|
Climate Of Rajasthan
The climate of Rajasthan in northwestern India is generally arid or semi-arid and features fairly hot temperatures over the year with extreme temperatures in both summer and winter. History Under the Köppen climate classification the greater part of Rajasthan falls under Desert climate#Hot desert climates, Hot Desert (BWh) and remaining portions of the state falls under Semi-arid climate#Hot semi-arid climates, Hot Semi Arid (BSh); the climate of the state ranges from arid to semi-arid. Rajasthan receives low and variable rainfalls and thereby is prone to droughts. As Rajasthan is the dry and hot state, Unbelievable hailstorm covered Nagaur, Rajasthan in a thin snow-like icy blanket in December 2019. Later on, it is clarified that this is not a snowfall but a hailstorm, endorse by western disturbances. The climate has changed in winters like never before. Seasons Summer Due to the Desert Geography, frequently climb above 40 to 45 degrees Celsius in most places. Due to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajasthan Canal Shivender
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern side, where it comprises most of the wide and inhospitable Thar Desert (also known as the Great Indian Desert) and shares a border with the Pakistani provinces of Punjab to the northwest and Sindh to the west, along the Sutlej-Indus River valley. It is bordered by five other Indian states: Punjab to the north; Haryana and Uttar Pradesh to the northeast; Madhya Pradesh to the southeast; and Gujarat to the southwest. Its geographical location is 23.3 to 30.12 North latitude and 69.30 to 78.17 East longitude, with the Tropic of Cancer passing through its southernmost tip. Its major features include the ruins of the Indus Valley civilisation at Kalibangan and Balathal, the Dilwara Temples, a Jain pilgrimage site at Rajasthan's only hill station, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaipur
Jaipur (; Hindi Language, Hindi: ''Jayapura''), formerly Jeypore, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Rajasthan. , the city had a population of 3.1 million, making it the List of cities in India by population, tenth most populous city in the country. Jaipur is also known as the ''Pink City'', due to the dominant colour scheme of its buildings. It is also known as the Paris of India, and C. V. Raman called it the ''Island of Glory''. It is located from the national capital New Delhi. Jaipur was founded in 1727 by the Kachhwaha Rajput ruler Jai Singh II, the ruler of Amer, India, Amer, after whom the city is named. It was one of the earliest planned cities of modern India, designed by Vidyadhar Bhattacharya. During the British Colonial period, the city served as the capital of Jaipur State. After independence in 1947, Jaipur was made the capital of the newly formed s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
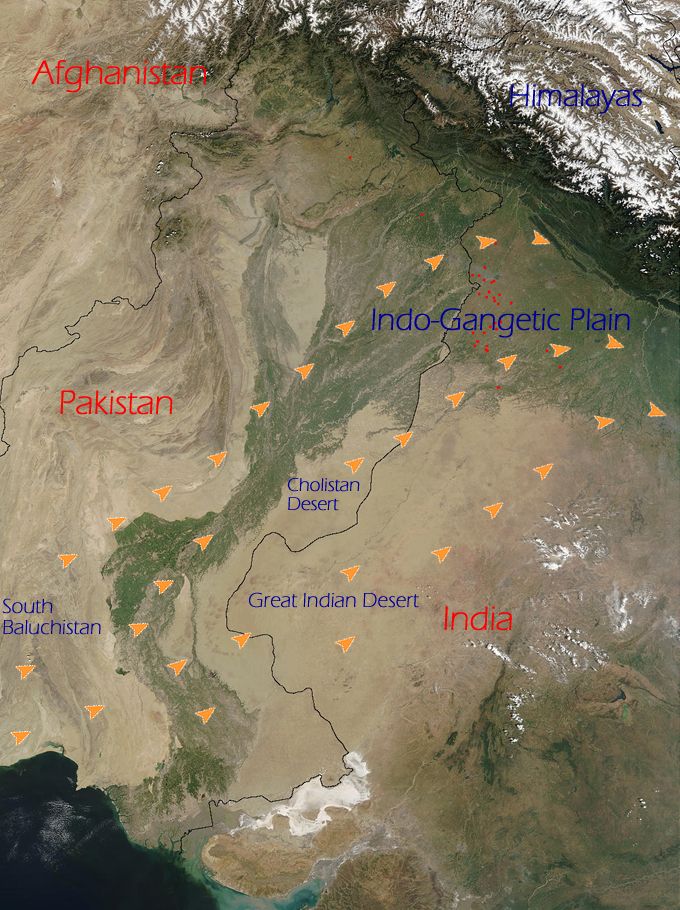
Thar Desert
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent, Subcontinent that covers an area of and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's List of deserts by area, 20th-largest desert, and the world's 9th-largest hot subtropical desert. About 85% of the Thar Desert is in India, and about 15% is in Pakistan. The Thar Desert is about 4.56% of the total geographical area of India. More than 60% of the desert lies in the Indian state of Rajasthan; the portion in India also extends into Gujarat, Punjab, India, Punjab, and Haryana. The portion in Pakistan extends into the provinces of Sindh and Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab (the portion in the latter province is referred to as the Cholistan Desert). History of desertification Ice-age desertification During the Last Glacial Maximum 20,000 before present, an approximately ice sheet covered the Tibetan Plateau#Glaciology, Tibetan P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loo (wind)
The Loo ( hi, लू, Urdu: لو) is a strong, dusty, gusty, hot and dry summer wind from the west which blows over the Indo-Gangetic Plain region of North India and Pakistan. It is especially strong in the months of May and June. Due to its very high temperatures (45 °C–50 °C or 115 °F–120 °F), exposure to it often leads to fatal heatstrokes. Since it causes extremely low humidity and high temperatures, the ''Loo'' also has a severe drying effect on vegetation leading to widespread browning in the areas affected by it during the months of May and June. Origin and ending The Loo mainly originates in the large desert regions of the northwestern Indian subcontinent: the Great Indian Desert, the Cholistan Desert and the desert areas of Southern Balochistan. The Loo ends in late summer, with the arrival of the Indian monsoon. In some areas of North India and Pakistan, there are brief, but violent, dust storms known as Kali Andhi (or ''black Storm'') b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Of India
The climate of India consists of a wide range of weather conditions across a vast geographic scale and varied topography. Based on the Köppen system, India hosts six major climatic sub types, ranging from arid deserts in the west, alpine tundra and glaciers in the north, and humid tropical regions supporting rain forests in the southwest and the island territories. Many regions have starkly different microclimates, making it one of the most climatically diverse countries in the world. The country's meteorological department follows the international standard of four seasons with some local adjustments: winter (December to February), summer (March to May), monsoon (rainy) season (June to September), and a post-monsoon period (October and November). India's geography and geology are climatically pivotal: the Thar Desert in the northwest and the Himalayas in the north work in tandem to create a culturally and economically important monsoonal regime. As Earth's highest and most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaisalmer
Jaisalmer , nicknamed "The Golden city", is a city in the Indian state of Rajasthan, located west of the state capital Jaipur. The town stands on a ridge of yellowish sandstone and is crowned by the ancient Jaisalmer Fort. This fort contains a royal palace and several ornate Jain temples. Many of the houses and temples of both the fort and of the town below are built of finely sculptured sandstone. The town lies in the heart of the Thar Desert (the Great Indian Desert) and has a population, including the residents of the fort, of about 78,000. It is the administrative headquarters of Jaisalmer District. Jaisalmer was once the capital of Jaisalmer State. Origin of name Jaisalmer was founded by Rawal Jaisal in 1156 AD. ''Jaisalmer'' means ''the Hill Fort of Jaisal''. Jaisalmer is sometimes called the "Golden City of India" because the yellow sandstone used throughout the architecture of both the fort and the town below, imbues both with a certain golden-yellow light. Geography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. Bikaner city is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division. Formerly the capital of the princely state of Bikaner, the city was founded by Rao Bika in 1488 CE and from its small origins it has developed into the fourth largest city in Rajasthan. The Ganges Canal, completed in 1928, and the Indira Gandhi Canal, completed in 1987, facilitated its development. History left, Bikaner coat of arms Prior to the mid 15th century, the region that is now Bikaner was a barren wilderness called Jangladesh. Rao Bika established the city of Bikaner in 1488. He was the first son of Maharaja Rao Jodha of the Rathore clan, the founder of Jodhpur and conquered the largely arid country in the north of Rajasthan. As the first son of Jodha he wanted to have his own kingdom, not inheriting Jodhpur from his father or the title of Maharaja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jodhpur
Jodhpur (; ) is the second-largest city in the Indian state of Rajasthan and officially the second metropolitan city of the state. It was formerly the seat of the princely state of Jodhpur State. Jodhpur was historically the capital of the Kingdom of Marwar, which is now part of Rajasthan. Jodhpur is a popular tourist destination, featuring many palaces, forts, and temples, set in the stark landscape of the Thar Desert. It is popularly known as the "Blue City" among people of Rajasthan and all over India. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and Jodhpur division. The old city circles the Mehrangarh Fort and is bounded by a wall with several gates. The city has expanded greatly outside the wall, though over the past several decades. Jodhpur lies near the geographic centre of the Rajasthan state, which makes it a convenient base for travel in a region much frequented by tourists. The city featured in ''The New York Timess "52 Places to Go in 2020 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Standard Time
Indian Standard Time (IST), sometimes also called India Standard Time, is the time zone observed throughout India, with a time offset of UTC+05:30. India does not observe daylight saving time or other seasonal adjustments. In military and aviation time, IST is designated E* ("Echo-Star"). It is indicated as Asia/Kolkata in the IANA time zone database. History After Independence in 1947, the Union government established IST as the official time for the whole country, although Kolkata and Mumbai retained their own local time (known as Calcutta Time and Bombay Time) until 1948 and 1955, respectively. The Central observatory was moved from Chennai to a location at Shankargarh Fort in Allahabad district, so that it would be as close to UTC+05:30 as possible. Daylight Saving Time (DST) was used briefly during the China–India War of 1962 and the Indo-Pakistani Wars of 1965 and 1971. Calculation Indian Standard Time is calculated from the clock tower in Mirzapur nearly exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India Meteorological Department
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) is an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Government of India. It is the principal agency responsible for meteorological observations, weather forecasting and seismology. IMD is headquartered in Delhi and operates hundreds of observation stations across India and Antarctica. Regional offices are at Chennai, Mumbai, Kolkata, Nagpur, Guwahati and New Delhi. IMD is also one of the six Regional Specialised Meteorological Centres of the World Meteorological Organisation. It has the responsibility for forecasting, naming and distribution of warnings for tropical cyclones in the Northern Indian Ocean region, including the Malacca Straits, the Bay of Bengal, the Arabian Sea and the Persian Gulf. History In 1686, Edmond Halley published his treatise on the Indian summer monsoon, which he attributed to a seasonal reversal of winds due to the differential heating of the Asian landmass and the Indian Ocean. The first meteorological obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon Of South Asia
The Monsoon of South Asia is among several geographically distributed global monsoons. It affects the Indian subcontinent, where it is one of the oldest and most anticipated weather phenomena and an economically important pattern every year from June through September, but it is only partly understood and notoriously difficult to predict. Several theories have been proposed to explain the origin, process, strength, variability, distribution, and general vagaries of the monsoon, but understanding and predictability are still evolving. The unique geographical features of the Indian subcontinent, along with associated atmospheric, oceanic, and geophysical factors, influence the behavior of the monsoon. Because of its effect on agriculture, on flora and fauna, and on the climates of nations such as Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka – among other economic, social, and environmental effects – the monsoon is one of the most anticipated, tracked, and studied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Sunset On The Dunes Of The Great Indian Thar Desert Rajasthan India
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, " a", and its variant " an", are indefinite articles. History The earliest certain ancestor of "A" is aleph (also written 'aleph), the first letter of the Phoenician alphabet, which consisted entirely of consonants (for that reason, it is also called an abjad to distinguish it fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |