|
Cloth Modeling
Cloth modeling is the term used for simulating cloth within a computer program, usually in the context of 3D computer graphics. The main approaches used for this may be classified into three basic types: geometric, physical, and particle/energy. Background Most models of cloth are based on "particles" of mass connected in some manner of mesh. Newtonian Physics is used to model each particle through the use of a "black box" called a physics engine. This involves using the basic law of motion (Newton's Second Law): : \vec = m \vec In all of these models, the goal is to find the position and shape of a piece of fabric using this basic equation and several other methods. Geometric methods André Weilpioneered the first of these, the geometric technique, in 1986. His work was focused on approximating the look of cloth by treating cloth like a collection of cables and using Hyperbolic cosine (catenary) curves. Because of this, it is not suitable for dynamic models but works very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloth Simulation
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: Domestic purposes onsumer textilesand technical textiles. In consumer textiles, aesthetics and comfort are the most important factors, but in technical textiles, functional properties are the priority. Geotextiles, industrial textiles, medical textiles, and many other areas are examples of technical textiles, whereas clothing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
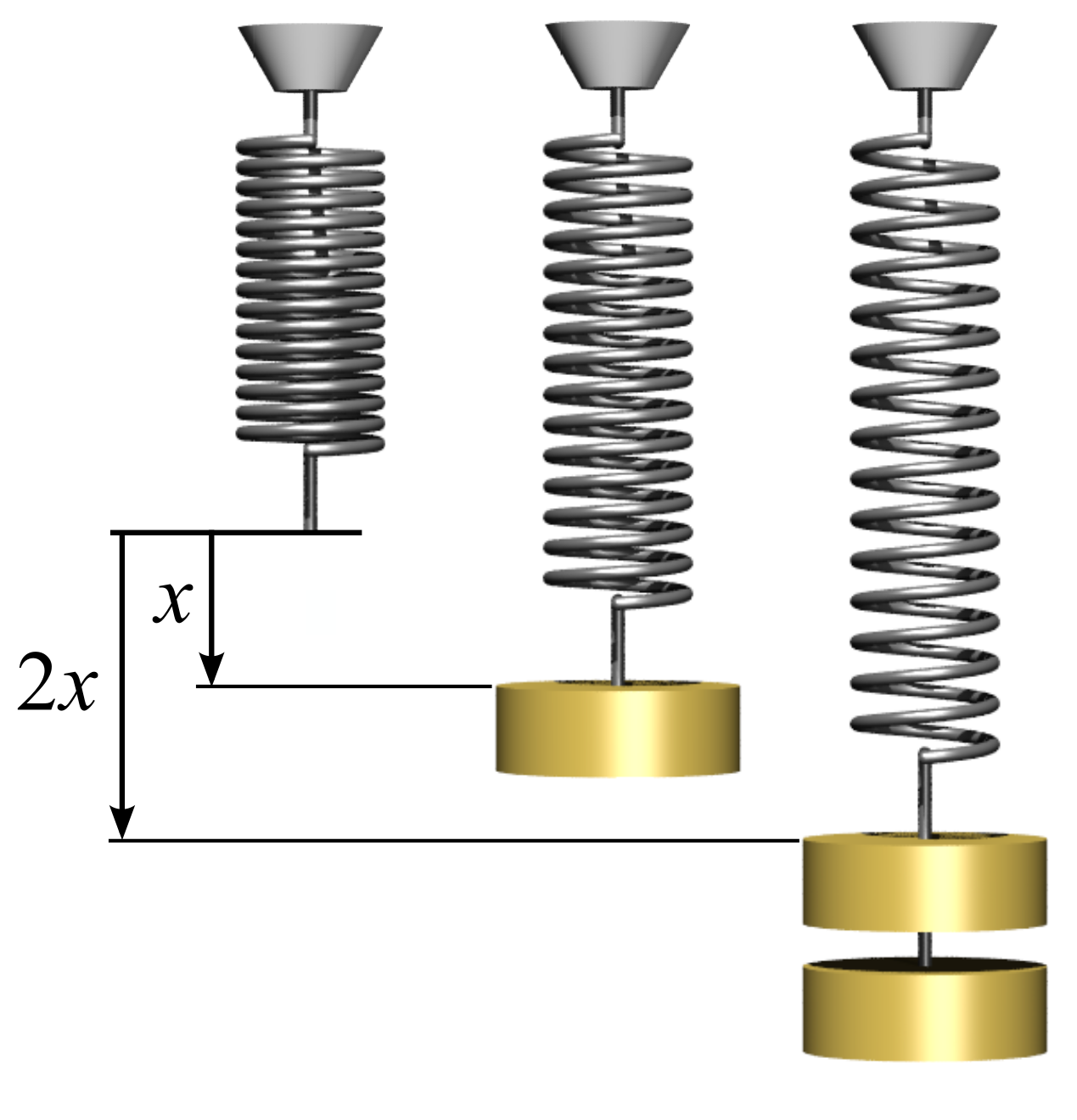
Hooke's Law
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring (device), spring by some distance () Proportionality (mathematics)#Direct_proportionality, scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of the spring (i.e., its stiffness), and is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. The law is named after 17th-century British physicist Robert Hooke. He first stated the law in 1676 as a Latin anagram. He published the solution of his anagram in 1678 as: ("as the extension, so the force" or "the extension is proportional to the force"). Hooke states in the 1678 work that he was aware of the law since 1660. Hooke's equation holds (to some extent) in many other situations where an elasticity (physics), elastic body is Deformation (physics), deformed, such as wind blowing on a tall building, and a musician plucking a string (music), string of a guitar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conceptual Models
Conceptual may refer to: Philosophy and Humanities *Concept *Conceptualism * Philosophical analysis (Conceptual analysis) *Theoretical definition (Conceptual definition) *Thinking about Consciousness (Conceptual dualism) *Pragmatism (Conceptual pragmatism) * Paradigm (Conceptual scheme) * Abstract and concrete (Conceptual object) * Conceptual attrition, an idea of Beverley Skeggs *Conceptual proliferation * Conceptual history * Conceptual necessity Linguistics and Semantics *Conceptual schema *Conceptual metaphor *Conceptual model *Conceptual blending *Conceptual semantics *Conceptual dictionary * Conceptual change * Conceptual dependency theory *Conceptual domain in Frame semantics (linguistics) *Inferential role semantics (Conceptual role semantics) Psychology *Priming (psychology) (Conceptual priming) *Spatial–temporal reasoning (Visuo-conceptual) *Conceptual act model of emotion *Conceptual space Science *Conceptual physics *Conceptual economy *Conceptual model (computer s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stretched Grid Method
The stretched grid method (SGM) is a numerical technique for finding approximate solutions of various mathematical and engineering problems that can be related to an elastic grid behavior. In particular, meteorologists use the stretched grid method for weather prediction and engineers use the stretched grid method to design tents and other tensile structures. FEM and BEM mesh refinement In recent decades the finite element and boundary element methods (FEM and BEM) have become a mainstay for industrial engineering design and analysis. Increasingly larger and more complex designs are being simulated using the FEM or BEM. However, some problems of FEM and BEM engineering analysis are still on the cutting edge. The first problem is a reliability of engineering analysis that strongly depends upon the quality of initial data generated at the pre-processing stage. It is known that automatic element mesh generation techniques at this stage have become commonly used tools for the analys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigid Body Dynamics
In the physical science of dynamics, rigid-body dynamics studies the movement of systems of interconnected bodies under the action of external forces. The assumption that the bodies are ''rigid'' (i.e. they do not deform under the action of applied forces) simplifies analysis, by reducing the parameters that describe the configuration of the system to the translation and rotation of reference frames attached to each body. This excludes bodies that display fluid, highly elastic, and plastic behavior. The dynamics of a rigid body system is described by the laws of kinematics and by the application of Newton's second law (kinetics) or their derivative form, Lagrangian mechanics. The solution of these equations of motion provides a description of the position, the motion and the acceleration of the individual components of the system, and overall the system itself, as a function of time. The formulation and solution of rigid body dynamics is an important tool in the computer si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics Engine
A physics engine is computer software that provides an approximate simulation of certain physical systems, such as rigid body dynamics (including collision detection), soft body dynamics, and fluid dynamics, of use in the domains of computer graphics, video games and film ( CGI). Their main uses are in video games (typically as middleware), in which case the simulations are in real-time. The term is sometimes used more generally to describe any software system for simulating physical phenomena, such as high-performance scientific simulation. Description There are generally two classes of physics engines: real-time and high-precision. High-precision physics engines require more processing power to calculate very precise physics and are usually used by scientists and computer animated movies. Real-time physics engines—as used in video games and other forms of interactive computing—use simplified calculations and decreased accuracy to compute in time for the game to respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Mechanics
Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. For objects governed by classical mechanics, if the present state is known, it is possible to predict how it will move in the future (determinism), and how it has moved in the past (reversibility). The earliest development of classical mechanics is often referred to as Newtonian mechanics. It consists of the physical concepts based on foundational works of Sir Isaac Newton, and the mathematical methods invented by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Joseph-Louis Lagrange, Leonhard Euler, and other contemporaries, in the 17th century to describe the motion of bodies under the influence of a system of forces. Later, more abstract methods were developed, leading to the reformulations of classical mechanics known as Lagrangian mechanics and Hamiltonian mechanics. These advances, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft Body Dynamics
Soft-body dynamics is a field of computer graphics that focuses on visually realistic physical simulations of the motion and properties of deformable objects (or ''soft bodies''). The applications are mostly in video games and films. Unlike in simulation of rigid bodies, the shape of soft bodies can change, meaning that the relative distance of two points on the object is not fixed. While the relative distances of points are not fixed, the body is expected to retain its shape to some degree (unlike a fluid). The scope of soft body dynamics is quite broad, including simulation of soft organic materials such as muscle, fat, hair and vegetation, as well as other deformable materials such as clothing and fabric. Generally, these methods only provide visually plausible emulations rather than accurate scientific/engineering simulations, though there is some crossover with scientific methods, particularly in the case of finite element simulations. Several physics engines currently provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Equilibrium
In classical mechanics, a particle is in mechanical equilibrium if the net force on that particle is zero. By extension, a physical system made up of many parts is in mechanical equilibrium if the net force on each of its individual parts is zero. In addition to defining mechanical equilibrium in terms of force, there are many alternative definitions for mechanical equilibrium which are all mathematically equivalent. In terms of momentum, a system is in equilibrium if the momentum of its parts is all constant. In terms of velocity, the system is in equilibrium if velocity is constant. In a rotational mechanical equilibrium the angular momentum of the object is conserved and the net torque is zero. More generally in conservative systems, equilibrium is established at a point in configuration space where the gradient of the potential energy with respect to the generalized coordinates is zero. If a particle in equilibrium has zero velocity, that particle is in static equilibrium. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloth
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and Nonwoven, non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to Bulletproof vest, bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and Medical gown, doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: Domestic purposes [consumer textiles] and technical textiles. In consumer textiles, Aesthetics (textile), aesthetics and Textile performance#Comfort, comfort are the most important factors, but in technical textiles, Textile performance#Properties, functional properties are the priority. Geotex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Gravity
The standard acceleration due to gravity (or standard acceleration of free fall), sometimes abbreviated as standard gravity, usually denoted by or , is the nominal gravitational acceleration of an object in a vacuum near the surface of the Earth. It is defined by standard as . This value was established by the 3rd CGPM (1901, CR 70) and used to define the standard weight of an object as the product of its mass and this nominal acceleration. The acceleration of a body near the surface of the Earth is due to the combined effects of gravity and centrifugal acceleration from the rotation of the Earth (but the latter is small enough to be negligible for most purposes); the total (the apparent gravity) is about 0.5% greater at the poles than at the Equator. Although the symbol is sometimes used for standard gravity, (without a suffix) can also mean the local acceleration due to local gravity and centrifugal acceleration, which varies depending on one's position on Earth (see Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hooke's Law
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring (device), spring by some distance () Proportionality (mathematics)#Direct_proportionality, scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of the spring (i.e., its stiffness), and is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. The law is named after 17th-century British physicist Robert Hooke. He first stated the law in 1676 as a Latin anagram. He published the solution of his anagram in 1678 as: ("as the extension, so the force" or "the extension is proportional to the force"). Hooke states in the 1678 work that he was aware of the law since 1660. Hooke's equation holds (to some extent) in many other situations where an elasticity (physics), elastic body is Deformation (physics), deformed, such as wind blowing on a tall building, and a musician plucking a string (music), string of a guitar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |