|
Continuous-wave Radar
Continuous-wave radar (CW radar) is a type of radar system where a known stable frequency continuous wave radio energy is transmitted and then received from any reflecting objects. Individual objects can be detected using the Doppler effect, which causes the received signal to have a different frequency from the transmitted signal, allowing it to be detected by filtering out the transmitted frequency. Doppler-analysis of radar returns can allow the filtering out of slow or non-moving objects, thus offering immunity to interference from large stationary objects and slow-moving clutter. This makes it particularly useful for looking for objects against a background reflector, for instance, allowing a high-flying aircraft to look for aircraft flying at low altitudes against the background of the surface. Because the very strong reflection off the surface can be filtered out, the much smaller reflection from a target can still be seen. CW radar systems are used at both ends of the ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna (radio), antenna with the purpose of signal transmission to a radio receiver. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the Antenna (radio), antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna Electromagnetic radiation, radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary component parts of all electronic devices that communicate by radio communication, radio, such as radio broadcasting, radio (audio) and television broadcasting stations, cell phones, walkie-talkies, Wireless LAN, wireless computer networks, Bluetooth enabled devices, garage door openers, two-way radios in aircraft, ships, spacecraft, radar sets and navigational beacons. The term ''transmitter'' is usually limited to equipment that generates radio waves fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppler Effect Diagrammatic
The Doppler effect (also Doppler shift) is the change in the frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave. The ''Doppler effect'' is named after the physicist Christian Doppler, who described the phenomenon in 1842. A common example of Doppler shift is the change of pitch (music), pitch heard when a vehicle sounding a horn approaches and recedes from an observer. Compared to the emitted frequency, the received frequency is higher during the approach, identical at the instant of passing by, and lower during the recession. When the source of the sound wave is moving towards the observer, each successive cycle of the wave is emitted from a position closer to the observer than the previous cycle. Hence, from the observer's perspective, the time between cycles is reduced, meaning the frequency is increased. Conversely, if the source of the sound wave is moving away from the observer, each cycle of the wave is emitted from a position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baseband
In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is the range of frequencies occupied by a signal that has not been modulated to higher frequencies. Baseband signals typically originate from transducers, converting some other variable into an electrical signal. For example, the electronic output of a microphone is a baseband signal that is analogous to the applied voice audio. In conventional analog radio broadcasting, the baseband audio signal is used to modulate an RF carrier signal of a much higher frequency. A baseband signal may have frequency components going all the way down to the DC bias, or at least it will have a high ratio bandwidth. A modulated baseband signal is called a passband signal. This occupies a higher range of frequencies and has a lower ratio and fractional bandwidth. Various uses Baseband signal A ''baseband signal'' or ''lowpass signal'' is a signal that can include frequencies that are very near zero, by comparison with its highest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
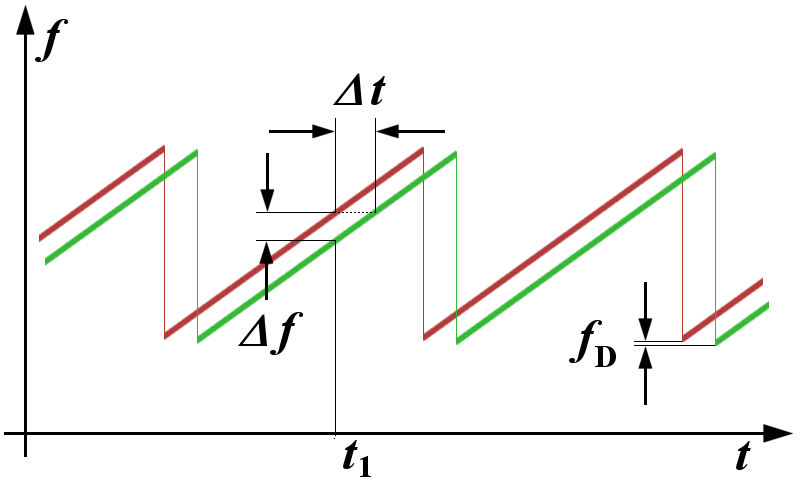
Fmcw Prinziple
Continuous-wave radar (CW radar) is a type of radar system where a known stable frequency continuous wave radio energy is transmitted and then received from any reflecting objects. Individual objects can be detected using the Doppler radar, Doppler effect, which causes the received signal to have a different frequency from the transmitted signal, allowing it to be detected by filtering out the transmitted frequency. Doppler-analysis of radar returns can allow the filtering out of slow or non-moving objects, thus offering immunity to interference from large stationary objects and slow-moving Clutter (radar), clutter. This makes it particularly useful for looking for objects against a background reflector, for instance, allowing a high-flying aircraft to look for aircraft flying at low altitudes against the background of the surface. Because the very strong reflection off the surface can be filtered out, the much smaller reflection from a target can still be seen. CW radar systems a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Wave (waveform)
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform, non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same duration at minimum and maximum. In an ideal square wave, the transitions between minimum and maximum are instantaneous. The square wave is a special case of a pulse wave which allows arbitrary durations at minimum and maximum amplitudes. The ratio of the high period to the total period of a pulse wave is called the duty cycle. A true square wave has a 50% duty cycle (equal high and low periods). Square waves are often encountered in electronics and signal processing, particularly digital electronics and digital signal processing. Its stochastic counterpart is a two-state trajectory. Origin and uses Square waves are universally encountered in digital switching circuits and are naturally generated by binary (two-level) logic devices. They are used as timing references or "clock signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle Wave
A triangular wave or triangle wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform named for its triangular shape. It is a periodic, piecewise linear, continuous real function. Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics. However, the higher harmonics roll off much faster than in a square wave (proportional to the inverse square of the harmonic number as opposed to just the inverse). Definitions Definition A triangle wave of period ''p'' that spans the range , 1is defined as x(t) = 2 \left, \frac - \left\lfloor \frac + \frac \right\rfloor \, where \lfloor\ \rfloor is the floor function. This can be seen to be the absolute value of a shifted sawtooth wave. For a triangle wave spanning the range the expression becomes x(t)= 2 \left , 2 \left( \frac - \left\lfloor \frac + \frac \right\rfloor \right) \ - 1. A more general equation for a triangle wave with amplitude a and period p using the modulo operation and absolute value is y(x) = \frac \left, \left ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawtooth Wave
The sawtooth wave (or saw wave) is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is so named based on its resemblance to the teeth of a plain-toothed saw with a zero rake angle. A single sawtooth, or an intermittently triggered sawtooth, is called a ramp waveform. The convention is that a sawtooth wave ramps upward and then sharply drops. In a reverse (or inverse) sawtooth wave, the wave ramps downward and then sharply rises. It can also be considered the extreme case of an asymmetric triangle wave. The equivalent piecewise linear functions x(t) = t - \lfloor t \rfloor x(t) = t \bmod 1 based on the floor function of time ''t'' is an example of a sawtooth wave with period 1. A more general form, in the range −1 to 1, and with period ''p'', is 2\left( - \left\lfloor + \right\rfloor\right) This sawtooth function has the same phase as the sine function. While a square wave is constructed from only odd harmonics, a sawtooth wave's sound is harsh and clear and its spectrum cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sine Wave
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or sinusoid (symbol: ∿) is a periodic function, periodic wave whose waveform (shape) is the trigonometric function, trigonometric sine, sine function. In mechanics, as a linear motion over time, this is ''simple harmonic motion''; as rotation, it corresponds to ''uniform circular motion''. Sine waves occur often in physics, including wind waves, sound waves, and light waves, such as monochromatic radiation. In engineering, signal processing, and mathematics, Fourier analysis decomposes general functions into a sum of sine waves of various frequencies, relative phases, and magnitudes. When any two sine waves of the same frequency (but arbitrary phase (waves), phase) are linear combination, linearly combined, the result is another sine wave of the same frequency; this property is unique among periodic waves. Conversely, if some phase is chosen as a zero reference, a sine wave of arbitrary phase can be written as the linear combination of two sine wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beat (acoustics)
In acoustics, a beat is an interference pattern between two sounds of slightly different frequencies, ''perceived'' as a periodic variation in volume whose rate is the difference of the two frequencies. With tuning instruments that can produce sustained tones, beats can be readily recognized. Tuning two tones to a unison will present a peculiar effect: when the two tones are close in pitch but not identical, the difference in frequency generates the beating. The volume varies as in a tremolo as the sounds alternately interfere constructively and destructively. As the two tones gradually approach unison, the beating slows down and may become so slow as to be imperceptible. As the two tones get further apart, their beat frequency starts to approach the range of human pitch perception, the beating starts to sound like a note, and a combination tone is produced. Mathematics and physics of beat tones This phenomenon is best known in acoustics or music, though it can be found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Radar
Wave radar is a type of radar for measuring wind waves. Several instruments based on a variety of different concepts and techniques are available, and these are all often called. This article (see also Grønlie 2004), gives a brief description of the most common ground-based radar remote sensing techniques. Instruments based on radar remote sensing techniques have become of particular interest in applications where it is important to avoid direct contact with the water surface and avoid structural interference. A typical case is wave measurements from an offshore platform in deep water, where swift currents could make mooring a wave buoy enormously difficult. Another interesting case is a ship under way, where having instruments in the sea is highly impractical and interference from the ship's hull must be avoided. Radar remote sensing Terms and definitions Basically there are two different ''classes'' of radar remote sensors for ocean waves. * Direct sensor measures dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Altimeter
A radar altimeter (RA), also called a radio altimeter (RALT), electronic altimeter, reflection altimeter, or low-range radio altimeter (LRRA), measures altitude above the terrain presently beneath an aircraft or spacecraft by timing how long it takes a beam of radio waves to travel to ground, reflect, and return to the craft. This type of altimeter provides the distance between the antenna and the ground directly below it, in contrast to a barometric altimeter which provides the distance above a defined vertical datum, usually mean sea level. Principle As the name implies, radar (radio detection and ranging) is the underpinning principle of the system. The system transmits radio waves down to the ground and measures the time it takes them to be reflected back up to the aircraft. The altitude above the ground is calculated from the radio waves' travel time and the speed of light. Radar altimeters required a simple system for measuring the time-of-flight that could be displayed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |