|
Continuously Variable Slope Delta Modulation
Continuously variable slope delta modulation (CVSD or CVSDM) is a voice coding method. It is a delta modulation with variable step size (i.e., special case of adaptive delta modulation), first proposed by Greefkes and Riemens in 1970. CVSD encodes at 1 bit per sample, so that audio sampled at 16 kHz is encoded at 16 kbit/s. The encoder maintains a reference sample and a step size. Each input sample is compared to the reference sample. If the input sample is larger, the encoder emits a ''1'' bit and adds the step size to the reference sample. If the input sample is smaller, the encoder emits a ''0'' bit and subtracts the step size from the reference sample. The encoder also keeps the previous ''N'' bits of output (''N'' = 3 or ''N'' = 4 are very common) to determine adjustments to the step size; if the previous ''N'' bits are all 1s or 0s, the step size is increased. Otherwise, the step size is decreased (usually in an exponential manner, with \tau being in the range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech Coding
Speech coding is an application of data compression of digital audio signals containing speech. Speech coding uses speech-specific parameter estimation using audio signal processing techniques to model the speech signal, combined with generic data compression algorithms to represent the resulting modeled parameters in a compact bitstream. Some applications of speech coding are mobile telephony and voice over IP (VoIP). The most widely used speech coding technique in mobile telephony is linear predictive coding (LPC), while the most widely used in VoIP applications are the LPC and modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) techniques. The techniques employed in speech coding are similar to those used in audio data compression and audio coding where knowledge in psychoacoustics is used to transmit only data that is relevant to the human auditory system. For example, in voiceband speech coding, only information in the frequency band 400 to 3500 Hz is transmitted but the reconst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-law Algorithm
An A-law algorithm is a standard companding algorithm, used in European 8-bit PCM digital communications systems to optimize, i.e. modify, the dynamic range of an analog signal for digitizing. It is one of two versions of the G.711 standard from ITU-T, the other version being the similar μ-law, used in North America and Japan. For a given input x, the equation for A-law encoding is as follows: F(x) = \sgn(x) \begin \dfrac, & , x, < \dfrac, \\ ex \dfrac, & \dfrac \leq , x, \leq 1, \end where is the compression parameter. In Europe, . A-law expansion is given by the inverse function: The reason for this encoding is that the wide |
Delta-sigma Modulation
Delta-sigma (ΔΣ; or sigma-delta, ΣΔ) modulation is a method for encoding analog signals into digital signals as found in an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). It is also used to convert high bit-count, low-frequency digital signals into lower bit-count, higher-frequency digital signals as part of the process to convert digital signals into analog as part of a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). In a conventional ADC, an analog signal is sampled with a sampling frequency and subsequently quantized in a multi-level quantizer into a digital signal. This process introduces quantization error noise. The first step in a delta-sigma modulation is delta modulation. In delta modulation the change in the signal (its delta) is encoded, rather than the absolute value. The result is a stream of pulses, as opposed to a stream of numbers as is the case with pulse-code modulation (PCM). In delta-sigma modulation, accuracy of the modulation is improved by passing the digital output throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
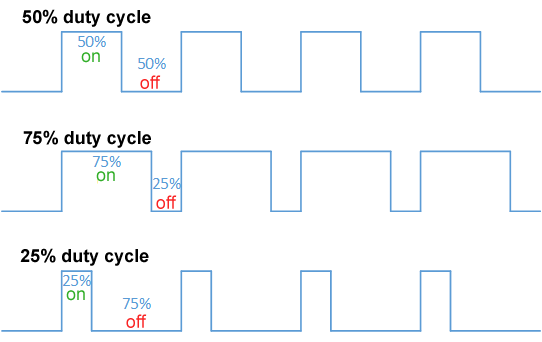
Pulse-width Modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), or pulse-duration modulation (PDM), is a method of reducing the average power delivered by an electrical signal, by effectively chopping it up into discrete parts. The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by turning the switch between supply and load on and off at a fast rate. The longer the switch is on compared to the off periods, the higher the total power supplied to the load. Along with maximum power point tracking (MPPT), it is one of the primary methods of reducing the output of solar panels to that which can be utilized by a battery. PWM is particularly suited for running inertial loads such as motors, which are not as easily affected by this discrete switching, because their inertia causes them to react slowly. The PWM switching frequency has to be high enough not to affect the load, which is to say that the resultant waveform perceived by the load must be as smooth as possible. The rate (or frequency) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Triangle Park
Research Triangle Park (RTP) is the largest research park in the United States, occupying in North Carolina and hosting more than 300 companies and 65,000 workers. The facility is named for its location relative to the three surrounding cities of Raleigh, Durham, and Chapel Hill, or more properly, for the three major research universities in them: North Carolina State University, Duke University and University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill respectively. The Research Triangle region of North Carolina received its name as an extension of the name of the park. Aside from the three anchor cities, the park is also bounded by the communities of Morrisville and Cary. Approximately one fourth of the Park's territory lies in Wake County, but the majority of its land is in Durham County. Overview Research Triangle Park is one of the most prominent high-tech research and development parks in the United States. It was created in 1959 by state and local governments, nearby universities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echo Suppressor
Echo suppression and echo cancellation are methods used in telephony to improve voice quality by preventing echo from being created or removing it after it is already present. In addition to improving subjective audio quality, echo suppression increases the capacity achieved through silence suppression by preventing echo from traveling across a telecommunications network. Echo suppressors were developed in the 1950s in response to the first use of satellites for telecommunications. Echo suppression and cancellation methods are commonly called acoustic echo suppression (AES) and acoustic echo cancellation (AEC), and more rarely line echo cancellation (LEC). In some cases, these terms are more precise, as there are various types and causes of echo with unique characteristics, including acoustic echo (sounds from a loudspeaker being reflected and recorded by a microphone, which can vary substantially over time) and line echo (electrical impulses caused by, e.g., coupling between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Business Systems
Satellite Business Systems (SBS) was a company founded by IBM, Aetna, COMSAT (and later wholly purchased by IBM and then subsequently sold to MCI), that provided private professional satellite communications through its SBS fleet of FSS geosynchronous satellites, and was the first company to do so. SBS was founded on December 15, 1975 by the aforementioned companies with the goal of providing a digital satellite communications network for business and other professional clients. History In late 1970, MCI Communications created a subsidiary company named MCI Satellite, Inc. The idea was that satellites could provide 'long distance' service from anywhere to anywhere without having to build thousands of miles of terrestrial network facilities. In early 1971, MCI and Lockheed Missiles and Space Company created a joint venture named MCI Lockheed Satellite Corp. which was the first company to request FCC authorization as a Specialized Common Carrier using satellite based communic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle (pinball)
''Space Shuttle'' (full title: ''Space Shuttle: Pinball Adventure'') is a Space Shuttle themed pinball machine designed by Barry Oursler and Joe Kaminkow and produced in 1984 by Williams Electronics. The machine's marketing slogan is "The fastest way to make your earnings really take off!". It is notable for its central ramp shot up a feature themed after the Space Shuttle. A sequel, ''Space Station: Pinball Rendezvous'', was released in 1987. Gameplay In ''Space Shuttle'' the main goal is to acquire the shuttle score value from spelling out "S H U T T L E" by hitting six stand up targets and one drop target - or by using the lit inlanes (if available). The reward for the shuttle score value is assigned randomly with each new ball, or by hitting a stand up target, at the top of a short ramp. It will be one of the following: *50,000 points plus a bonus holdover, *an extra ball (a score award is given if 5 extra balls are earned during game), *a special, *100,000 points, * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgar
''Gorgar'' is a 1979 pinball machine designed by Barry Oursler and released by WMS Industries, Williams Electronics. It was the first speech synthesis, speech-synthesized ("talking") pinball machine, containing a vocabulary of seven words ("Gorgar", "speaks", "beat", "you", "me", "hurt", "got") that were combined to form varying broken-English phrases, such as "Gorgar speaks" and "Me got you". The pinball machine also has a heartbeat sound effect that increases in speed during longer gameplay. Digital versions ''Gorgar'' was available on FarSight Studios' 2012 release ''The Pinball Arcade'' for multiple platforms until June 29, 2018, when the license for inclusion of Williams and Bally tables in the game expired. The table is included in the ''Pinball Hall of Fame: The Williams Collection''. Unauthorized reproductions of this table are available for ''Visual Pinball''. In popular culture The machine appears in the 5th episode of the 2nd season of Highway to Heaven, appropriately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smash TV
''Smash TV'' is a 1990 arcade video game created by Eugene Jarvis and Mark Turmell for Williams Electronics Games. It is a dual-stick shooter (one for moving and the other for firing) in the same vein as 1982's '' Robotron: 2084'' (co-created by Jarvis). The Super NES, Genesis, Master System, and Game Gear versions are titled ''Super Smash TV''. The plot centers on a dystopian television show during the then-future year of 1999, where one or two contestants must shoot their way to fame and fortune; the show is taped in front of a live studio audience with broadcast via satellite worldwide. The goal of the game show is to kill or be killed, and once all of the challengers in each arena have been massacred, the contestant(s) will proceed to survive the next gauntlet. Gameplay 250px, left, Arcade screenshot The play mechanic is similar to that of Eugene Jarvis' earlier '' Robotron: 2084'', with dual-joystick controls and series of single-screen arenas. While most of the enemies i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinistar
''Sinistar'' is a 1983 multidirectional shooter arcade game developed and manufactured by Williams Electronics. It was created by Sam Dicker, Jack Haeger, Noah Falstein, RJ Mical, Python Anghelo, and Richard Witt. Players control a spacecraft pilot who battles the eponymous Sinistar. In addition to the game's use of digitized speech for its antagonist, ''Sinistar'' is known for its high difficulty level. Gameplay The player pilots a lone spacecraft, mining drifting planetoids and catching the crystals which are released. Shooting a planetoid too rapidly destroys it without releasing any crystals. Each collected crystal turns into a "Sinibomb", which is needed to defeat the game boss, Sinistar, an animated spacecraft with a demonic skull face. Sinistar does not exist at the start of the game, but is constructed by enemy worker ships. Enemy worker ships collect crystals which they use to construct the Sinistar. Enemy warrior ships can directly attack the player's ship, shoot pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |