|
Compound Operation (other)
Compound operation may refer to: * Compound operation (dies), in die manufacturing * Compound operation (computing), in computing ** Compound assignment, in computing * Compound operation (engines), in engines * Compound operation (steam engines), in steam engines * Compound operation (locomotives), in locomotives See also * Compound operator * Fused operation * Transpositional inversion * Compound (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Operation (dies)
A die is a specialized machine tool used in manufacturing industries to cut and/or Forming (metalworking), form material to a desired shape or profile. ''Stamping (metalworking), Stamping dies'' are used with a machine press, press, as opposed to ''Draw plate, drawing dies'' (used in the manufacture of wire) and ''Die casting, casting dies'' (used in Molding (process), molding) which are not. Like molds, dies are generally customized to the item they are used to create. Products made with dies range from simple paper clips to complex pieces used in advanced technology. Continuous production, Continuous-feed laser cutting may displace the analogous die-based process in the automotive industry, among others. Die stamping Blanking and piercing are two Shearing (manufacturing), die cutting operations, and Bending (metalworking), bending is an example of a die forming operation. Die forming Forming operations work by deforming materials like sheet metal or plastic using force (Compre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Operation (computing)
In computer programming, an operator is a programming language construct that provides functionality that may not be possible to define as a user-defined function (i.e. sizeof in C) or has syntax different than a function (i.e. infix addition as in a+b). Like other programming language concepts, ''operator'' has a generally accepted, although debatable meaning among practitioners while at the same time each language gives it specific meaning in that context, and therefore the meaning varies by language. Some operators are represented with symbols characters typically not allowed for a function identifier to allow for presentation that is more familiar looking than typical function syntax. For example, a function that tests for greater-than could be named gt, but many languages provide an infix symbolic operator so that code looks more familiar. For example, this: if gt(x, y) then return Can be: if x > y then return Some languages allow a language-defined operator to be o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Assignment
Compound may refer to: Architecture and built environments * Compound (enclosure), a cluster of buildings having a shared purpose, usually inside a fence or wall ** Compound (fortification), a version of the above fortified with defensive structures * Compound (migrant labour), a hostel for migrant workers such as those historically connected with mines in South Africa * The Compound, an area of Palm Bay, Florida, US * Komboni or compound, a type of slum in Zambia Government and law * Composition (fine), a legal procedure in use after the English Civil War ** Committee for Compounding with Delinquents, an English Civil War institution that allowed Parliament to compound the estates of Royalists * Compounding treason, an offence under the common law of England * Compounding a felony, a previous offense under the common law of England Linguistics * Compound (linguistics), a word that consists of more than one radical element * Compound sentence (linguistics), a type of sentenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
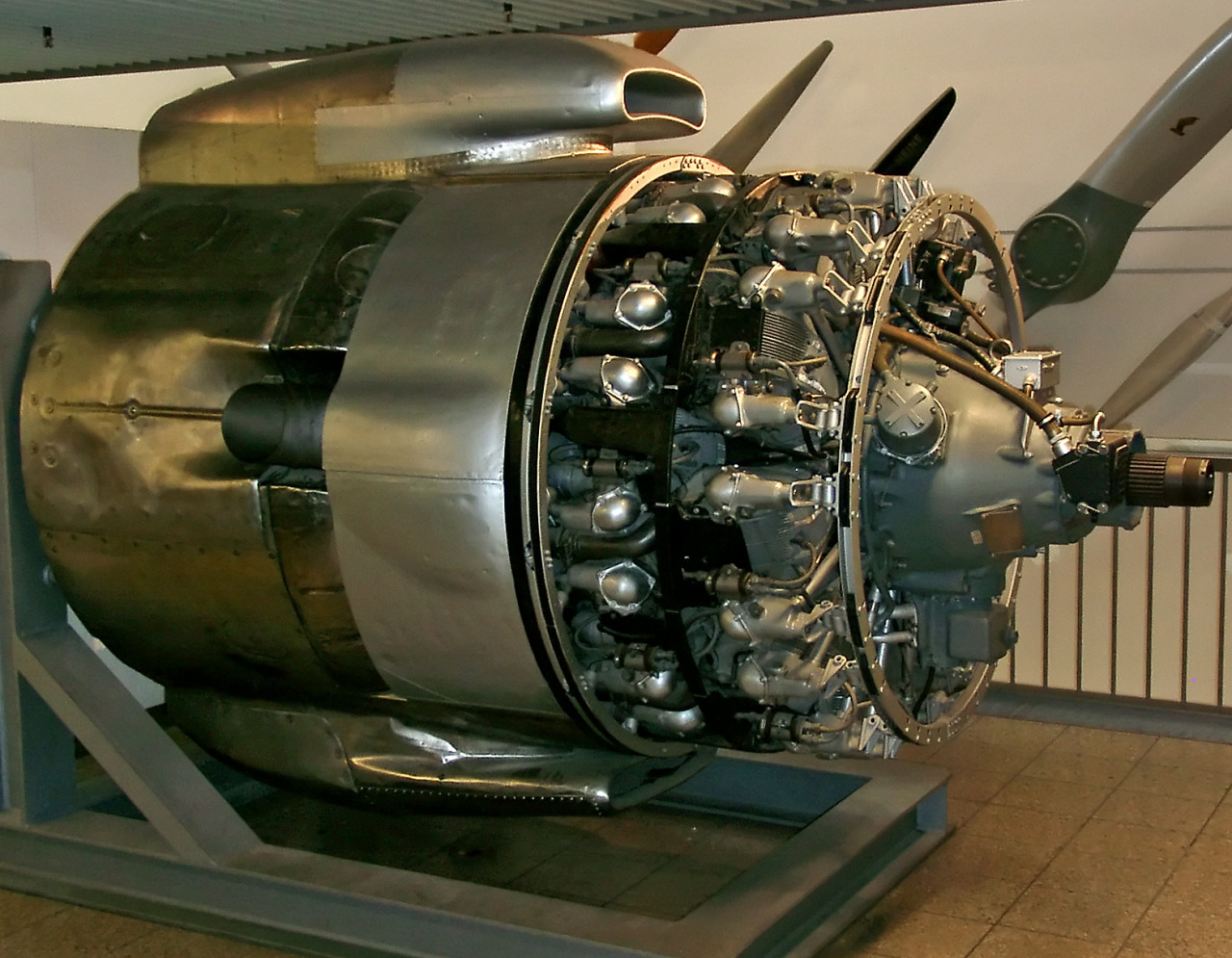
Compound Operation (engines)
A compound engine is an engine that has more than one stage for recovering energy from the same working fluid, with the exhaust from the first stage passing through the second stage, and in some cases then on to another subsequent stage or even stages. Originally invented as a means of making steam engines more efficient, the compounding of engines by use of several stages has also been used on internal combustion engines and continues to have niche markets there. The stages of a compound engine may be either of differing or of similar technologies, for example: * In a turbo-compound engine, the exhaust gas from the cylinders passes through a turbine, the two stages being dissimilar. * In a compound steam locomotive, the steam passes from the high-pressure cylinder or cylinders to the low-pressure cylinder or cylinders, the two stages being similar. * In a triple-expansion steam engine, the steam passes through three successive cylinders of increasing size and decreasing pressu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
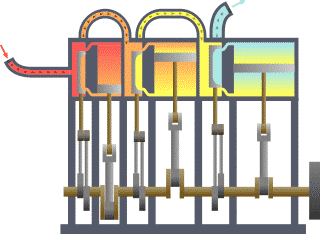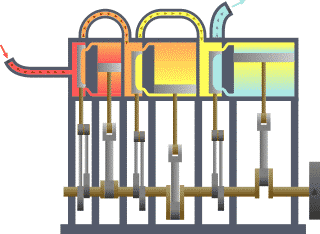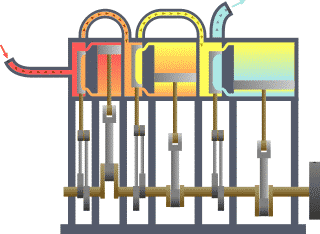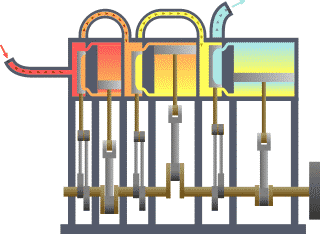
Compound Operation (steam Engines)
A compound steam engine unit is a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. A typical arrangement for a compound engine is that the steam is first expanded in a high-pressure (HP) cylinder, then having given up heat and losing pressure, it exhausts directly into one or more larger-volume low-pressure (LP) cylinders. Multiple-expansion engines employ additional cylinders, of progressively lower pressure, to extract further energy from the steam. Invented in 1781, this technique was first employed on a Cornish beam engine in 1804. Around 1850, compound engines were first introduced into Lancashire textile mills. Compound systems There are many compound systems and configurations, but there are two basic types, according to how HP and LP piston strokes are phased and hence whether the HP exhaust is able to pass directly from HP to LP ( Woolf compounds) or whether pressure fluctuation necessitates an intermediate "buffer" space in the form of a steam che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
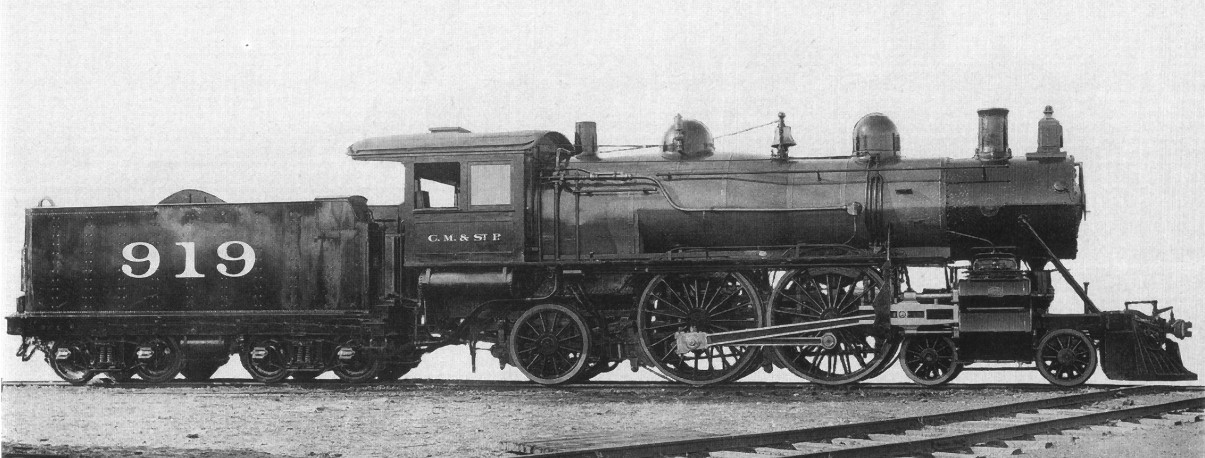
Compound Operation (locomotives)
A compound locomotive is a steam locomotive which is powered by a compound engine, a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. The locomotive was only one application of compounding. Two and three stages were used in ships, for example. Compounding became popular for railway locomotives from the early 1880s and by the 1890s were becoming common. Large numbers were constructed, mostly two- and four-cylinder compounds, in Germany, Austria, Hungary, and the United States. It declined in popularity due to a perceived increased maintenance requirement. Nonetheless, compound Mallets were built by the Norfolk and Western Railway up to 1952 and more importantly, Compound locomotives continued to be designed and built in France until the end of steam in the 1970's. French compounding of railway engines became so highly developed, eventually incorporating reheaters between the high and low pressure stages as well as the initial use of superheaters, that France ach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Operator
In computer programming, an operator is a programming language construct that provides functionality that may not be possible to define as a user-defined function (i.e. sizeof in C) or has syntax different than a function (i.e. infix addition as in a+b). Like other programming language concepts, ''operator'' has a generally accepted, although debatable meaning among practitioners while at the same time each language gives it specific meaning in that context, and therefore the meaning varies by language. Some operators are represented with symbols characters typically not allowed for a function identifier to allow for presentation that is more familiar looking than typical function syntax. For example, a function that tests for greater-than could be named gt, but many languages provide an infix symbolic operator so that code looks more familiar. For example, this: if gt(x, y) then return Can be: if x > y then return Some languages allow a language-defined operator to be o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fused Operation
In computer programming, an operator is a programming language construct that provides functionality that may not be possible to define as a user-defined function (i.e. sizeof in C) or has syntax different than a function (i.e. infix addition as in a+b). Like other programming language concepts, ''operator'' has a generally accepted, although debatable meaning among practitioners while at the same time each language gives it specific meaning in that context, and therefore the meaning varies by language. Some operators are represented with symbols characters typically not allowed for a function identifier to allow for presentation that is more familiar looking than typical function syntax. For example, a function that tests for greater-than could be named gt, but many languages provide an infix symbolic operator so that code looks more familiar. For example, this: if gt(x, y) then return Can be: if x > y then return Some languages allow a language-defined operator to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transpositional Inversion
In music theory, an inversion is a rearrangement of the top-to-bottom elements in an interval, a chord, a melody, or a group of contrapuntal lines of music. In each of these cases, "inversion" has a distinct but related meaning. The concept of inversion also plays an important role in musical set theory. Intervals An interval is inverted by raising or lowering either of the notes by one or more octaves so that the higher note becomes the lower note and vice versa. For example, the inversion of an interval consisting of a C with an E above it (the third measure below) is an E with a C above it – to work this out, the C may be moved up, the E may be lowered, or both may be moved. : The tables to the right show the changes in interval quality and interval number under inversion. Thus, perfect intervals remain perfect, major intervals become minor and vice versa, and augmented intervals become diminished and vice versa. (Doubly diminished intervals become doubly augment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |