|
Convertible Bond
In finance, a convertible bond, convertible note, or convertible debt (or a convertible debenture if it has a maturity of greater than 10 years) is a type of bond that the holder can convert into a specified number of shares of common stock in the issuing company or cash of equal value. It is a hybrid security with debt- and equity-like features. It originated in the mid-19th century, and was used by early speculators such as Jacob Little and Daniel Drew to counter market cornering. Convertible bonds are also considered debt security because the companies agree to give fixed or floating interest rate as they do in common bonds for the funds of investor. To compensate for having additional value through the option to convert the bond to stock, a convertible bond typically has a coupon rate lower than that of similar, non-convertible debt. The investor receives the potential upside of conversion into equity while protecting downside with cash flow from the coupon payments a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finance
Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and Academic discipline, discipline of money, currency, assets and Liability (financial accounting), liabilities. As a subject of study, is a field of Business administration, Business Administration wich study the planning, organizing, leading, and controlling of an organization's resources to achieve its goals. Based on the scope of financial activities in financial systems, the discipline can be divided into Personal finance, personal, Corporate finance, corporate, and public finance. In these financial systems, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as Currency, currencies, loans, Bond (finance), bonds, Share (finance), shares, stocks, Option (finance), options, Futures contract, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, Investment, invested, and Insurance, insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, Financial risk, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. Due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
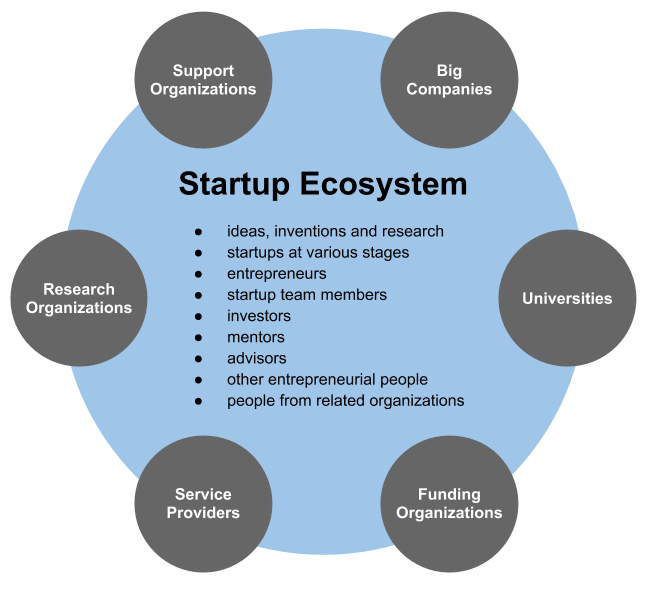
Startup Company
A startup or start-up is a company or project undertaken by an Entrepreneurship, entrepreneur to seek, develop, and validate a scalable business model. While entrepreneurship includes all new businesses including self-employment and businesses that do not intend to Initial public offering, go public, startups are new businesses that intend to grow large beyond the solo-founder. During the beginning, startups face high uncertainty and have high rates of failure, but a minority of them do go on to become successful and influential, such as unicorn (finance), unicorns.Erin Griffith (2014)Why startups fail, according to their founders, Fortune.com, 25 September 2014; accessed 27 October 2017 Actions Startups typically begin by a founder (solo-founder) or co-founders who have a way to solve a problem. The founder of a startup will do the market validation by problem interview, solution interview, and building a minimum viable product (MVP), i.e. a prototype, to develop and validate thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Par Value
In finance and accounting, par value means stated value or face value of a financial instrument. Expressions derived from this term include at par (at the par value), over par (over par value) and under par (under par value). Bonds A bond selling at par is priced at 100% of face value. Par can also refer to a bond's original issue value or its value upon redemption at maturity. Stock The par value of stock has no relation to market value and, as a concept, is somewhat archaic. The par value of a share is the value stated in the corporate charter below which shares of that class cannot be sold upon initial offering; the issuing company promises not to issue further shares below par value, so investors can be confident that no one else will receive a more favorable issue price. Thus, par value is the nominal value of a security which is determined by the issuing company to be its minimum price. This was far more important in unregulated equity markets than in the regulated marke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Share (finance)
In finance, financial markets, a share (sometimes referred to as stock or Equity (finance), equity) is a unit of Equity (finance), equity ownership in the Stock, capital stock of a corporation. It can refer to units of mutual funds, limited partnerships, and real estate investment trusts. Share capital refers to all of the shares of an enterprise. The owner of shares in a company is a shareholder (or stockholder) of the corporation. A share expresses the ownership relationship between the company and the shareholder. The denominated value of a share is its face value, and the total of the face value of issued shares represent the Financial capital, capital of a company, which may not reflect the market value of those shares. The income received from the ownership of shares is a dividend. There are different types of shares such as equity shares, preference shares, deferred shares, redeemable shares, bonus shares, right shares, and employee stock option plan shares. Terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrinsic Value (finance)
In finance, the intrinsic value of an asset or security is its ''value'' as calculated with regard to an inherent, objective measure. A distinction, is re the asset's ''price'', which is determined ''relative'' to other similar assets. The intrinsic approach to valuation may be somewhat simplified, in that it ignores elements other than the measure in question. Options For an option, the intrinsic value is the absolute value of the difference between the current price (''S'') of the underlying and the strike price (''K'') of the option, to the extent that this is in favor of the option holder. Thus, the option is said to have intrinsic value if the option is in-the-money; when out-of-the-money, its intrinsic value is ''zero''. For an option, then, the intrinsic value is the same as the "immediate value" or the "current value" of the contract, which is the profit that could be gained by exercising the option immediately. Formulaically: :IV_= 0 :IV_=\left \vert S-K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Price
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation expected, required, or given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, especially when the product is a service rather than a physical good, the price for the service may be called something else such as "rent" or "tuition". Prices are influenced by production costs, supply of the desired product, and demand for the product. A price may be determined by a monopolist or may be imposed on the firm by market conditions. Price can be quoted in currency, quantities of goods or vouchers. * In modern economies, prices are generally expressed in units of some form of currency. (More specifically, for raw materials they are expressed as currency per unit weight, e.g. euros per kilogram or Rands per KG.) * Although prices could be quoted as quantities of other goods or services, this sort of barter exchange is rarely seen. Prices are sometimes quoted in terms of vouch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Over-the-counter (finance)
Over-the-counter (OTC) or off-exchange trading or pink sheet trading is done directly between two parties, without the supervision of an exchange. It is contrasted with exchange trading, which occurs via exchanges. A stock exchange has the benefit of facilitating liquidity, providing transparency, and maintaining the current market price. In an OTC trade, the price is not necessarily publicly disclosed. OTC trading, as well as exchange trading, occurs with commodities, financial instruments (including stocks), and derivatives of such products. Products traded on traditional stock exchanges, and other regulated bourse platforms, must be well standardized. This means that exchanged deliverables match a narrow range of quantity, quality, and identity which is defined by the exchange and identical to all transactions of that product. This is necessary for there to be transparency in stock exchange-based equities trading. The OTC market does not have this limitation. Parties may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe, The Middle East And Africa
Europe, the Middle East and Africa, commonly known by its acronym EMEA among the North American business spheres, is a geographical region used by institutions, governments and global spheres of marketing, media and business when referring to this region. The acronym EMEA is a shorthand way of referencing the two continents (Africa and Europe) and the Middle Eastern sub-continent all at once. As the name suggests, the region includes all of the countries found on the continents of Africa and Europe, as well as the countries that make up the Middle East. The region is generally accepted to include all European nations and all African nations, and extends east to Iran, including part of Russia. Typically, the acronym does not include overseas territories of mainland countries in the region, such as French Guiana. However, the term is not completely clear, and while it usually refers to Europe, the Middle East and Africa, it is not uncommon for businesses and other institutions to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diluted EPS
Dilution may refer to: * Reducing the concentration of a chemical * Serial dilution, stepwise * Homeopathic dilution * Dilution (equation), an equation to calculate the rate a gas dilutes *Trademark dilution, weakening of a trademark by unauthorised use *Stock dilution Stock dilution, also known as equity dilution, is the decrease in existing shareholders' ownership percentage of a company as a result of the company issuing new equity. New equity increases the total shares outstanding which has a dilutive ef ..., issuing of new company shares * Dilution gene, lightening animal coat color * Dilution ratio * Hemodynamics#Hemodilution, of blood * Dilution refrigerator, cryogenic device See also * Delusion (other) * Dilation (other) {{disambig zh:稀释 nl:Verdunning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilutive Security
Dilutive securities are financial instruments—usually stock options, warrants, convertible bonds—which increase the number of common shares if exercised; this then reduces, or "dilutes", the basic EPS (earnings per share). Thus, only where the diluted EPS is less than the basic EPS is the transaction classified as dilutive. Compare Accretion (finance). Some examples of dilutive securities are convertible debt, convertible preferred stock, options, warrants, participating securities, two-class common stocks, and contingent shares. The concept of dilutive securities is often a purely theoretical one, since these instruments will not be converted into common stock unless the price at which they can be purchased will generate a profit Profit may refer to: Business and law * Profit (accounting), the difference between the purchase price and the costs of bringing to market * Profit (economics), normal profit and economic profit * Profit (real property), a nonposse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cliquet
A cliquet option or ratchet option is an exotic option consisting of a series of consecutive forward start options. The first is active immediately. The second becomes active when the first expires, etc. Each option is struck at-the-money when it becomes active. A cliquet is, therefore, a series of at-the-money options but where the total premium is determined in advance. A cliquet can be thought of as a series of "pre-purchased" at-the-money options. The payout on each option can either be paid at the final maturity, or at the end of each reset period.http://docs.fincad.com/support/developerFunc/mathref/cliquet.htm FiNCAD - Cliquet options] Example A three-year cliquet with reset dates each year would have three payoffs. * The first would pay off at the end of the first year and has the same payoff as a normal ATM option. * The second year's payoff has the same payoff as a one-year option, but with the strike price In finance, the strike price (or exercise price) of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |