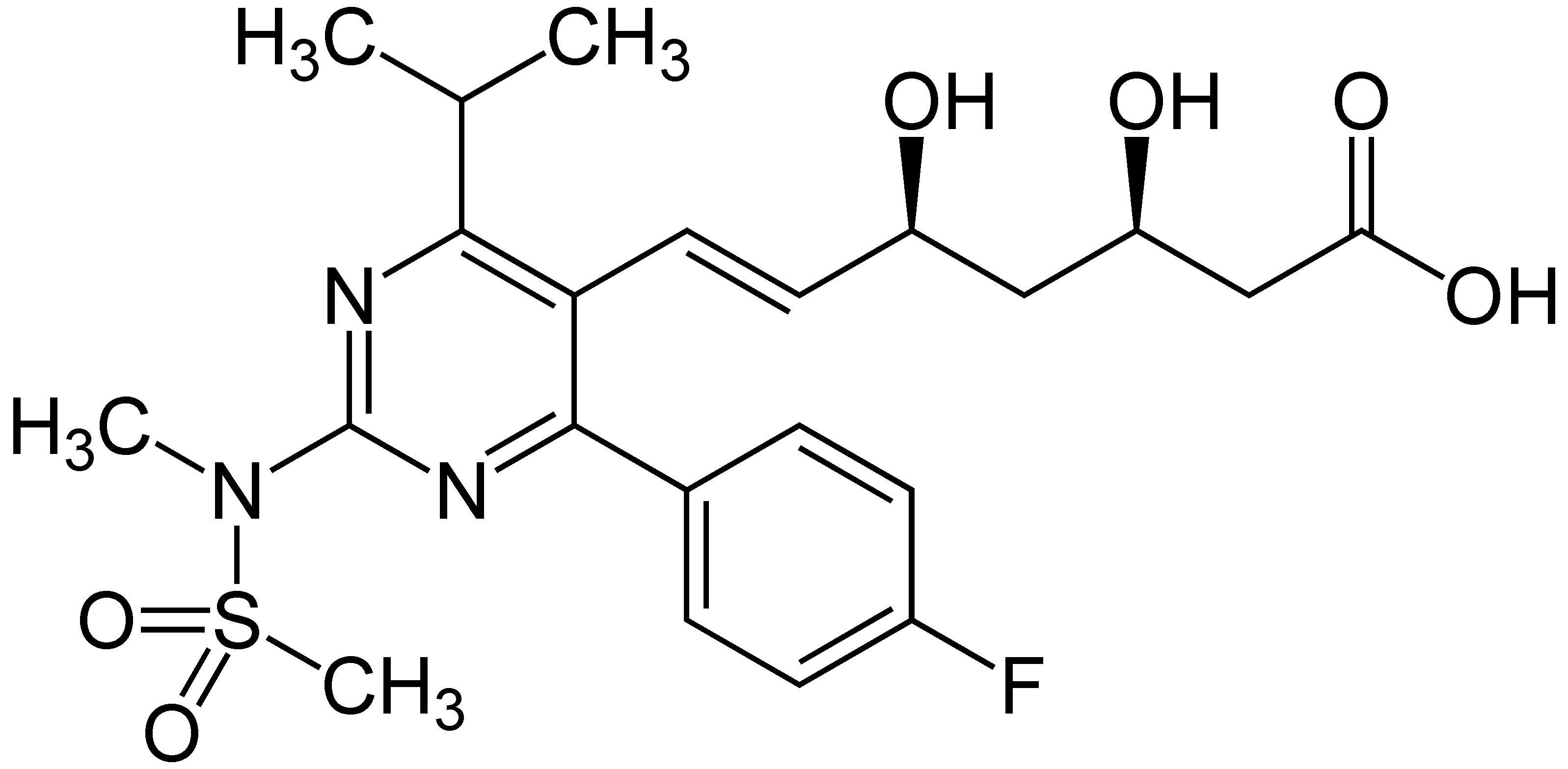
DOTA-TATE
DOTA-TATE (DOTATATE, DOTA-octreotate, oxodotreotide, DOTA-(Tyr3)-octreotate, and DOTA-0-Tyr3-Octreotate) is an eight amino acid long peptide, with a covalently bonded DOTA bifunctional chelator. DOTA-TATE can be reacted with the radionuclides gallium-68 (T1/2 = 68 min), lutetium-177 (T1/2 = 6.65 d) and copper-64 (T1/2 = 12.7 h) to form radiopharmaceuticals for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging or radionuclide therapy. 177Lu DOTA-TATE therapy is a form of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) which targets somatostatin receptors (SSR). In that form of application it is a form of targeted drug delivery. Chemistry and mechanism of action DOTA-TATE is a compound containing tyrosine3-octreotate, an SSR agonist, and the bifunctional chelator DOTA (tetraxetan). SSRs are found with high density in numerous malignancies, including CNS, breast, lung, and lymphatics. The role of SSR agonists (i.e. somatostatin and its analogs such as octreotide, somatuline and vapreo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiopharmaceuticals
Radiopharmaceuticals, or medicinal radiocompounds, are a group of pharmaceutical drugs containing radioactive isotopes. Radiopharmaceuticals can be used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Radiopharmaceuticals emit radiation themselves, which is different from contrast media which absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound. Radiopharmacology is the branch of pharmacology that specializes in these agents. The main group of these compounds are the radiotracers used to diagnose dysfunction in body tissues. While not all medical isotopes are radioactive, radiopharmaceuticals are the oldest and still most common such drugs. Drug nomenclature As with other pharmaceutical drugs, there is standardization of the drug nomenclature for radiopharmaceuticals, although various standards coexist. The International Nonproprietary Names (INNs), United States Pharmacopeia (USP) names, and IUPAC names for these agents are usually similar other than trivial style differences. The de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drugs
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DOTA (chelator) Derivatives
''Dota'' is a series of strategy video games by Valve. The series began in 2003 with the release of ''Defense of the Ancients'' (''DotA''), a fan-developed multiplayer online battle arena (MOBA) mod for the video game '' Warcraft III: Reign of Chaos'' and its expansion, '' The Frozen Throne''. The original mod features gameplay centered around two teams of up to five players who assume control of individual characters called "heroes", which must coordinate to destroy the enemy's central base structure called an "Ancient", to win the game. Ownership and development of ''DotA'' were passed on multiple times since its initial release until Valve hired the mod's lead designer IceFrog and after an ongoing legal dispute with Blizzard Entertainment, the developer of ''Warcraft III'', brokered a deal that allowed for Valve to inherit the trademark to the ''Dota'' name. The first standalone installment in the series, '' Dota 2'', was released by Valve in July 2013. A sequel to ''DotA'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)