|
Computability Logic
Computability logic (CoL) is a research program and mathematical framework for redeveloping logic as a systematic formal theory of computability, as opposed to classical logic which is a formal theory of truth. It was introduced and so named by Giorgi Japaridze in 2003. In classical logic, formulas represent true/false statements. In CoL, formulas represent computational problems. In classical logic, the validity of a formula depends only on its form, not on its meaning. In CoL, validity means being always computable. More generally, classical logic tells us when the truth of a given statement always follows from the truth of a given set of other statements. Similarly, CoL tells us when the computability of a given problem ''A'' always follows from the computability of other given problems ''B1,...,Bn''. Moreover, it provides a uniform way to actually construct a solution (algorithm) for such an ''A'' from any known solutions of ''B1,...,Bn''. CoL formulates computational pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computability
Computability is the ability to solve a problem in an effective manner. It is a key topic of the field of computability theory within mathematical logic and the theory of computation within computer science. The computability of a problem is closely linked to the existence of an algorithm to solve the problem. The most widely studied models of computability are the Turing-computable and μ-recursive functions, and the lambda calculus, all of which have computationally equivalent power. Other forms of computability are studied as well: computability notions weaker than Turing machines are studied in automata theory, while computability notions stronger than Turing machines are studied in the field of hypercomputation. Problems A central idea in computability is that of a (computational) problem, which is a task whose computability can be explored. There are two key types of problems: * A decision problem fixes a set ''S'', which may be a set of strings, natural numbers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequent Calculus
In mathematical logic, sequent calculus is a style of formal logical argumentation in which every line of a proof is a conditional tautology (called a sequent by Gerhard Gentzen) instead of an unconditional tautology. Each conditional tautology is inferred from other conditional tautologies on earlier lines in a formal argument according to rules and procedures of inference, giving a better approximation to the natural style of deduction used by mathematicians than to David Hilbert's earlier style of formal logic, in which every line was an unconditional tautology. More subtle distinctions may exist; for example, propositions may implicitly depend upon non-logical axioms. In that case, sequents signify conditional theorems in a first-order language rather than conditional tautologies. Sequent calculus is one of several extant styles of proof calculus for expressing line-by-line logical arguments. * Hilbert style. Every line is an unconditional tautology (or theorem). * Gentze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computability Theory
Computability theory, also known as recursion theory, is a branch of mathematical logic, computer science, and the theory of computation that originated in the 1930s with the study of computable functions and Turing degrees. The field has since expanded to include the study of generalized computability and definability. In these areas, computability theory overlaps with proof theory and effective descriptive set theory. Basic questions addressed by computability theory include: * What does it mean for a function on the natural numbers to be computable? * How can noncomputable functions be classified into a hierarchy based on their level of noncomputability? Although there is considerable overlap in terms of knowledge and methods, mathematical computability theorists study the theory of relative computability, reducibility notions, and degree structures; those in the computer science field focus on the theory of subrecursive hierarchies, formal methods, and formal languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logics For Computability
Logics for computability are formulations of logic which capture some aspect of computability as a basic notion. This usually involves a mix of special logical connectives as well as semantics which explains how the logic is to be interpreted in a computational way. Probably the first formal treatment of logic for computability is the ''realizability interpretation'' by Stephen Kleene in 1945, who gave an interpretation of intuitionistic number theory in terms of Turing machine computations. His motivation was to make precise the '' Heyting-Brouwer-Kolmogorov (BHK) interpretation'' of intuitionism, according to which proofs of mathematical statements are to be viewed as constructive procedures. With the rise of many other kinds of logic, such as modal logic and linear logic, and novel semantic models, such as game semantics, logics for computability have been formulated in several contexts. Here we mention two. Modal logic for computability Kleene's original realizability interpre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the science of deductively valid inferences or of logical truths. It is a formal science investigating how conclusions follow from premises in a topic-neutral way. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Formal logic contrasts with informal logic, which is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. While there is no general agreement on how formal and informal logic are to be distinguished, one prominent approach associates their difference with whether the studied arguments are expressed in formal or informal languages. Logic plays a central role in multiple fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics. Logic studies arguments, which consist of a set of premises together with a conclusion. Premises and conclusions are usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Semantics
Game semantics (german: dialogische Logik, translated as '' dialogical logic'') is an approach to formal semantics that grounds the concepts of truth or validity on game-theoretic concepts, such as the existence of a winning strategy for a player, somewhat resembling Socratic dialogues or medieval theory of Obligationes. History In the late 1950s Paul Lorenzen was the first to introduce a game semantics for logic, and it was further developed by Kuno Lorenz. At almost the same time as Lorenzen, Jaakko Hintikka developed a model-theoretical approach known in the literature as ''GTS'' (game-theoretical semantics). Since then, a number of different game semantics have been studied in logic. Shahid Rahman (Lille) and collaborators developed dialogical logic into a general framework for the study of logical and philosophical issues related to logical pluralism. Beginning 1994 this triggered a kind of renaissance with lasting consequences. This new philosophical impulse experienced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Many-one Reduction
In computability theory and computational complexity theory, a many-one reduction (also called mapping reduction) is a reduction which converts instances of one decision problem L_1 into instances of a second decision problem L_2 where the instance reduced to is in the language L_2 if the initial instance was in its language L_1 and is not in the language L_2 if the initial instance was not in its language L_1. Thus if we can decide whether L_2 instances are in the language L_2, we can decide whether L_1 instances are in its language by applying the reduction and solving L_2. Thus, reductions can be used to measure the relative computational difficulty of two problems. It is said that L_1 reduces to L_2 if, in layman's terms L_2 is harder to solve than L_1. That is to say, any algorithm that solves L_2 can also be used as part of a (otherwise relatively simple) program that solves L_1. Many-one reductions are a special case and stronger form of Turing reductions. With many-one re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turing Reduction
In computability theory, a Turing reduction from a decision problem A to a decision problem B is an oracle machine which decides problem A given an oracle for B (Rogers 1967, Soare 1987). It can be understood as an algorithm that could be used to solve A if it had available to it a subroutine for solving ''B''. The concept can be analogously applied to function problems. If a Turing reduction from A to B exists, then every algorithm for B can be used to produce an algorithm for A, by inserting the algorithm for B at each place where the oracle machine computing A queries the oracle for B. However, because the oracle machine may query the oracle a large number of times, the resulting algorithm may require more time asymptotically than either the algorithm for B or the oracle machine computing A. A Turing reduction in which the oracle machine runs in polynomial time is known as a Cook reduction. The first formal definition of relative computability, then called relative reducibili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computation In The Limit
In computability theory, a function is called limit computable if it is the limit of a uniformly computable sequence of functions. The terms computable in the limit, limit recursive and recursively approximable are also used. One can think of limit computable functions as those admitting an eventually correct computable guessing procedure at their true value. A set is limit computable just when its characteristic function is limit computable. If the sequence is uniformly computable relative to ''D'', then the function is limit computable in ''D''. Formal definition A total function r(x) is limit computable if there is a total computable function \hat(x,s) such that : \displaystyle r(x) = \lim_ \hat(x,s) The total function r(x) is limit computable in ''D'' if there is a total function \hat(x,s) computable in ''D'' also satisfying : \displaystyle r(x) = \lim_ \hat(x,s) A set of natural numbers is defined to be computable in the limit if and only if its characteristic functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recursively Enumerable Set
In computability theory, a set ''S'' of natural numbers is called computably enumerable (c.e.), recursively enumerable (r.e.), semidecidable, partially decidable, listable, provable or Turing-recognizable if: *There is an algorithm such that the set of input numbers for which the algorithm halts is exactly ''S''. Or, equivalently, *There is an algorithm that enumerates the members of ''S''. That means that its output is simply a list of all the members of ''S'': ''s''1, ''s''2, ''s''3, ... . If ''S'' is infinite, this algorithm will run forever. The first condition suggests why the term ''semidecidable'' is sometimes used. More precisely, if a number is in the set, one can ''decide'' this by running the algorithm, but if the number is not in the set, the algorithm runs forever, and no information is returned. A set that is "completely decidable" is a computable set. The second condition suggests why ''computably enumerable'' is used. The abbreviations c.e. and r.e. are oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decidability (logic)
In logic, a true/false decision problem is decidable if there exists an effective method for deriving the correct answer. Zeroth-order logic (propositional logic) is decidable, whereas first-order and higher-order logic are not. Logical systems are decidable if membership in their set of logically valid formulas (or theorems) can be effectively determined. A theory (set of sentences closed under logical consequence) in a fixed logical system is decidable if there is an effective method for determining whether arbitrary formulas are included in the theory. Many important problems are undecidable, that is, it has been proven that no effective method for determining membership (returning a correct answer after finite, though possibly very long, time in all cases) can exist for them. Decidability of a logical system Each logical system comes with both a syntactic component, which among other things determines the notion of provability, and a semantic component, which determine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
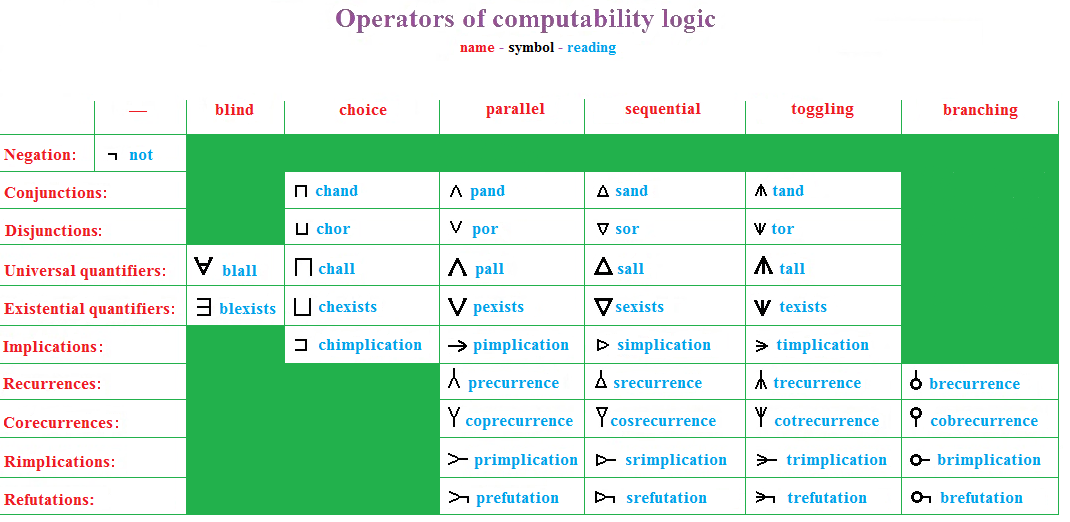
Operators Of Computability Logic
Operator may refer to: Mathematics * A symbol indicating a mathematical operation * Logical operator or logical connective in mathematical logic * Operator (mathematics), mapping that acts on elements of a space to produce elements of another space, e.g.: ** Linear operator ** Differential operator ** Integral operator (other) Computers * Computer operator, an occupation * Operator (computer programming), a type of computer program function * Operator (extension), an extension for the Firefox web browser, for reading microformats * Ableton Operator, a software synthesizer developed by Ableton Science * Operator (biology), a segment of DNA regulating the activity of genes * Operator (linguistics), a special category including wh- interrogatives * Operator (physics), mathematical operators in quantum physics Music * Operator (band), an American hard rock band * Operators, a synth pop band led by Dan Boeckner * ''Operator'' (album), a 2016 album by Mstrkrft * "Operat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |