|
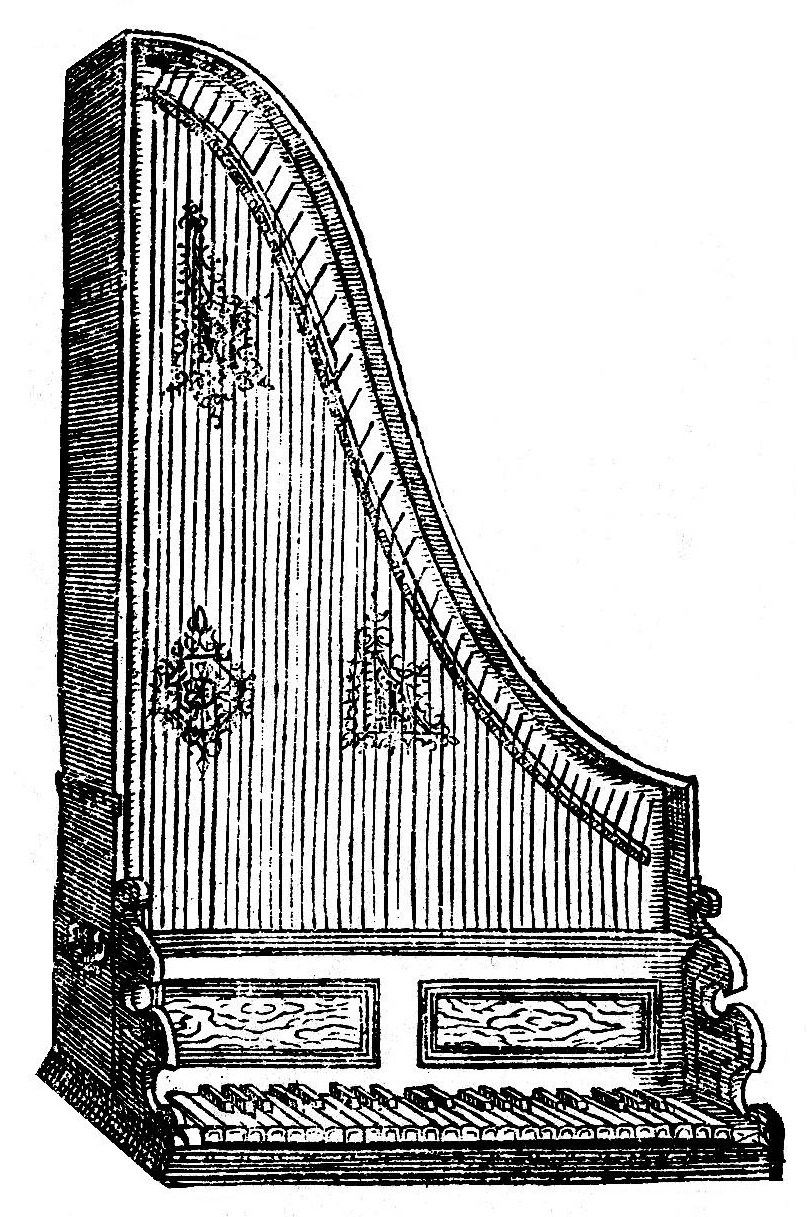
Clavicytherium
A clavicytherium is a harpsichord in which the soundboard and strings are mounted vertically facing the player. The primary purpose of making a harpsichord vertical is the same as in the later upright piano, namely to save floor space. In a clavicytherium, the jacks move horizontally without the assistance of gravity, so that clavicytherium actions are more complex than those of other harpsichords. Design In any harpsichord, the strings are plucked by small plectra, held by jacks, which are thin strips of wood. In a standard harpsichord, the strings are placed horizontally and the jacks are vertical. Thus to make the jack return to position (after it has been lifted by a key to pluck) is a simple matter of gravity; with proper adjustment the jack will simply fall back into its rest position (for details and diagrams see ''harpsichord''). A clavicytherium sacrifices this simplicity and must find some other means to make the jacks return. In some instruments, this is accomplished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Delin (harpsichord Maker)
Albert Delin (17 April 1712, Ath – 26 Nov 1771, Tournai; also known as Albertus Delin) was a harpsichord maker in the Low Countries. Biography Born in Ath in Southern Netherlands (now in Belgium), he soon moved to the nearby town of Tournai to practice his trade. Little is known of his training but a remarkable number of his instruments have survived. His building style is quite contrary to his more famous contemporaries, like his neighbours Dulckens in Antwerp, the Hass family in Hamburg or the Taskins of Paris, that at the time created complex machines with an extensive variety of registers and knee levers. Delin's surviving instruments are simple, reminiscent of the old Ruckers instruments of a century before and of good workmanship as witnessed by the number of surviving instruments. Surviving instruments *Two surviving harpsichords (1750 and1768), both have a single manual and have only two 8' choirs and a buff stop, with all battens protruding through the instruments side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harpsichord
A harpsichord ( it, clavicembalo; french: clavecin; german: Cembalo; es, clavecín; pt, cravo; nl, klavecimbel; pl, klawesyn) is a musical instrument played by means of a musical keyboard, keyboard. This activates a row of levers that turn a trigger mechanism that plucks one or more strings with a small plectrum made from quill or plastic. The strings are under tension on a Sound board (music), soundboard, which is mounted in a wooden case; the soundboard amplifies the vibrations from the strings so that the listeners can hear it. Like a pipe organ, a harpsichord may have more than one keyboard Manual (music), manual, and even a #Pedal harpsichord, pedal board. Harpsichords may also have Organ stop, stop buttons which add or remove additional octaves. Some harpsichords may have a buff stop, which brings a strip of buff leather or other material in contact with the strings, muting their sound to simulate the sound of a plucked lute. The term denotes the whole family of similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal College Of Music
The Royal College of Music is a music school, conservatoire established by royal charter in 1882, located in South Kensington, London, UK. It offers training from the Undergraduate education, undergraduate to the Doctorate, doctoral level in all aspects of Western Music including performance, composition, conducting, music theory and history. The RCM also undertakes research, with particular strengths in performance practice and performance science. The college is one of the four conservatories of the ABRSM, Associated Board of the Royal Schools of Music and a member of Conservatoires UK. Its buildings are directly opposite the Royal Albert Hall on Prince Consort Road, next to Imperial College and among the museums and cultural centres of Albertopolis. History Background The college was founded in 1883 to replace the short-lived and unsuccessful National Training School for Music (NTSM). The school was the result of an earlier proposal by the Albert, Prince Consort, Prince Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartolomeo Cristofori
Bartolomeo Cristofori di Francesco (; May 4, 1655 – January 27, 1731) was an Italian maker of musical instruments famous for inventing the piano. Life The available source materials on Cristofori's life include his birth and death records, two wills, the bills he submitted to his employers, and a single interview carried out by Scipione Maffei. From the latter, both Maffei's notes and the published journal article are preserved. Cristofori was born in Padua in the Republic of Venice. Nothing is known of his early life. A tale is told that he served as an apprentice to the great violin maker Nicolò Amati, based on the appearance in a 1680 census record of a "Christofaro Bartolomei" living in Amati's house in Cremona. However, as Stewart Pollens points out, this person cannot be Bartolomeo Cristofori, since the census records an age of 13, whereas Cristofori according to his baptismal record would have been 25 at the time. Pollens also gives strong reasons to doubt the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonie Universelle
''Harmonie universelle'' ("Universal Harmony"; complete title: ''Harmonie universelle, contenant la théorie et la pratique de la musique'') is a work by Marin Mersenne, published in Paris in 1636. It represented the sum of musical knowledge during his lifetime. This was a major work since it represented the most complete description of music theory near the middle of the 17th century in France. It covers all aspects including theoretical, practical, stylistic, organological, mathematical, acoustical, and theological. Content The title page specifies the scope of the topics covered by the book including the nature of sounds, movements, consonance, dissonance, genres, modes of composition, voice, singing, and all kinds of harmonic instruments. This monumental treatise is abundant in illustrations (including musical engravings), and in systematic tables. It also remains the only source of certain musical works from Jacques Mauduit, Eustache Du Caurroy, Antoine de Sewn, or Pierre d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 census it had a population of 1,173,179, while the preliminary results of the 2022 census recorded that County Dublin as a whole had a population of 1,450,701, and that the population of the Greater Dublin Area was over 2 million, or roughly 40% of the Republic of Ireland's total population. A settlement was established in the area by the Gaels during or before the 7th century, followed by the Vikings. As the Kingdom of Dublin grew, it became Ireland's principal settlement by the 12th century Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland. The city expanded rapidly from the 17th century and was briefly the second largest in the British Empire and sixth largest in Western Europe after the Acts of Union in 1800. Following independence in 1922, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tournai
Tournai or Tournay ( ; ; nl, Doornik ; pcd, Tornai; wa, Tornè ; la, Tornacum) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies southwest of Brussels on the river Scheldt. Tournai is part of Eurometropolis Lille–Kortrijk–Tournai, which had 2,155,161 residents in 2008. Tournai is one of the oldest cities in Belgium and has played an important role in the country's cultural history. It was the first capital of the Frankish Empire, with Clovis I being born here. Geography Tournai is located in the Picardy Wallonia and Romance Flanders region of Belgium, at the southern limit of the Flemish plain, in the basin of the River Scheldt (''Escaut'' in French, ''Schelde'' in Dutch). Administratively, the town is part of the Province of Hainaut, itself part of Wallonia. It is also a municipality that is part of the French-speaking Community of Belgium. Tournai has its own arrondissements, both administrative and judicial. Its ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopédie Méthodique
The ''Encyclopédie méthodique par ordre des matières'' ("Methodical Encyclopedia by Order of Subject Matter") was published between 1782 and 1832 by the French publisher Charles Joseph Panckoucke, his son-in-law Henri Agasse, and the latter's wife, Thérèse-Charlotte Agasse. Arranged by disciplines, it was a revised and much expanded version, in roughly 210 to 216 volumes (different sets were bound differently), of the alphabetically arranged ''Encyclopédie'', edited by Denis Diderot and Jean le Rond d'Alembert. The full title was ''L'Encyclopédie méthodique ou par ordre de matières par une société de gens de lettres, de savants et d'artistes; précédée d'un vocabulaire universel, servant de table pour tout l'ouvrage, ornée des portraits de MM. Diderot et d'Alembert, premiers éditeurs de l'Encyclopédie.'' Development Two sets of Diderot's ''Encyclopédie'' and its supplements were cut up into articles. Each subject category was entrusted to a specialized editor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marin Mersenne
Marin Mersenne, OM (also known as Marinus Mersennus or ''le Père'' Mersenne; ; 8 September 1588 – 1 September 1648) was a French polymath whose works touched a wide variety of fields. He is perhaps best known today among mathematicians for Mersenne prime numbers, those which can be written in the form for some integer . He also developed Mersenne's laws, which describe the harmonics of a vibrating string (such as may be found on guitars and pianos), and his seminal work on music theory, '' Harmonie universelle'', for which he is referred to as the "father of acoustics". Mersenne, an ordained Catholic priest, had many contacts in the scientific world and has been called "the center of the world of science and mathematics during the first half of the 1600s" and, because of his ability to make connections between people and ideas, "the post-box of Europe". He was also a member of the Minim religious order and wrote and lectured on theology and philosophy. Life Mersenne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
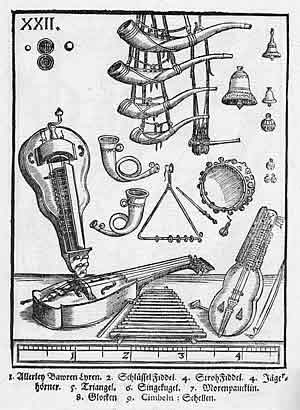
Syntagma Musicum
''Syntagma Musicum (1614-1620)'' is a musical treatise in three volumes by the German composer, organist, and music theorist Michael Praetorius. It was published in Wittenberg and Wolfenbüttel. It is one of the most commonly used research sources for seventeenth-century music theory and performance practice The second volume, ''De Organographia,'' illustrates and describes musical instruments and their use; this volume in particular became a valuable guide for research and reconstruction of early instruments in the twentieth century, and thus an integral part of the early music revival. Though never published, Praetorius intended a fourth volume on musical composition. The three extant volumes are: * I: ''Musicae Artis Analecta'' * II: ''De Organographia'' * III: ''Termini musicali'' Contents Volume One: Musicae Artis Analecta The first volume was written in Latin and divided into two parts, published separately. The first part, "on sacred or ecclesiastical music," shows Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Praetorius
Michael Praetorius (probably 28 September 1571 – 15 February 1621) was a German composer, organist, and music theorist. He was one of the most versatile composers of his age, being particularly significant in the development of musical forms based on Protestant hymns. Life Praetorius was born Michael Schultze, the youngest son of a Lutheran pastor, in Creuzburg, in present-day Thuringia. After attending school in Torgau and Zerbst, he studied divinity and philosophy at the University of Frankfurt (Oder). He was fluent in a number of languages. After receiving his musical education, from 1587 he served as organist at the Marienkirche in Frankfurt. From 1592/3 he served at the court in Wolfenbüttel, under the employ of Henry Julius, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg. He served in the duke's State Orchestra, first as organist and later (from 1604) as '' Kapellmeister'' (court music director). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |