|
Cognitive Science And Neuropsychology Program Of Szeged
The Cognitive Science and Neuropsychology Program was organised by Csaba Pléh, in 1999 at the Institute of Psychology, University of Szeged. The aim of the program is to introduce the theories and methods of cognitive science and neuropsychology both to undergraduate students and researchers from other fields. The program welcome guest professors, international students and other interested students and researchers for participation and collaboration. The program has the intent of becoming an interface between cognitive labs and disciplines in cognitive science, broadly conceived in Central Europe. In 2011-2012 the members of this group left University of Szeged. This group is not exist anymore. The members went to the University of Debrecen, the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Eötvös Loránd University, etc. Cognitive Science and Neuropsychology Group in Szeged Members (until 2011) * WINKLER, István * SZOKOLSZKY, Ágnes * RACSMÁNY, Mihály * KRAJCSI, Attila * NÉME ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Szeged
, mottoeng = Truth. Bravery. Freedom. , established = , type = Public research university , founder = Emperor Franz Joseph I , affiliation = European University Association, Science Without Borders, Confucius Institute , budget = US$220 million , chancellor = Judit Fendler , rector = László Rovó , students = 22,693 , undergrad = 17,384 , postgrad = 2,668 , doctoral = 714 , other = 3,997 (international) , city = Szeged , country = Hungary , coordinates = , campus = Urban , language = Hungarian, English , colours = Blue , website = , academic_staff = 1,968 , administrative_staff = 2,200 The University of Szeged ( hu, Szegedi Tudományegyetem, ) is a public research university in Szeged, Hungary. Established as the Jesuit Academy of Kolozsvár in present-day Cluj-Napoca in 1581, the institution was re-established as a university in 1872 by Emperor Franz Joseph I. The university relocated to Szeged in 1921, making it one of the oldest research universitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
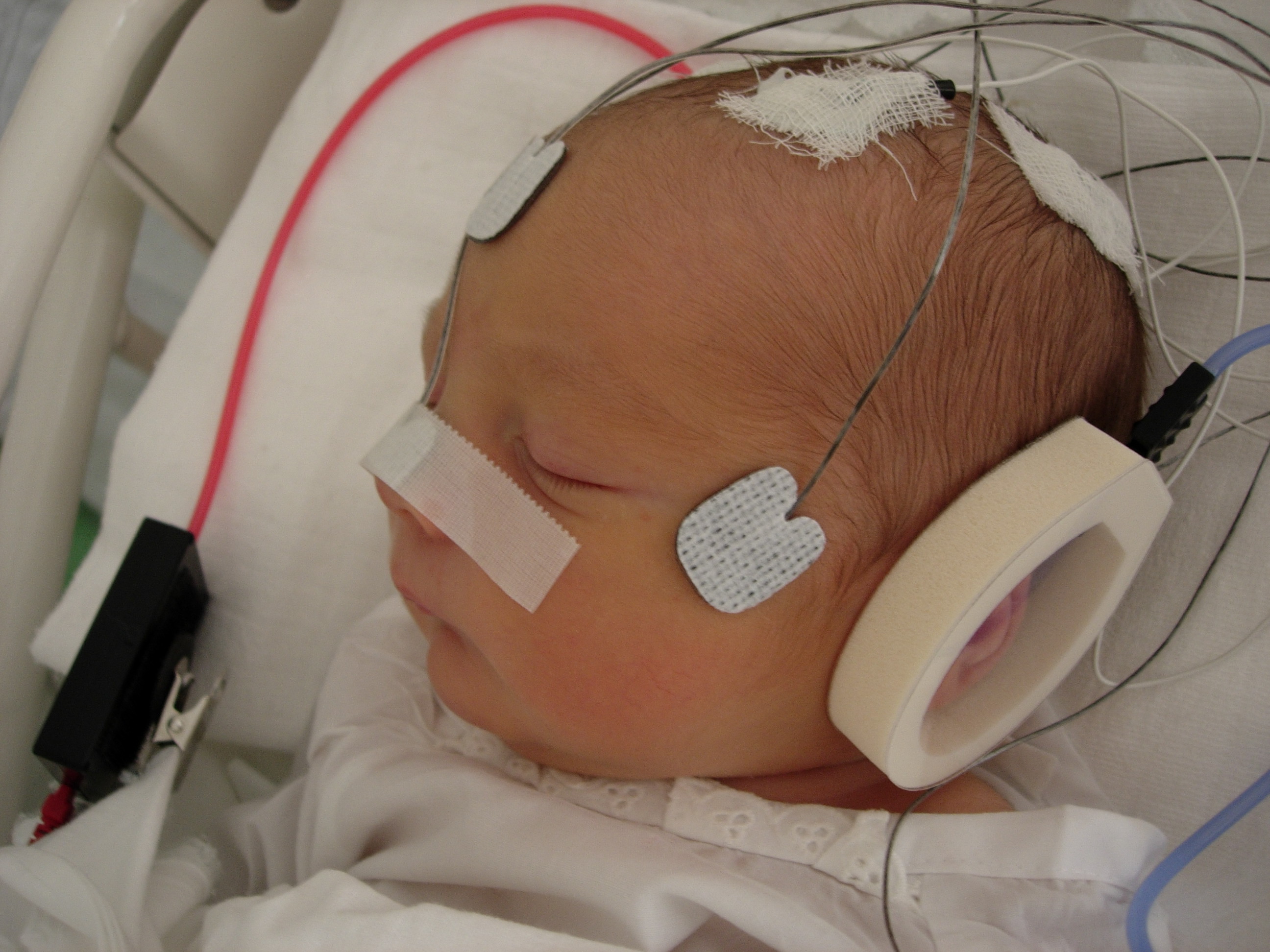
Neuropsychology
Neuropsychology is a branch of psychology concerned with how a person's cognition and behavior are related to the brain and the rest of the nervous system. Professionals in this branch of psychology often focus on how injuries or illnesses of the brain affect cognitive and behavioral functions. It is both an experimental and clinical field of psychology, thus aiming to understand how behavior and cognition are influenced by brain function and concerned with the medical diagnosis, diagnosis and therapy, treatment of behavioral and cognitive effects of neurological disorders. Whereas classical neurology focuses on the pathology of the nervous system and classical psychology is largely divorced from it, neuropsychology seeks to discover how the brain neural correlates of consciousness, correlates with the mind through the study of neurological patients. It thus shares concepts and concerns with neuropsychiatry and with behavioral neurology in general. The term ''neuropsychology'' h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dezső Németh
Dezső Németh (1 September 1975, Szeged) is a Hungarian psychologist and cognitive neuroscientist at INSERM, research team leader iLyon Neuroscience Research Center (CRNL) Dezső Németh graduated from the Endre Ságvári High School, in 1994, Szeged. He learned psychology at the Eötvös Loránd University, 1994–1999. He graduated in 1999. He worked as a visiting professor at the Department of Neuroscience of Georgetown University (Washington DC) in 2007-2008 and in 2011-2012 at University of Texas, Austin (Russell Poldrack's Lab). He worked at the University of Szeged, Hungary (1999-2012) and the Institute of Psychology at Eötvös Loránd University (2012-present). Németh obtained his PhD at ELTE (Budapest, 2005), habilitation at University of Pécs (Pécs, 2011) and DSc at Hungarian Academy of Sciences (Budapest, 2018). Awards * Mérei Ferenc Award (2005)Award is from Hungarian Psychological Association for his publications * MTA Bolyai Research Fellowship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attila Krajcsi
Attila (, ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in March 453. He was also the leader of a tribal empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Bulgars, among others, in Central and Eastern Europe. During his reign, he was one of the most feared enemies of the Western and Eastern Roman Empires. He crossed the Danube twice and plundered the Balkans, but was unable to take Constantinople. His unsuccessful campaign in Persia was followed in 441 by an invasion of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire, the success of which emboldened Attila to invade the West. He also attempted to conquer Roman Gaul (modern France), crossing the Rhine in 451 and marching as far as Aurelianum (Orléans), before being stopped in the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains. He subsequently invaded Italy, devastating the northern provinces, but was unable to take Rome. He planned for further campaigns against the Romans, but died in 453. After Att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mihály Racsmány
Mihály () is a Hungarian masculine given name, It is a cognate of the English Michael and may refer to: * Mihály András (1917–1993), Hungarian cellist, composer, and academic teacher *Mihály Apafi (1632–1690), Hungarian Prince of Transylvania * Mihály Babák (born 1947), Hungarian politician and member of the Hungarian National Assembly * Mihály Babits (1883– 1941), Hungarian poet, writer and translator * Mihály Bakos (ca. 1742-1803), Hungarian-Slovene Lutheran priest, author, and educator *Mihály Balázs (born 1948), Hungarian historian and professor of religious history *Mihály Balla (born 1965) Hungarian politician and member of the Hungarian National Assembly *Mihály Barla (ca 1778–1824), Slovene evangelic pastor, writer and poet *Mihály Bertalanits (1788–1853), Slovene cantor, teacher, and poet in Hungary *Mihály Bíró (1914-????), Hungarian football forward *Mihály Bozsi (1911–1984), Hungarian water polo player and Olympic medalist * Mihály Csák ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ágnes Szokolszky
Ágnes Szokolszky (6 July 1956) is a Hungarian educator and psychologist, a habilitated associate professor and director of the Institute of Psychology, Szeged. Her fields of research are ecological psychology (with special regard to James and Eleanor J. Gibson’s schools), cognitive science (inside this certain theories of cognitive developmental psychology), history of psychology and its methods of research. Empirical research interests: symbolic play and metaphor production of childhood. Biography Ágnes Szokolszky was born in an educator family, her father, István Szokolszky (1915–1968) was one of the significant representatives of Hungarian pedagogy, her grandfather Rezső Szokolszky held a position of instructor and royal school-inspector. For Ágnes Szokolszky it was natural to carry on the family's tradition of following a profession in education. This was also pressed by her father's untimely death. She made her studies at the Faculty of Humanities of the Eötvös ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
István Winkler
István Winkler (born 8 February 1958) is a Hungarian psychologist. He is Scientific Advisor (2005–present) and Head of the Department of General Psychology (2000–present) at the Institute for Psychology of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences and Professor of the Institute of Psychology, Szeged, since 2008. His fields of research are perception, memory and event-related brain potentials. Biography Winkler was born in Budapest and graduated from the Radnóti Miklós Training High School of the Eötvös Loránd University. He then studied at the Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, and graduated in 1981. From 1980, he studied psychology at the Faculty of Humanities of the Eötvös Loránd University, and went on to attain a diploma in psychology in 1985. Having made a commitment to psychology, he entered the psychology PhD program at the University of Helsinki in 1990, and received his PhD degree there, in 1993. In 1996, he was qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eötvös Loránd University
Eötvös Loránd University ( hu, Eötvös Loránd Tudományegyetem, ELTE) is a Hungarian public research university based in Budapest. Founded in 1635, ELTE is one of the largest and most prestigious public higher education institutions in Hungary. The 28,000 students at ELTE are organized into nine faculties, and into research institutes located throughout Budapest and on the scenic banks of the Danube. ELTE is affiliated with 5 Nobel laureates, as well as winners of the Wolf Prize, Fulkerson Prize and Abel Prize, the latest of which was Abel Prize winner László Lovász in 2021. The predecessor of Eötvös Loránd University was founded in 1635 by Cardinal Péter Pázmány in Nagyszombat, Kingdom of Hungary (today Trnava, Slovakia) as a Catholic university for teaching theology and philosophy. In 1770, the university was transferred to Buda. It was named Royal University of Pest until 1873, then University of Budapest until 1921, when it was renamed Royal Hungarian Pázmá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Academy Of Sciences
The Hungarian Academy of Sciences ( hu, Magyar Tudományos Akadémia, MTA) is the most important and prestigious learned society of Hungary. Its seat is at the bank of the Danube in Budapest, between Széchenyi rakpart and Akadémia utca. Its main responsibilities are the cultivation of science, dissemination of scientific findings, supporting research and development, and representing Hungarian science domestically and around the world. History The history of the academy began in 1825 when Count István Széchenyi offered one year's income of his estate for the purposes of a ''Learned Society'' at a district session of the Diet in Pressburg (Pozsony, present Bratislava, seat of the Hungarian Parliament at the time), and his example was followed by other delegates. Its task was specified as the development of the Hungarian language and the study and propagation of the sciences and the arts in Hungarian. It received its current name in 1845. Its central building was inaugurate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Debrecen
ThUniversity of Debrecen( hu, Debreceni Egyetem) is a university located in Debrecen, Hungary. It is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, oldest continuously operating institution of higher education in Hungary ever since its establishment in 1538 by Suleiman the Magnificent following the Ottoman conquest of the Kingdom after the Battle of Mohács (1526). The university has a well established programme in the English language for international students, particularly in the Medical and Engineering field, which first established education in English in 1886. There are nearly 6000 international students studying at the university. Until 2014 technical Academy Awards (Oscars) have been awarded to five former students. The university also operates an associated Basic Medicine campus in Geochang County, South Korea. The University of Debrecen's acceptance rate is 25% making it one of the most competitive universities in Central Europe. University of Debrecen is ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area's history. The concept of "Central Europe" appeared in the 19th century. Central Europe comprised most of the territories of the Holy Roman Empire and those of the two neighboring kingdoms of Poland and Hungary. Hungary and parts of Poland were later part of the Habsburg monarchy, which also significantly shaped the history of Central Europe. Unlike their Western European (Portugal, Spain et al.) and Eastern European (Russia) counterparts, the Central European nations never had any notable colonies (either overseas or adjacent) due to their inland location and other factors. It has often been argued that one of the contributing causes of both World War I and World War II was Germany's lack of original overseas colonies. After World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |