|
Coastal Artillery Of The Dardanelles Strait
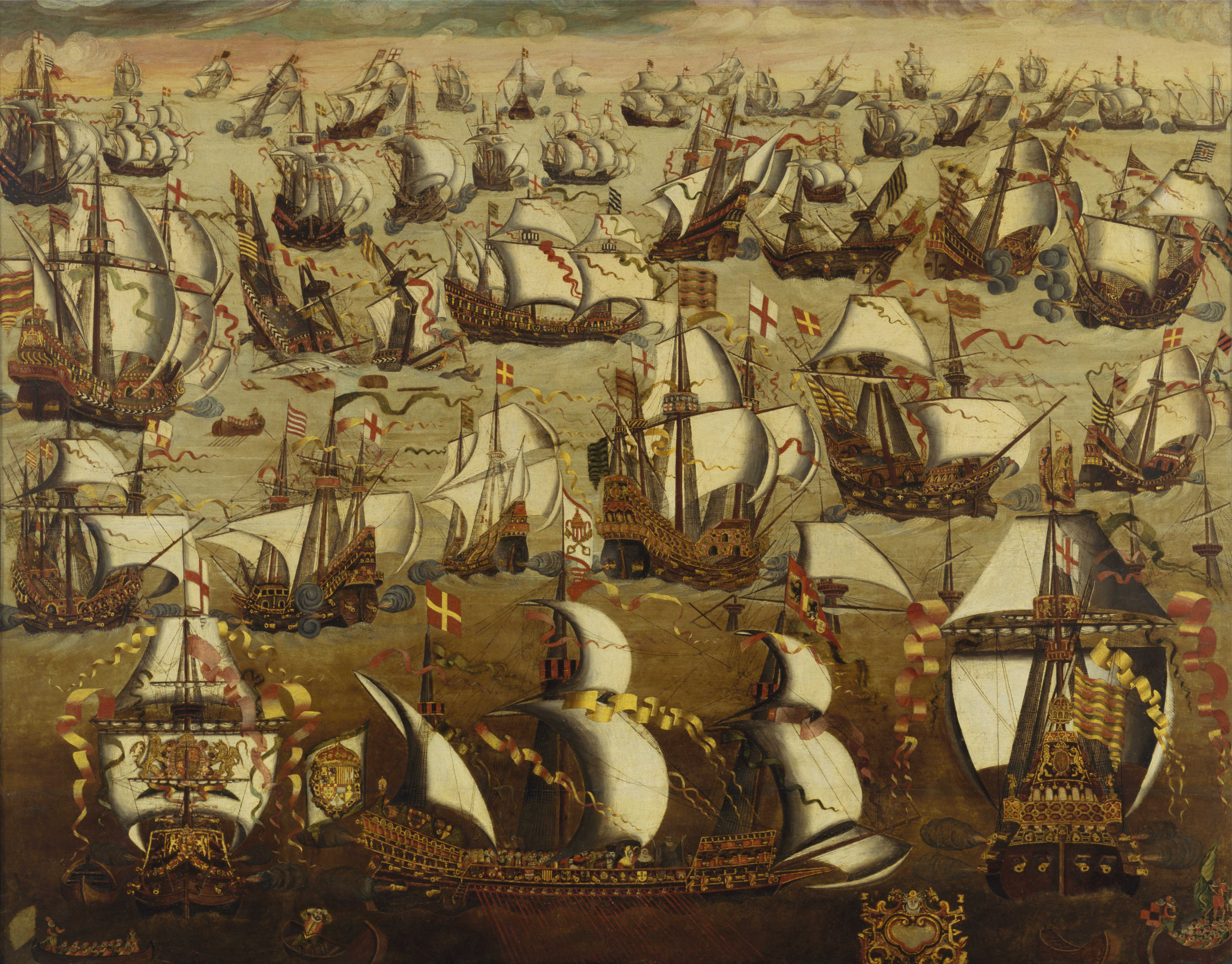
Coastal artillery of the Dardanelles Strait ( tr, Çanakkale Tabyaları) are a series of redoubts on each side of the Dardanelles Strait which controlled the strait in the First World War during the Naval operations in the Dardanelles Campaign. Some castles located in the background also supported the coastal artillery. Bouvet The corporal Seyit Çabuk of the Rumeli Mecidiye artillery was responsible in sinking the French battleship Bouvet ''Bouvet'' was a pre-dreadnought battleship of the French Navy that was built in the 1890s. She was a member of a group of five broadly similar battleships, along with , , , and , which were ordered in response to the British . ''Bouvet'' was ... on 18 April 1915. Turgut Özakman'':Diriliş'', , p170-171 References {{coord missing, Turkey 1915 in the Ottoman Empire Naval battles of World War I involving the Ottoman Empire Gallipoli campaign Coastal artillery Buildings and structures in Çanakkale Province Buildings and structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
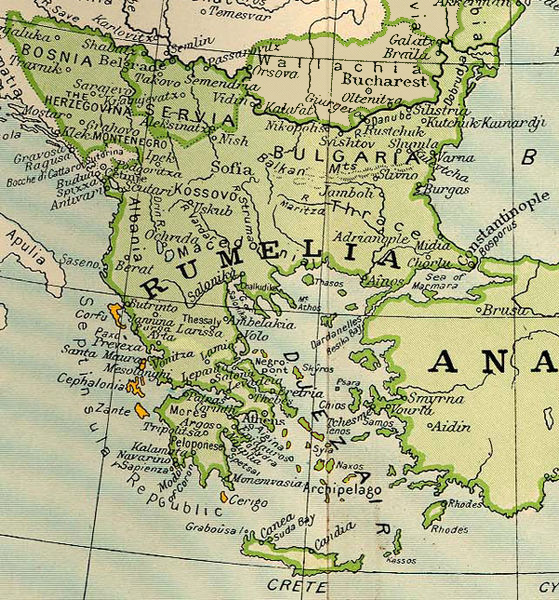
Dardanelles Strait
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; grc-x-classical, Ἑλλήσποντος, translit=Hellēspontos, lit=Sea of Helle), is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey that forms part of the continental boundary between Asia and Europe and separates Asian Turkey from European Turkey. Together with the Bosporus, the Dardanelles forms the Turkish Straits. One of the world's narrowest straits used for international navigation, the Dardanelles connects the Sea of Marmara with the Aegean and Mediterranean seas while also allowing passage to the Black Sea by extension via the Bosporus. The Dardanelles is long and wide. It has an average depth of with a maximum depth of at its narrowest point abreast the city of Çanakkale. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turhan Hatice Sultan
Turhan Hatice Sultan ( ota, تورخان سلطان, "''nobility of the Khan''" or ''mercy of the Khan'' " and "''respecful lady''"; 1627 – 4 August 1683) was the first Haseki Sultan of the Ottoman Sultan Ibrahim (reign 1640–48) and Valide Sultan as the mother of Mehmed IV (reign 1648–87). Turhan was prominent for the regency of her young son and her building patronage. She and her mother-in-law, Kösem Sultan, are the only two women in Ottoman history to be regarded as official regents and had supreme control over the Ottoman Empire. As a result, Turhan became one of the prominent figures during the era known as Sultanate of Women. As imperial consort Of Rus' origin, [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Çanakkale Province
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal Artillery
Coastal artillery is the branch of the armed forces concerned with operating anti-ship artillery or fixed gun batteries in coastal fortifications. From the Middle Ages until World War II, coastal artillery and naval artillery in the form of cannons were highly important to military affairs and generally represented the areas of highest technology and capital cost among materiel. The advent of 20th-century technologies, especially military aviation, naval aviation, jet aircraft, and guided missiles, reduced the primacy of cannons, battleships, and coastal artillery. In countries where coastal artillery has not been disbanded, these forces have acquired amphibious capabilities. In littoral warfare, mobile coastal artillery armed with surface-to-surface missiles can still be used to deny the use of sea lanes. It was long held as a rule of thumb that one shore-based gun equaled three naval guns of the same caliber, due to the steadiness of the coastal gun which allow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Battles Of World War I Involving The Ottoman Empire
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It includes anything conducted by surface ships, amphibious ships, submarines, and seaborne aviation, as well as ancillary support, communications, training, and other fields. The strategic offensive role of a navy is projection of force into areas beyond a country's shores (for example, to protect sea-lanes, deter or confront piracy, ferry troops, or attack other navies, ports, or shore installations). The strategic defensive purpose of a navy is to frustrate seaborne projection-of-force by enemies. The strategic task of the navy also may incorporate nuclear deterrence by use of submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Naval operations can be broadly divided between riverine and littoral applications (brown-water navy), open-ocean applications ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1915 In The Ottoman Empire ...
The following lists events that happened during 1915 in the Ottoman Empire. Incumbents *Sultan: Mehmed V *Grand Vizier: Said Halim Pasha Events April * April 24 - The deportation of Armenian notables from Istanbul. * April 25 - Start of the Gallipoli Campaign; Landing at Anzac Cove by Australian and New Zealand Army Corps and landing at Cape Helles by British and French troops to begin the Allied invasion of the Gallipoli peninsula in the Ottoman Empire. References {{Year in Asia, 1915 Years of the 20th century in the Ottoman Empire 1910s in the Ottoman Empire Ottoman Empire Ottoman Empire Ottoman Empire The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Battleship Bouvet
''Bouvet'' was a pre-dreadnought battleship of the French Navy that was built in the 1890s. She was a member of a group of five broadly similar battleships, along with , , , and , which were ordered in response to the British . ''Bouvet'' was the last vessel of the group to be built, and her design was based on that of ''Charles Martel''. Like her half-sisters, she was armed with a main battery of two guns and two guns in individual turrets. She had a top speed of , which made her one of the fastest battleships in the world at the time. ''Bouvet'' proved to be the most successful design of the five, and she was used as the basis for the subsequent . Nevertheless, she suffered from design flaws that reduced her stability and contributed to her loss in 1915. ''Bouvet'' spent the majority of her peacetime career in the Mediterranean Squadron conducting routine training exercises. This period was relatively uneventful, though she was involved in a collision with the battleship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seyit Çabuk
Seyit Ali Çabuk (1889–1939), usually called Corporal Seyit ( tr, Seyit Onbaşı) was a First World War gunner in the Ottoman Army. He is famous for having carried three shells to an artillery piece during the Allied attempt to force the Dardanelles on 18 March 1915. Personal life and military career Born in the village of Havran, he enlisted into the army in April 1909. After serving in the Balkan Wars of 1912–1913, he was transferred to Mecidiye Coastal Battery defending the Mediterranean entrance to the Çanakkale. Following the heavy naval bombardment of the forts guarding the Narrows on 18 March 1915, the gun he was serving in the Mecidiye fort remained operational, but its shell crane had been damaged and the other gunners in the area were injured. Corporal Seyit, by himself, is said to have carried three artillery shells each weighing 276 kg to the 240/35 mm gun and enabled it to continue firing on the Allied Fleet. He shot three rounds at the British pre-d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rumelia
Rumelia ( ota, روم ايلى, Rum İli; tr, Rumeli; el, Ρωμυλία), etymologically "Land of the Romans", at the time meaning Eastern Orthodox Christians and more specifically Christians from the Byzantine rite, was the name of a historical region in Southeastern Europe that was administered by the Ottoman Empire, corresponding to the Balkans. In its wider sense, it was used to refer to all Ottoman possessions and vassals in Europe that would later be geopolitically classified as "the Balkans". During the period of its existence, it was more often known in English as Turkey in Europe. Etymology ''Rûm'' in this context means "Greek", or a Christian Greek speaker and ''ėli'' means "land" and ''Rumelia'' ( ota, روم ايلى, ''Rūm-ėli''; Turkish: ''Rumeli'') means "Land of the Romans" in Ottoman Turkish. It refers to the lands conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans, which formerly belonged to the Byzantine Empire, known by its contemporaries as the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdülmecit
ʻAbd al-Majīd (ALA-LC romanization of ar, عبد المجيد) is a Muslim male given name and, in modern usage, surname. It is built from the Arabic words ''Abd (Arabic), ʻabd'' and ''al-Majīd'', one of the names of God in the Qur'an, which give rise to the List of Arabic theophoric names, Muslim theophoric names. It means "servant of the All-glorious". It is rendered in Turkish language, Turkish as ''Abdülmecid''. There is a distinct but closely related name, ʻAbd al-Mājid ( ar, عبد الماجد), with a similar meaning, formed on the Qur'anic name ''al-Mājid''. Some of the names below are instance of the latter one. 'Abd al-Majid may refer to: Males Given name *Abdülmecid I (1823–1861), Sultan of the Ottoman Empire *Abdülmecid II (1868–1944), Head of the Ottoman Imperial House and the final Ottoman Caliph *Abdul Madzhid (Dagestan rebel) (died 2008), leader in the Second Chechen War *Abdul Majeed (cricketer, born 1993), Pakistani cricketer *Abdul Majeed (Kalat c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |