|
Community Recognition
Community recognition is the acknowledgement by a community or social group of a notable achievement. It is often followed by awards and celebrations, such as the annual Phoenix, Arizona Community Recognition Awards and related breakfast. The core of it is to bring attention to the contributions made to the community. In ''The Forms of Capital'' (1986) Pierre Bourdieu distinguishes between three forms of capital: economic capital, cultural capital and social capital. He defines social capital as "the aggregate of the actual or potential resources which are linked to possession of a durable network of more or less institutionalized relationships of mutual acquaintance and recognition." Thus, community recognition can be defined as a form of social capital. Recognition by community members, whether by subordinates, peers or superiors, is also part of motivation theory. The reward of an individual creates a positive feedback loop, incenting them, and others who are inspired by their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenix, Arizona
Phoenix ( ; nv, Hoozdo; es, Fénix or , yuf-x-wal, Banyà:nyuwá) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Arizona, with 1,608,139 residents as of 2020. It is the fifth-most populous city in the United States, and the only U.S. state capital with a population of more than one million residents. Phoenix is the anchor of the Phoenix metropolitan area, also known as the Valley of the Sun, which in turn is part of the Salt River Valley. The metropolitan area is the 11th largest by population in the United States, with approximately 4.85 million people . Phoenix, the seat of Maricopa County, has the largest area of all cities in Arizona, with an area of , and is also the 11th largest city by area in the United States. It is the largest metropolitan area, both by population and size, of the Arizona Sun Corridor megaregion. Phoenix was settled in 1867 as an agricultural community near the confluence of the Salt and Gila Rivers and was incorporated as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Bourdieu
Pierre Bourdieu (; 1 August 1930 – 23 January 2002) was a French sociologist and public intellectual. Bourdieu's contributions to the sociology of education, the theory of sociology, and sociology of aesthetics have achieved wide influence in several related academic fields (e.g. anthropology, media and cultural studies, education, popular culture, and the arts). During his academic career he was primarily associated with the School for Advanced Studies in the Social Sciences in Paris and the Collège de France. Bourdieu's work was primarily concerned with the dynamics of power in society, especially the diverse and subtle ways in which power is transferred and social order is maintained within and across generations. In conscious opposition to the idealist tradition of much of Western philosophy, his work often emphasized the corporeal nature of social life and stressed the role of practice and embodiment in social dynamics. Building upon and criticizing the theories o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital (economics)
In economics, capital goods or capital are "those durable produced goods that are in turn used as productive inputs for further production" of goods and services. At the macroeconomic level, "the nation's capital stock includes buildings, equipment, software, and inventories during a given year." A typical example is the machinery used in factories. Capital can be increased by the use of the factors of production, which however excludes certain durable goods like homes and personal automobiles that are not used in the production of saleable goods and services. Adam Smith defined capital as "that part of man's stock which he expects to afford him revenue". In economic models, capital is an input in the production function. The total physical capital at any given moment in time is referred to as the capital stock (not to be confused with the capital stock of a business entity). Capital goods, real capital, or capital assets are already-produced, durable goods or any n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Capital
In the field of sociology, cultural capital comprises the social assets of a person (education, intellect, style of speech, style of dress, etc.) that promote social mobility in a stratified society. Cultural capital functions as a social relation within an economy of practices (i.e. system of exchange), and includes the accumulated cultural knowledge that confers social status and power; thus cultural capital comprises the material and symbolic goods, without distinction, that society considers rare and worth seeking. There are three types of cultural capital: (i) embodied capital, (ii) objectified capital, and (iii) institutionalised capital. Pierre Bourdieu and Jean-Claude Passeron coined and defined the term ''cultural capital'' in the essay "Cultural Reproduction and Social Reproduction" (1977). Bourdieu then developed the concept in the essay "The Forms of Capital" (1985) and in the book ''The State Nobility: Élite Schools in the Field of Power'' (1996) to explain that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Capital
Social capital is "the networks of relationships among people who live and work in a particular society, enabling that society to function effectively". It involves the effective functioning of social groups through interpersonal relationships, a shared sense of identity, a shared understanding, shared norms, shared values, trust, cooperation, and reciprocity. Social capital is a measure of the value of resources, both tangible (e.g., public spaces, private property) and intangible (e.g., actors, human capital, people), and the impact that ideal creators have on the resources involved in each relationship, and on larger groups. Some have described it as a form of capital that produces public goods for a common purpose, although this does not align with how it has been measured. Social capital has been used to explain the improved performance of diverse groups, the growth of entrepreneurial firms, superior managerial performance, enhanced supply chain relations, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motivation
Motivation is the reason for which humans and other animals initiate, continue, or terminate a behavior at a given time. Motivational states are commonly understood as forces acting within the agent that create a disposition to engage in goal-directed behavior. It is often held that different mental states compete with each other and that only the strongest state determines behavior. This means that we can be motivated to do something without actually doing it. The paradigmatic mental state providing motivation is desire. But various other states, such as beliefs about what one ought to do or intentions, may also provide motivation. Motivation is derived from the word 'motive', which denotes a person's needs, desires, wants, or urges. It is the process of motivating individuals to take action in order to achieve a goal. The psychological elements fueling people's behavior in the context of job goals might include a desire for money. Various competing theories have been proposed co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
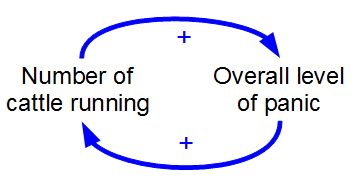
Positive Feedback Loop
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, ''A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A''.Keesing, R.M. (1981). Cultural anthropology: A contemporary perspective (2nd ed.) p.149. Sydney: Holt, Rinehard & Winston, Inc. In contrast, a system in which the results of a change act to reduce or counteract it has negative feedback. Both concepts play an important role in science and engineering, including biology, chemistry, and cybernetics. Mathematically, positive feedback is defined as a positive loop gain around a closed loop of cause and effect. That is, positive feedback is in phase with the input, in the sense that it adds to make the input larger. Positive feedback tends to cause system instability. When the loop gain is pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Reinforcement
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Nega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Community Building
Community building is a field of practices directed toward the creation or enhancement of community among individuals within a regional area (such as a neighborhood) or with a common need or interest. It is often encompassed under the fields of community organizing, community organization, community work, and community development. A wide variety of practices can be utilized for community building, ranging from simple events like potlucks and small book clubs, to larger–scale efforts such as mass festivals and building construction projects that involve local participants rather than outside contractors. Activists and community workers engaged in community building efforts in industrialized nations see the apparent loss of community in these societies as a key cause of social disintegration and the emergence of many harmful behaviors. They may see building community as a means to address perceived social inequality and injustice, individual and collective well-bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Networks
A social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing the structure of whole social entities as well as a variety of theories explaining the patterns observed in these structures. The study of these structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns, locate influential entities, and examine network dynamics. Social networks and the analysis of them is an inherently interdisciplinary academic field which emerged from social psychology, sociology, statistics, and graph theory. Georg Simmel authored early structural theories in sociology emphasizing the dynamics of triads and "web of group affiliations". Jacob Moreno is credited with developing the first sociograms in the 1930s to study interpersonal relationships. These approaches were mathematically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Economy
The social economy is formed by a rich diversity of enterprises and organisations, such as cooperatives, mutuals, associations, foundations, social enterprises and paritarian institutions, sharing common values and features: * Primacy of the individual and the social objective over capital * Voluntary and open membership * Democratic governance * Combination of interests of members/users and/or the general interest * Defence and application of the principles of solidarity and responsibility * Autonomous management and independence from public authorities, though cross-sector collaboration is common * Reinvestment of at least most of the profits to carry out sustainable development objectives, services of interest to members or of general interest Social economy enterprises and organisations have different sizes, ranging from SMEs to large companies and groups that are leaders in their markets, and operate in all the economic sectors. History Third sector As a field of st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Influence
Social influence comprises the ways in which individuals adjust their behavior to meet the demands of a social environment. It takes many forms and can be seen in conformity, socialization, peer pressure, obedience, leadership, persuasion, sales, and marketing. Typically social influence results from a specific action, command, or request, but people also alter their attitudes and behaviors in response to what they perceive others might do or think. In 1958, Harvard psychologist Herbert Kelman identified three broad varieties of social influence. #Compliance is when people appear to agree with others but actually keep their dissenting opinions private. # Identification is when people are influenced by someone who is liked and respected, such as a famous celebrity. #Internalization is when people accept a belief or behavior and agree both publicly and privately. Morton Deutsch and Harold Gerard described two psychological needs that lead humans to conform to the expectations of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |