|
Constantine (son Of Leo V)
Symbatios ( el, Συμβάτιος, from the Armenian ''Smbat''), variously also Sabbatios (Σαββάτιος) or Sambates (Σαμβάτης) in some sources, was the eldest son of the Byzantine emperor Leo V the Armenian (). Soon after the coronation of his father, he was crowned co-emperor and renamed Constantine (Κωνσταντῖνος, ''Kōnstantînos''). He reigned nominally along with his father until the latter's deposition in 820, after which he was exiled to Prote, one of the Princes Islands, as a monk. Biography Symbatios was the eldest son of the emperor Leo V the Armenian () and his wife, Theodosia. His father was an Armenian commander in Byzantine service, possibly descended from the Gnuni family. He had risen to high command as a protégé of Bardanes Tourkos, but deserted him when the latter rebelled against Nikephoros I (). His mother was also of Armenian origin, the daughter of the ''patrikios'' Arsaber who attempted an unsuccessful usurpation against Nik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
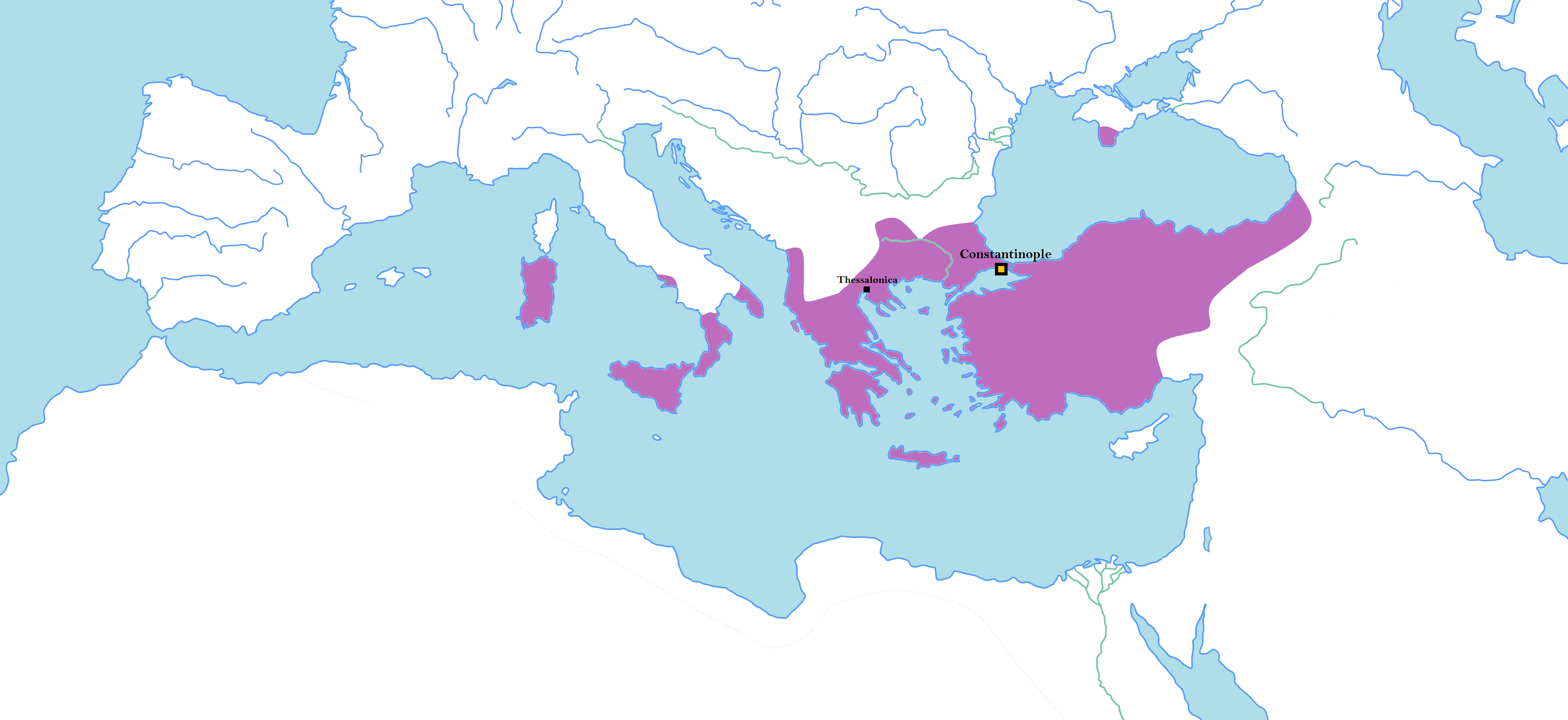
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros I
Nikephoros I or Nicephorus I ( gr, Νικηφόρος; 750 – 26 July 811) was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. Having served Empress Irene as '' genikos logothetēs'', he subsequently ousted her from power and took the throne himself. In reference to his career before becoming emperor, he is sometimes surnamed "the Logothete" (ὁ Λογοθέτης) and "Genikos" or "Genicus" (ὁ Γενικός). Nikephoros pursued wars against the Arabs and Bulgarians, with mixed results; while invading Bulgaria he was defeated and killed at the Battle of Pliska. Background Sources outside the Byzantine context, including Michael the Syrian, al-Tabari, and Mas'udi, preserve the tradition that Nikephoros was of Ghassanid Arab origin. al-Tabari claims that he derived this information from Byzantine sources, but no surviving Byzantine chronicle makes explicit mention of the emperor's ethnic background. The modern scholar Paul Julius Alexander suggests that al-Tabari did transmit informat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine V
Constantine V ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντῖνος, Kōnstantīnos; la, Constantinus; July 718 – 14 September 775), was Byzantine emperor from 741 to 775. His reign saw a consolidation of Byzantine security from external threats. As an able military leader, Constantine took advantage of civil war in the Muslim world to make limited offensives on the Arab frontier. With this eastern frontier secure, he undertook repeated campaigns against the Bulgars in the Balkans. His military activity, and policy of settling Christian populations from the Arab frontier in Thrace, made Byzantium's hold on its Balkan territories more secure. Religious strife and controversy was a prominent feature of his reign. His fervent support of Iconoclasm and opposition to monasticism led to his vilification by later Byzantine historians and writers, who denigrated him with the nicknames "the Dung-Named" ( grc-gre, Κοπρώνυμος, Koprónimos; la, Copronymus), because he allegedly defaecated dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo III The Isaurian
Leo III the Isaurian ( gr, Λέων ὁ Ἴσαυρος, Leōn ho Isauros; la, Leo Isaurus; 685 – 18 June 741), also known as the Syrian, was Byzantine Emperor from 717 until his death in 741 and founder of the Isaurian dynasty. He put an end to the Twenty Years' Anarchy, a period of great instability in the Byzantine Empire between 695 and 717, marked by the rapid succession of several emperors to the throne. He also successfully defended the Empire against the invading Umayyads and forbade the veneration of icons. Early life Of Syrian extraction, Leo was born in Germanikeia, Commagene (modern Kahramanmaraş in Turkey). His original name was Konon ( gr, Κόνων; la, Conon or ''Cononus''). Some, including the Byzantine chronicler Theophanes, have claimed that Konon's family had been resettled in Thrace, where he entered the service of Emperor Justinian II, when the latter was advancing on Constantinople with an army of loyalist followers, and horsemen provided by Terve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Iconoclasm
The Byzantine Iconoclasm ( gr, Εικονομαχία, Eikonomachía, lit=image struggle', 'war on icons) were two periods in the history of the Byzantine Empire when the use of religious images or icons was opposed by religious and imperial authorities within the Orthodox Church and the temporal imperial hierarchy. The First Iconoclasm, as it is sometimes called, occurred between about 726 and 787, while the Second Iconoclasm occurred between 814 and 842. According to the traditional view, Byzantine Iconoclasm was started by a ban on religious images promulgated by the Byzantine Emperor Leo III the Isaurian, and continued under his successors. It was accompanied by widespread destruction of religious images and persecution of supporters of the veneration of images. The Papacy remained firmly in support of the use of religious images throughout the period, and the whole episode widened the growing divergence between the Byzantine and Carolingian traditions in what was still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine The Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterranea (now Niš, Serbia), he was the son of Constantius Chlorus, Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer of Illyrians, Illyrian origin who had been one of the four rulers of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, mother of Constantine I, Helena, was a Greeks, Greek Christian of low birth. Later canonized as a saint, she is traditionally attributed with the conversion of her son. Constantine served with distinction under the Roman emperors Diocletian and Galerius. He began his career by campaigning in the eastern provinces (against the Sasanian Empire, Persians) before being recalled in the west (in AD 305) to fight alongside his father in Roman Britain, Britain. After his father's death in 306, Constantine be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosopography Of The Byzantine Empire
The Prosopography of the Byzantine World (PBW) is a project to create a prosopographical database of individuals named in textual sources in the Byzantine Empire and surrounding areas in the period from 642 to 1265. The project is a collaboration between the British Academy and the Berlin-Brandenburg Academy of Sciences and Humanities. Origins The project was begun in the 1980s with the aim of completing the work on later Roman Empire and Byzantine prosopography begun by Theodore Mommsen in the 19th century and carried on by A.H.M. Jones and J. R. Martindale, which produced ''The Prosopography of the Later Roman Empire'' (three volumes, Cambridge, 1971–1992), covering the period from 260 (the accession of Gallienus) to 641 (the death of Heraclius, marking the end of late Antiquity). In 1993, the British Academy signed a collaboration agreement with the Berlin-Brandenburg Academy. The work is divided into three periods, 641–867 (Heraclian dynasty to the Amorian dynasty), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warren Treadgold
Warren T. Treadgold (born April 30, 1949, Oxford, England) is an American historian and specialist in Byzantine studies. He is the National Endowment for the Humanities Professor of Byzantine Studies at Saint Louis University. His interest in the political, economic, military, social, and cultural history of the Byzantine Empire extends to the Byzantine historians themselves. Treadgold has also taught at UCLA, Stanford, Hillsdale, Berkeley, and Florida International University. He is married since September 25, 1982 to Irina Andreescu-Treadgold. Education Treadgold holds an AB from Harvard University (1970) and a PhD from the same university (1977). Books * ''The University We Need: Reforming America’s Higher Education'' (New York: Encounter Books, 2018); * ''The Middle Byzantine Historians'' (New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2013); * ''The Early Byzantine Historians'' (New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2007); * ''A Concise History of Byzantium'' (New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2001 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Browning (Byzantinist)
Robert Browning, FBA (; 15 January 1914 – 11 March 1997) was a Scottish Byzantinist and university professor. Early career Browning was born in Glasgow in 1914. He attended Kelvinside Academy in that city. He entered the Humanities department of Glasgow University in 1931, graduating in 1935. As Snell Exhibitioner at Balliol College, Oxford, he acquired first class degrees in Mods and Greats as well as several prizes (Nowlands, Ireland, Craven, Ferguson, De Paravicini, and Jenkyns). During his time at Glasgow University, Browning became proficient in several Eastern European languages, beginning with Albanian. In 1939, Browning received a second degree from Glasgow, and began a seven-year service with the Royal Artillery. During that time he mastered the Georgian language. He served on the General Staff in Italy, and on the Allied Control Commission in Sofia, Bulgaria. In Belgrade, Yugoslavia, he was assistant to the British Military Attaché. Lecturing career, honour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scriptor Incertus
''Scriptor Incertus de Leone Armenio'' ("unknown writer on Leo the Armenian") is the conventional Latin designation given to the anonymous author of a 9th-century Byzantine historical work, of which only two fragments survive. The first fragment, preserved in the 13th-century ''Vat. gr. 2014'' manuscript (interposed into descriptions of the Avaro-Persian siege of Constantinople and the Second Arab Siege of Constantinople, as well as hagiographical texts) in the Vatican Library, deals with the 811 campaign of Emperor Nikephoros I () against the Bulgars, which ended in the disastrous Battle of Pliska. Discovered and published in 1936 by I. Dujčev, it is also known as the ''Chronicle of 811'', or the Dujčev Fragment. The second, which is preserved in the early 11th-century ''B.N. gr. 1711'' manuscript in the Bibliotheque Nationale in Paris along with the chronicle of the so-called "Leo Grammaticus", deals with the reigns of Michael I Rhangabe () and Leo V the Armenian () that fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire ( cu, блъгарьско цѣсарьствиѥ, blagarysko tsesarystviye; bg, Първо българско царство) was a medieval Bulgar- Slavic and later Bulgarian state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led by Asparuh, moved south to the northeastern Balkans. There they secured Byzantine recognition of their right to settle south of the Danube by defeatingpossibly with the help of local South Slavic tribesthe Byzantine army led by Constantine IV. During the 9th and 10th century, Bulgaria at the height of its power spread from the Danube Bend to the Black Sea and from the Dnieper River to the Adriatic Sea and became an important power in the region competing with the Byzantine Empire. It became the foremost cultural and spiritual centre of south Slavic Europe throughout most of the Middle Ages. As the state solidified its position in the Balka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Versinikia
The Battle of Versinikia ( bg, Битката при Версиникия; el, Μάχη της Βερσινικίας) was fought in 813 between the Byzantine Empire and the Bulgarian Empire, near the city of Adrianople (Edirne). While the Bulgarians, led by Krum, had an army about half the size of the Byzantine Empire, they were victorious, resulting in the dethroning of Byzantine Emperor Michael I Rangabe (811–813) by Leo V the Armenian. The battle was a major success for the Bulgarians and further strengthened the Bulgarian position after their victory over Nicephorus I two years earlier. After the battle they took ''de facto'' control of the whole of Eastern Thrace (until the Byzantine–Bulgarian Treaty of 815) with the exception of a few castles that remained in Byzantine control. For the first time in Bulgarian history, the way to Constantinople was opened. Krum died at the height of the preparation for the final siege of the Byzantine capital on the 13th of April 814. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)


