|
Communication And Leadership During Change
Communication and leadership during change encompasses topics of communication (transmission of information) and leadership (influence or guidance) during change. The goal of leader development is "the expansion of the person's capacity to be effective in leadership roles and processes." The two central elements to this are leadership can be learned, people do learn, grow, and change, and that leader development helps to make a person effective in a variety of formal and informal leadership roles. Leader development promotes personal growth by helping individuals develop their abilities to manage themselves, to work effectively with others, and to ensure that the work gets done. Leadership development promotes organizational growth, helping the group as a whole develop the leaders it needs to carry out such tasks, such as securing the commitment of members and setting direction. Establishing connections between people who can help achieve someone's goals will increase your chanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquiry studying them. There are many disagreements about its precise definition. John Peters argues that the difficulty of defining communication emerges from the fact that communication is both a universal phenomenon and a specific discipline of institutional academic study. One definitional strategy involves limiting what can be included in the category of communication (for example, requiring a "conscious intent" to persuade). By this logic, one possible definition of communication is the act of developing meaning among entities or groups through the use of sufficiently mutually understood signs, symbols, and semiotic conventions. An important distinction is between verbal communication, which happens through the use of a language, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtue
Virtue ( la, virtus) is morality, moral excellence. A virtue is a trait or quality that is deemed to be morally good and thus is Value (ethics), valued as a foundation of principle and good moral being. In other words, it is a behavior that shows high moral standards: doing what is right and avoiding what is wrong. The opposite of virtue is vice. Other examples of this notion include the concept of Merit (Buddhism), merit in Asian traditions as well as ''De (Chinese), De'' (Chinese language, Chinese 德). Buddhism's four brahmavihara ("Divine States") can be regarded as virtues in the European sense. Etymology The ancient Romans used the Latin word ''virtus'' (derived from ''vir'', their word for ''man'') to refer to all of the "excellent qualities of men, including physical strength, valorous conduct, and moral rectitude." The French words ''vertu'' and ''virtu'' came from this Latin root. In the 13th century, the word ''virtue'' was "borrowed into English". Ancient Egypt Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belief
A belief is an attitude that something is the case, or that some proposition is true. In epistemology, philosophers use the term "belief" to refer to attitudes about the world which can be either true or false. To believe something is to take it to be true; for instance, to believe that snow is white is comparable to accepting the truth of the proposition "snow is white". However, holding a belief does not require active introspection. For example, few carefully consider whether or not the sun will rise tomorrow, simply assuming that it will. Moreover, beliefs need not be ''occurrent'' (e.g. a person actively thinking "snow is white"), but can instead be ''dispositional'' (e.g. a person who if asked about the color of snow would assert "snow is white"). There are various different ways that contemporary philosophers have tried to describe beliefs, including as representations of ways that the world could be ( Jerry Fodor), as dispositions to act as if certain things are true ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour ( British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as well as the inanimate physical environment. It is the computed response of the system or organism to various stimuli or inputs, whether internal or external, conscious or subconscious, overt or covert, and voluntary or involuntary. Taking a behavior informatics perspective, a behavior consists of actor, operation, interactions, and their properties. This can be represented as a behavior vector. Models Biology Although disagreement exists as to how to precisely define behavior in a biological context, one common interpretation based on a meta-analysis of scientific literature states that "behavior is the internally coordinated responses (actions or inactions) of whole living organisms (individuals or groups) to internal and/or exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attitude (psychology)
In psychology, attitude is a psychological construct that is a mental and emotional entity that inheres or characterizes a person, their attitude to approach to something, or their personal view on it. Attitude involves their mindset, outlook and feelings. Attitudes are complex and are an acquired state through life experience. Attitude is an individual's predisposed state of mind regarding a value and it is precipitated through a responsive expression towards oneself, a person, place, thing, or event (the attitude object) which in turn influences the individual's thought and action. Most simply understood attitudes in psychology are the feelings individuals have about themselves and the world. Prominent psychologist Gordon Allport described this latent psychological construct as "the most distinctive and indispensable concept in contemporary social psychology."Allport, Gordon. (1935). "Attitudes," in A Handbook of Social Psychology, ed. C. Murchison. Worcester, MA: Clark U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, transcendental, and spiritual elements; however, there is no scholarly consensus over what precisely constitutes a religion. Different religions may or may not contain various elements ranging from the divine, sacred things, faith,Tillich, P. (1957) ''Dynamics of faith''. Harper Perennial; (p. 1). a supernatural being or supernatural beings or "some sort of ultimacy and transcendence that will provide norms and power for the rest of life". Religious practices may include rituals, sermons, commemoration or veneration (of deities or saints), sacrifices, festivals, feasts, trances, initiations, funerary services, matrimonial services, meditation, prayer, music, art, dance, public service, or other aspects of human culture. Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 Common Era, BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the Universe, physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of History of science in classical antiquity, Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Development
Personal development or self improvement consists of activities that develop a person's capabilities and potential, build human capital, facilitate employability, and enhance quality of life and the realization of dreams and aspirations. Personal development may take place over the course of an individual's entire lifespan and is not limited to one stage of a person's life. It can include official and informal actions for developing others in roles such as teacher, guide, counselor, manager, coach, or mentor, and it is not restricted to self-help. When personal development takes place in the context of institutions, it refers to the methods, programs, tools, techniques, and assessment systems offered to support positive adult development at the individual level in organizations. Overview Among other things, personal development may include the following activities: * Improving self-awareness * Improving self-knowledge * Improving skills and/or learning new ones * Buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrapersonal Communication
Intrapersonal communication is the process by which an individual communicates within themselves, acting as both sender and receiver of messages, and encompasses the use of unspoken words to consciously engage in self-talk and inner speech. Intrapersonal communication, also referred to as internal monologue, autocommunication, self-talk, inner speech, or internal discourse, is a person's inner voice which provides a running monologue of thoughts while they are conscious. It is usually tied to a person's sense of self. It is particularly important in planning, problem solving, self-reflection, self-image, critical thinking, emotions, and subvocalization (reading in one's head). As a result, it is relevant to a number of mental disorders, such as depression, and treatments like cognitive behavioral therapy which seek to alleviate symptoms by providing strategies to regulate cognitive behaviour. It may reflect both conscious and subconscious beliefs. Intrapersonal communication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the production, use, and management of scarce resources'. A given economy is a set of processes that involves its culture, values, education, technological evolution, history, social organization, political structure, legal systems, and natural resources as main factors. These factors give context, content, and set the conditions and parameters in which an economy functions. In other words, the economic domain is a social domain of interrelated human practices and transactions that does not stand alone. Economic agents can be individuals, businesses, organizations, or government A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organizational Life Cycle
The organizational life cycle is the life cycle of an organization from its creation to its termination. It also refers to the expected sequence of advancements experienced by an organization, as opposed to a randomized occurrence of events. The relevance of a biological life cycle relating to the growth of an organization, was discovered by organizational researchers many years ago. This was apparent as organizations had a distinct conception, periods of expansion and eventually, termination. Development Comparisons between organisations and living organisms originated as early as 1890 by the economist Alfred Marshall who compared firms with trees in the forest, using the metaphor: "But here we may read a lesson from the young trees of the forest as they struggle upwards through the benumbing shade of their older rivals". Sixty years later, Kenneth Boulding presented the idea that organisations pass through a lifecycle similar to that of living organisms. Shortly after, Mason Haire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
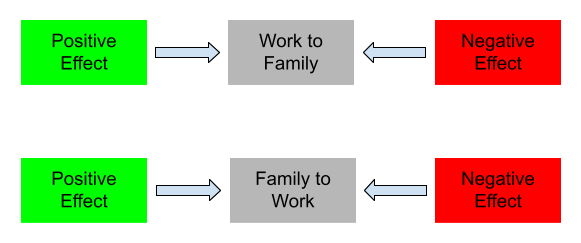
Work–life Interface
Work–life interface is the intersection of work and personal life. There are many aspects of one's personal life that can intersect with work including family, leisure, and health. Work–life interface is bidirectional; for instance, work can interfere with private life, and private life can interfere with work. This interface can be adverse in nature (e.g., work–life conflict) or can be beneficial (e.g., work–life enrichment) in nature. Recent research has shown that the work–life interface has become more boundary-less, especially for technology-enabled workers. Work–life balance is the equilibrium between personal life and career work. Dominant theories of the relationship Several theories explain different aspects of the relationship between the work and family life. Boundary theory and border theory are the two fundamental theories that researchers have used to study these role conflicts. Other theories are built upon the foundations of these two theories. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_per_capita_in_2020.png)