|
Colin Lindsay, 3rd Earl Of Balcarres
Colin Lindsay, 3rd Earl of Balcarres (1652–1722) was a Scottish aristocrat and politician, one of the most important supporters of James II of England. Biography Early life Colin Lindsay was baptized at Kilconquhar on 23 August 1652, the second surviving son of Alexander Lindsay, first Earl of Balcarres by his wife, Lady Anna Mackenzie, daughter and coheiress of Colin Mackenzie, 1st Earl of Seaforth. He succeeded to the earldom, while still a child, on the death at the age of twelve, of his brother Charles, second earl, 15 Oct. 1662. In 1670 at the age of sixteen, he was presented at court by his cousin the Duke of Lauderdale, when Charles II, partly because he conceived a liking for him personally, and partly in recognition of his father's services, gave him command of a select cavalry troop manned by gentlemen in reduced circumstances. Not long afterwards he was married to Mademoiselle Mauritiade Nassau, sister of Lady Arlington and the Countess of Nassau, and daughter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James II Of England
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was deposed in the Glorious Revolution of 1688. He was the last Catholic monarch of England, Scotland, and Ireland. His reign is now remembered primarily for conflicts over religious tolerance, but it also involved struggles over the principles of absolutism and the divine right of kings. His deposition ended a century of political and civil strife in England by confirming the primacy of the English Parliament over the Crown. James succeeded to the thrones of England, Ireland, and Scotland following the death of his brother with widespread support in all three countries, largely because the principles of eligibility based on divine right and birth were widely accepted. Tolerance of his personal Catholicism did not extend to tolerance of Catholicism in general, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Drummond, 4th Earl Of Perth
James Drummond, 1st Duke of Perth KT PC (164811 May 1716), also 4th Earl of Perth and 7th Lord Drummond, was a Scottish statesman, and Jacobite. Family The eldest son of James Drummond, 3rd Earl of Perth by his spouse Lady Anne, daughter of George Gordon, 2nd Marquess of Huntly, he was educated at the University of St Andrews, and succeeded his father on 2 June 1675, and was served heir to him on 1 October. Political career In 1678 he was appointed a member of the Scottish Privy Council and supported Lord Lauderdale's policy of giving up the disaffected western shires of Scotland to highland raids, before joining Hamilton's faction in opposition to Lauderdale. After Lauderdale's retirement in 1680 he was one of the Committee of Seven which managed Scottish affairs. He was appointed Lord Justice General in 1682 and an Extraordinary Lord of Session on 16 November the same year. He introduced the use of the thumbscrew in Scotland. He was also Lord Chancellor of Scotland, 168 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Bayle
Pierre Bayle (; 18 November 1647 – 28 December 1706) was a French philosopher, author, and lexicographer. A Huguenot, Bayle fled to the Dutch Republic in 1681 because of religious persecution in France. He is best known for his '' Historical and Critical Dictionary'', whose publication began in 1697. Bayle was a notable advocate of religious toleration, and his skeptical philosophy had a significant influence on the subsequent growth and development of the European Age of Enlightenment. Bayle is commonly regarded as a forerunner of the ''Encyclopédistes'' of the mid-18th century. Biography Bayle was born at Carla-le-Comte (later renamed Carla-Bayle in his honour), near Pamiers, Ariège, France. He was educated by his father, a Calvinist minister, and at an academy at Puylaurens. In 1669, he entered a Jesuit college at Toulouse and became a Roman Catholic a month later. After seventeen months, he returned to Calvinism and fled to Geneva, where he learned about the teachin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
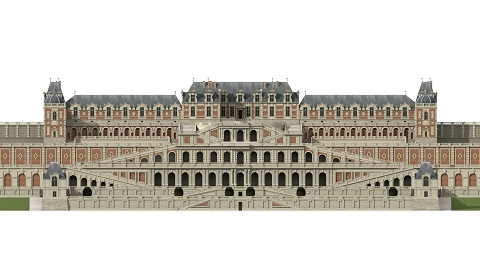
Château De Saint-Germain-en-Laye
The Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye () is a former royal palace in the commune of Saint-Germain-en-Laye, in the ''département'' of Yvelines, about 19 km west of Paris, France. Today, it houses the ''musée d'Archéologie nationale'' (National Museum of Archaeology). History 12th–13th centuries The first castle, named the ''Grand Châtelet'', was built on the site by Louis VI in 1124. The castle was expanded by Louis IX in the 1230s. Louis IX's chapelle Saint Louis at the castle belongs to the Rayonnant phase of French Gothic architecture. A 1238 charter of Louis IX instituting a regular religious service at the chapel is the first mention of a chapel having been built at the royal castle. This was a ''Sainte Chapelle'', to house a relic of the Crown of Thorns or the True Cross. Its plan and architecture prefigure the major Sainte-Chapelle which Saint Louis built within the Palais de la Cité at Paris between 1240 and 1248. Both buildings were built by Louis's fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English College, Douai
The English College (''College des Grands Anglais'') was a Catholic seminary in Douai, France (also previously spelled Douay, and in English Doway), associated with the University of Douai. It was established in 1568, and was suppressed in 1793. It is known for a Bible translation referred to as the Douay–Rheims Bible. Of over 300 priests from Douai sent on the English mission, about one-third were executed. The dissolution of the college at the time of the French Revolution led to the founding of Crook Hall near Lanchester in County Durham (which became St. Cuthbert's College), and St Edmund's College, Ware. It is popularly believed that the indemnification funds paid by the French for the seizure of Douai's property were diverted by the British commissioners to complete the furnishings of George IV's Royal Pavilion at Brighton. History University of Douai As part of a general programme of consolidation of the Spanish Low Countries, in 1560–1562, Philip II of Spain esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pistoles
Pistole is the French name given to a Spanish gold coin in use from 1537; it was a doubloon or double escudo, the gold unit. The name was also given to the Louis d'Or of Louis XIII of France, and to other European gold coins of about the value of the Spanish coin. One pistole was worth approximately ten livres or three écus, but higher figures are also seen. The derivation is uncertain; the term may come from the Czech ''píšťala'' ("whistle", a term for a hand cannon), or from the Italian town of Pistoia; either way, it was originally spelled ''pistolet'' and originated in military slang, and probably has the same root as pistol. A small number of gold pistoles and double pistoles were minted in Ireland in 1646, during the Irish Confederate Wars and the reign of Charles I. James Butler, 1st Duke of Ormond authorised the issue in order to prevent troop defections, as there was a shortage of silver coins for paying soldiers. The coins had an approximate value of 13 shilli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montgomery Plot
Sir James Montgomery, 4th Baronet (or Montgomerie, died 1694) was the tenth laird of Skelmorlie. He was a Scottish politician known for the Montgomery Plot, a Jacobite scheme to restore King James VII and II to the thrones of Scotland and England. Early years He was eldest son of Sir Robert Montgomery, 3rd Baronet, by his wife Anna or Antonia, second daughter and coheiress of Sir John Scott of Rossie, Fife. His father died on 7 February 1684, and James became his heir on 3 February 1685. In April 1684 his widowed mother made a strong appeal to him to make suitable provision for her and her fatherless children, but to this he replied that, for the sake of peace, he had already conceded more than legal obligations required. On 2 October 1684 Montgomery was imprisoned and fined for harbouring covenanters, religious rebels, and on 7 May 1685 he and his mother were pursued on account of conventicles held in his father's lifetime, but both pleaded that they were not responsible. Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convention Of Estates (1689)
The 1689 Convention of Estates sat between 16 March 1689 and 5 June 1689 to determine the settlement of the Scottish throne, following the deposition of James VII in the 1688 Glorious Revolution. The Convention of the Estates of Scotland was a sister-institution to Parliament, comprising the three estates of bishops, barons and representatives of the Burghs. Historically, it had been summoned by the king of Scots for the limited purpose of raising taxes, and could not pass other legislation. Unlike the English Convention Parliament of 1689, the 1689 Scottish Convention was also a contest for control of the Church of Scotland or Kirk. While Scotland played no part in the landing in England and there was little enthusiasm for William and Mary, by November 1688 only a tiny minority actively supported James. Many of William's exile advisors were Scots, including Melville, Argyll, his personal chaplain, William Carstares, and Gilbert Burnet, his chief propagandist. News of James's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Gordon, 1st Duke Of Gordon
George Gordon, 1st Duke of Gordon KT, PC (1643 – 7 December 1716), known as Marquess of Huntly from 1661 to 1684, was a Scottish peer. George Gordon, 4th Marquess of Huntly was born in 1643, the son of Lewis Gordon, 3rd Marquess of Huntly and Mary Grant. He was originally styled the Earl of Enzie until his succession as Marquess in December 1653, when he was around four years old. The young Marquess was educated at a Catholic seminary in France, following a tradition within the Huntly family. In 1673, when he was aged 24, he entered the French Army of Louis XIV and served under the famous Marshal de Turenne before returning to Scotland sometime around 1675. In October of the following year, 1676, he married Lady Elizabeth Howard, the second daughter of Henry Howard, 6th Duke of Norfolk. However, he was described by the historian Macky as someone "made for the company of ladies, but is covetous which extremely eclipses him." The marriage was not wholly successful and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth. Edinburgh is Scotland's List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, second-most populous city, after Glasgow, and the List of cities in the United Kingdom, seventh-most populous city in the United Kingdom. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament and the Courts of Scotland, highest courts in Scotland. The city's Holyrood Palace, Palace of Holyroodhouse is the official residence of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarchy in Scotland. The city has long been a centre of education, particularly in the fields of medicine, Scots law, Scottish law, literature, philosophy, the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Mall (London)
The Mall () is a road in the City of Westminster, central London, between Buckingham Palace at its western end and Trafalgar Square via Admiralty Arch to the east. Near the east end at Trafalgar Square and Whitehall it is met by Horse Guards Road and Spring Gardens where the Metropolitan Board of Works and London County Council were once based. It is closed to traffic on Saturdays, Sundays, public holidays and on ceremonial occasions. History The Mall began as a field for playing pall-mall. In the 17th and 18th centuries it was a fashionable promenade, bordered by trees. It was envisioned as a ceremonial route in the early 20th century, matching the creation of similar ceremonial routes in other cities such as Berlin, Mexico City, Oslo, Paris, Saint Petersburg, Vienna and Washington, D.C. These routes were intended to be used for major national ceremonies. As part of the development – designed by Aston Webb – a new façade was constructed for Buckingham Palace, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitehall
Whitehall is a road and area in the City of Westminster, Central London. The road forms the first part of the A roads in Zone 3 of the Great Britain numbering scheme, A3212 road from Trafalgar Square to Chelsea, London, Chelsea. It is the main thoroughfare running south from Trafalgar Square towards Parliament Square. The street is recognised as the centre of the Government of the United Kingdom and is lined with numerous departments and ministries, including the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), Ministry of Defence, Horse Guards (building), Horse Guards and the Cabinet Office. Consequently, the name "Whitehall" is used as a metonymy, metonym for the British Civil Service (United Kingdom), civil service and British government, government, and as the geographic name for the surrounding area. The name was taken from the Palace of Whitehall that was the residence of Kings Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII through to William III of England, William III, before its destruction b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |