|
Cloud Albedo
Cloud albedo is a measure of the albedo or reflectivity of a cloud. Clouds regulate the amount of solar radiation absorbed by a planet and its solar surface irradiance. Generally, increased cloud cover correlates to a higher albedo and a lower absorption of solar energy. Cloud albedo strongly influences the Earth's energy budget, accounting for approximately half of Earth's albedo. Cloud albedo depends on the total mass of water, the size and shape of the droplets or particles and their distribution in space. Thick clouds (such as stratocumulus) reflect a large amount of incoming solar radiation, translating to a high albedo. Thin clouds (such as cirrus) tend to transmit more solar radiation and, therefore, have a low albedo. Changes in cloud albedo caused by variations in cloud properties have a significant effect on global climate. Cloud condensation nuclei and cloud albedo On a microscopic scale, clouds are formed through the condensation of water on cloud condensation nucle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Graphic Representing The Distribution Of Solar Radiation
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Water Path
Liquid water path - in units of g/m2 is a measure of the total amount of liquid water present between two points in the atmosphere. LWP is an important quantity in understanding radiative transfer in the atmosphere. It is defined as the integral of liquid water content between two points in the atmosphere. For nadir observations and whole atmospheric column we have :LWP=\int_^\infty \rho_ r_L dz' where is the liquid water mixing ratio and is the density of air (including water loading). The atmosphere is in approximate hydrostatic equilibrium and hydrostatic equation for atmospheric pressure is given by :\frac= - \rho_ g which gives :LWP=\int_0^ r_L dp/g where is gravitational acceleration, is the pressure increment between two layers in the atmosphere and integration is between surface and top of the atmosphere. Liquid water path can also be defined between any two selected points. The liquid water path can be approximately retrieved from passive and active remote sensing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Feedback
Cloud feedback is the coupling between cloudiness and surface air temperature where a surface air temperature change leads to a change in clouds, which could then amplify or diminish the initial temperature perturbation. Cloud feedbacks can affect the magnitude of internally generated climate variability or they can affect the magnitude of climate change resulting from external radiative forcings. Global warming is expected to change the distribution and type of clouds. Seen from below, clouds emit infrared radiation back to the surface, and so exert a warming effect; seen from above, clouds reflect sunlight and emit infrared radiation to space, and so exert a cooling effect. Cloud representations vary among global climate models, and small changes in cloud cover have a large impact on the climate. Differences in planetary boundary layer cloud modeling schemes can lead to large differences in derived values of climate sensitivity. A model that decreases boundary layer clouds in re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
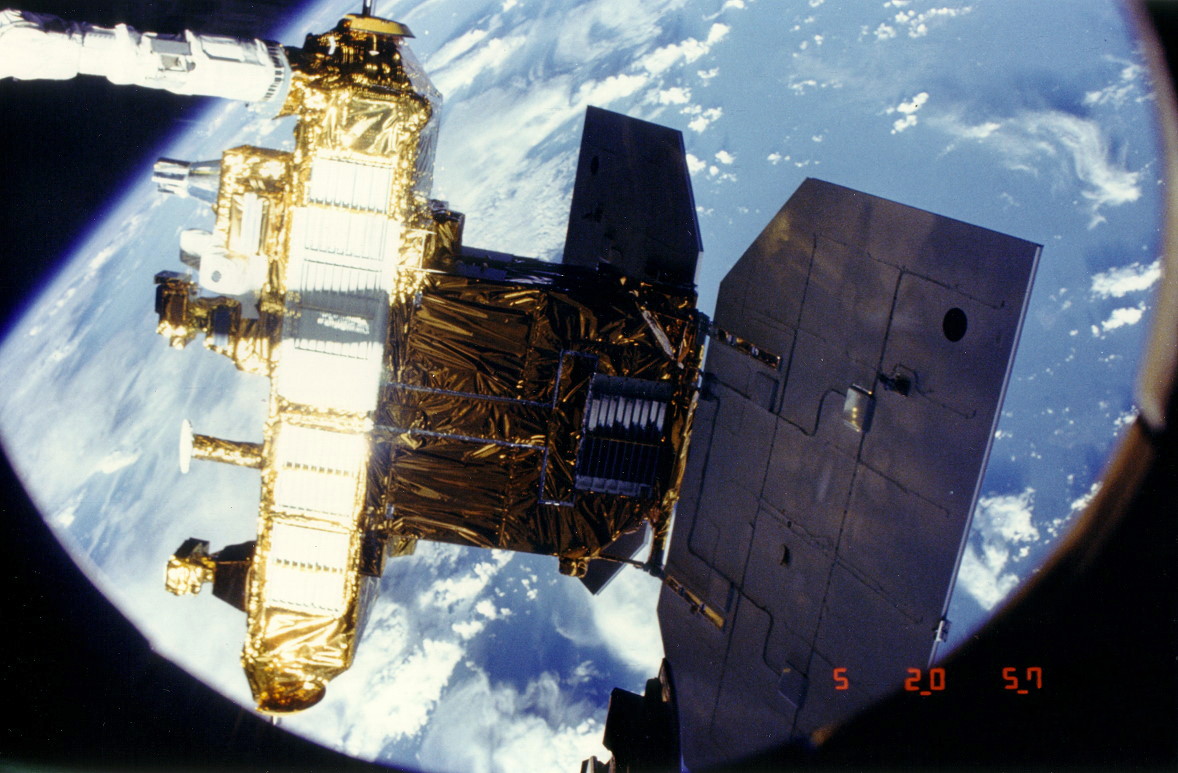
Earth Radiation Budget Experiment
The Earth Radiation Budget Satellite (ERBS) is a NASA scientific research satellite within NASA's ERBE (Earth Radiation Budget Experiment) Research Program - a three-satellite mission, designed to investigate the Earth radiation budget. It also carried an instrument that studied stratospheric aerosol and gases. ERBS was launched on October 5, 1984, by the Space Shuttle ''Challenger'' during the STS-41-G mission and deactivated on October 14, 2005. It is expected to re-enter the Earth's atmosphere in 2023 After 39 Years in Space. Mission The ERBS spacecraft was deployed from Space Shuttle Challenger on October 5, 1984 (first day of flight) using the Canadian-built RMS (Remote Manipulator System), a mechanical arm of about 16 m in length. On deployment, one of the solar panels of ERBS failed initially to extend properly. Hence, mission specialist Sally Ride had to shake the satellite with the remotely-controlled robotic arm and then finally place the stuck panel into sunlight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Cover
Cloud cover (also known as cloudiness, cloudage, or cloud amount) refers to the fraction of the sky obscured by clouds on average when observed from a particular location. Okta is the usual unit for measurement of the cloud cover. The cloud cover is correlated to the sunshine duration as the least cloudy locales are the sunniest ones while the cloudiest areas are the least sunny places, as clouds can block sunlight, especially on sunrise and sunset where sunlight is already limited. The global cloud cover averages around 0.68 when analyzing clouds with optical depth larger than 0.1. This value is lower (0.56) when considering clouds with an optical depth larger than 2, and higher when counting subvisible cirrus clouds. Particularly over the oceans cloud cover is persistent with an average 72% of cloud cover. Role in the climate system Clouds play multiple critical roles in the climate system and diurnal cycle. In particular, being bright objects in the visible part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Forcing
In meteorology, cloud forcing, cloud radiative forcing (CRF) or cloud radiative effect (CRE) is the difference between the radiation budget components for average cloud conditions and cloud-free conditions. Much of the interest in cloud forcing relates to its role as a feedback process in the present period of global warming. Measuring cloud forcing The following equation calculates this change in the radiation budget at the top of the atmosphere : \Delta R_ = R_ - R_ The net cloud radiative effect can be decomposed into its longwave and shortwave components. This is because net radiation is absorbed solar minus the outgoing longwave radiation shown by the following equations : \Delta R_ = \Delta Q_ - \Delta OLR The first term on the right is the shortwave cloud effect (''Q''abs ) and the second is the longwave effect (OLR). The shortwave cloud effect is calculated by the following equation : \Delta Q_ = (S_o/4) \cdot (1 - \alpha_) - (S_o/4) \cdot (1 - \alpha_) Where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the large-scale structure of its circulation remains fairly constant. The smaller scale weather systems – mid-latitude depressions, or tropical convective cells – occur chaotically, and long-range weather predictions of those cannot be made beyond ten days in practice, or a month in theory (see chaos theory and the butterfly effect). The Earth's weather is a consequence of its illumination by the Sun and the laws of thermodynamics. The atmospheric circulation can be viewed as a heat engine driven by the Sun's energy and whose energy sink, ultimately, is the blackness of space. The work produced by that engine causes the motion of the masses of air, and in that process it redistributes the energy absorbed by the Earth's surface near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrological Cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly constant over time but the partitioning of the water into the major reservoirs of ice, fresh water, saline water (salt water) and atmospheric water is variable depending on a wide range of climatic variables. The water moves from one reservoir to another, such as from river to ocean, or from the ocean to the atmosphere, by the physical processes of evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation, infiltration, surface runoff, and subsurface flow. In doing so, the water goes through different forms: liquid, solid (ice) and vapor. The ocean plays a key role in the water cycle as it is the source of 86% of global evaporation. The water cycle involves the exchange of energy, which leads to temperature changes. When water evaporates, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption (electromagnetic Radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is how matter (typically electrons bound in atoms) takes up a photon's energy — and so transforms electromagnetic energy into internal energy of the absorber (for example, thermal energy). A notable effect is attenuation, or the gradual reduction of the intensity of light waves as they propagate through a medium. Although the absorption of waves does not usually depend on their intensity (linear absorption), in certain conditions (optics) the medium's transparency changes by a factor that varies as a function of wave intensity, and saturable absorption (or nonlinear absorption) occurs. Quantifying absorption Many approaches can potentially quantify radiation absorption, with key examples following. * The absorption coefficient along with some closely related derived quantities * The attenuation coefficient (NB used infrequently with meaning synonymous with "absorption coefficient") * The Molar attenuation coefficient (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scattering
Scattering is a term used in physics to describe a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiation) in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of reflected radiation from the angle predicted by the law of reflection. Reflections of radiation that undergo scattering are often called ''diffuse reflections'' and unscattered reflections are called ''specular'' (mirror-like) reflections. Originally, the term was confined to light scattering (going back at least as far as Isaac Newton in the 17th century). As more "ray"-like phenomena were discovered, the idea of scattering was extended to them, so that William Herschel could refer to the scattering of "heat rays" (not then recognized as electromagnetic in nature) in 1800. John Tyndall, a pioneer in light scattering researc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
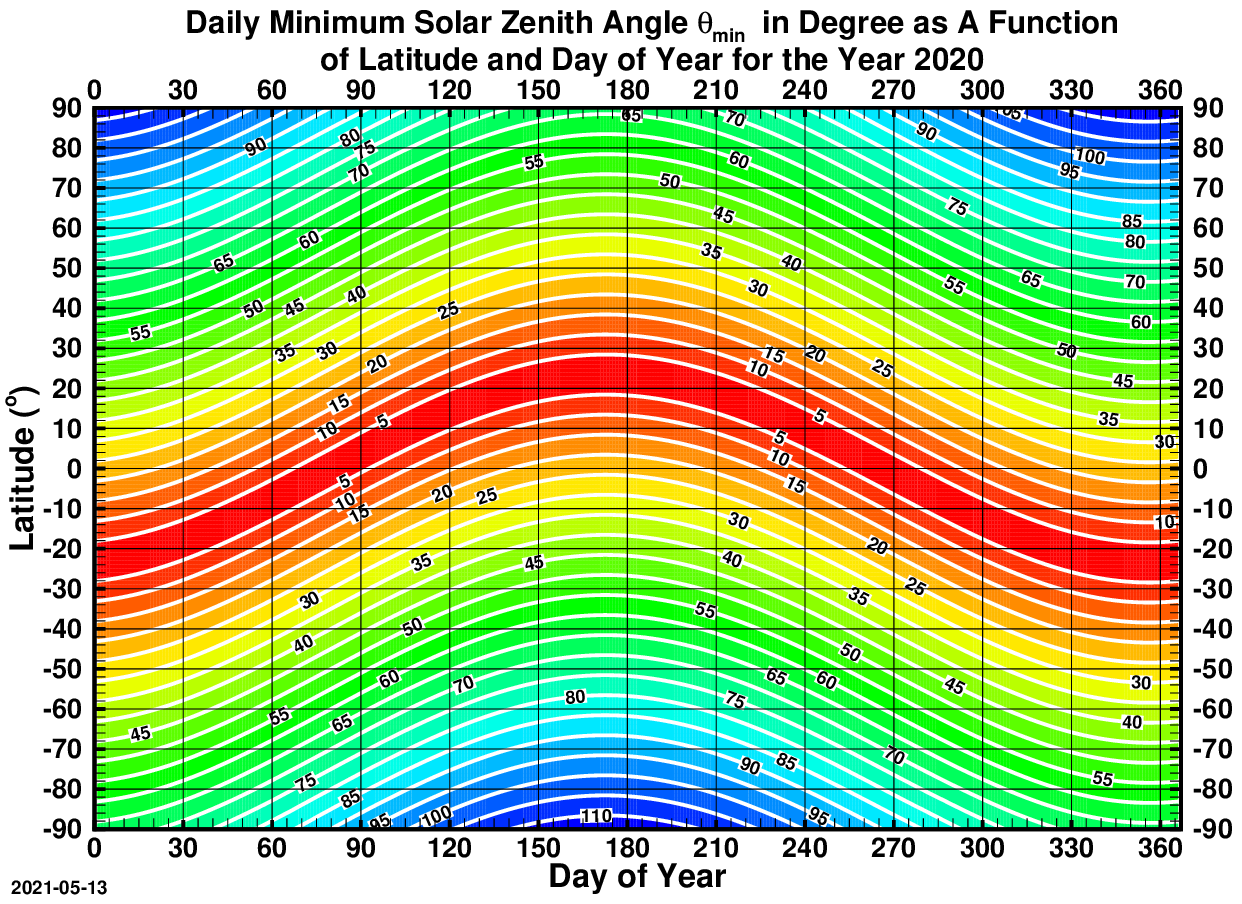
Solar Zenith Angle
The solar zenith angle is the zenith angle of the sun, i.e., the angle between the sun’s rays and the vertical direction. It is the complement to the solar altitude or solar elevation, which is the altitude angle or elevation angle between the sun’s rays and a horizontal plane. At solar noon, the zenith angle is at a minimum and is equal to latitude minus solar declination angle. This is the basis by which ancient mariners navigated the oceans. Solar zenith angle is normally used in combination with the solar azimuth angle to determine the position of the Sun as observed from a given location on the surface of the Earth. Formula : \cos \theta_s = \sin \alpha_s = \sin \Phi \sin \delta + \cos \Phi \cos \delta \cos h where * \theta_s is the ''solar zenith angle'' * \alpha_s is the ''solar altitude angle'', \alpha_s = 90° – \theta_s * h is the hour angle, in the local solar time. * \delta is the current declination of the Sun * \Phi is the local latitude. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albrecht Effect
The Albrecht effect describes how cloud condensation nuclei (CCN), possibly from anthropogenic pollution, may increase cloud lifetime and hence increase the amount of solar radiation reflected from clouds. Because it does not directly interact with incoming or outgoing radiation, it has an indirect effect on climate. Aerosol particles act as CCNs creating more droplets of a smaller size. These take more time to coalesce to raindrop size reducing precipitation efficiency and hence increasing the lifetime of the cloud. The increased scattering of incoming radiation leads to a cooling of −0.3 to IPCC 4th Assessment Report, 2005 This effect is not as well understood as the Twomey effect The Twomey effect describes how additional cloud condensation nuclei (CCN), possibly from anthropogenic pollution, may increase the amount of solar radiation reflected by clouds. This is an indirect effect (or radiative forcing) by such particles, .... There are many other effects, indirect and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |