|
Citrus Tristeza Virus
Citrus tristeza virus (CTV) is a viral species of the genus ''Closterovirus'' that causes the most economically damaging disease to its namesake plant genus, ''Citrus''. The disease has led to the death of millions of ''Citrus'' trees all over the world and has rendered millions of others useless for production. Farmers in Brazil and other South American countries gave it the name "tristeza", meaning sadness in Portuguese and Spanish, referring to the devastation produced by the disease in the 1930s. The virus is transmitted most efficiently by the brown citrus aphid. The pathogen CTV is a flexuous rod virus with dimensions of 2000 nm long and 12 nm in diameter. The CTV genome is typically between 19.2 and 19.3 kb long and consists of a single strand of (+)-sense RNA enclosed by two types of capsid proteins. The size of its genome makes CTV one of the largest RNA viruses known. The CTV genome contains 12 open reading frames, which could encode at least 17 proteins.U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Species
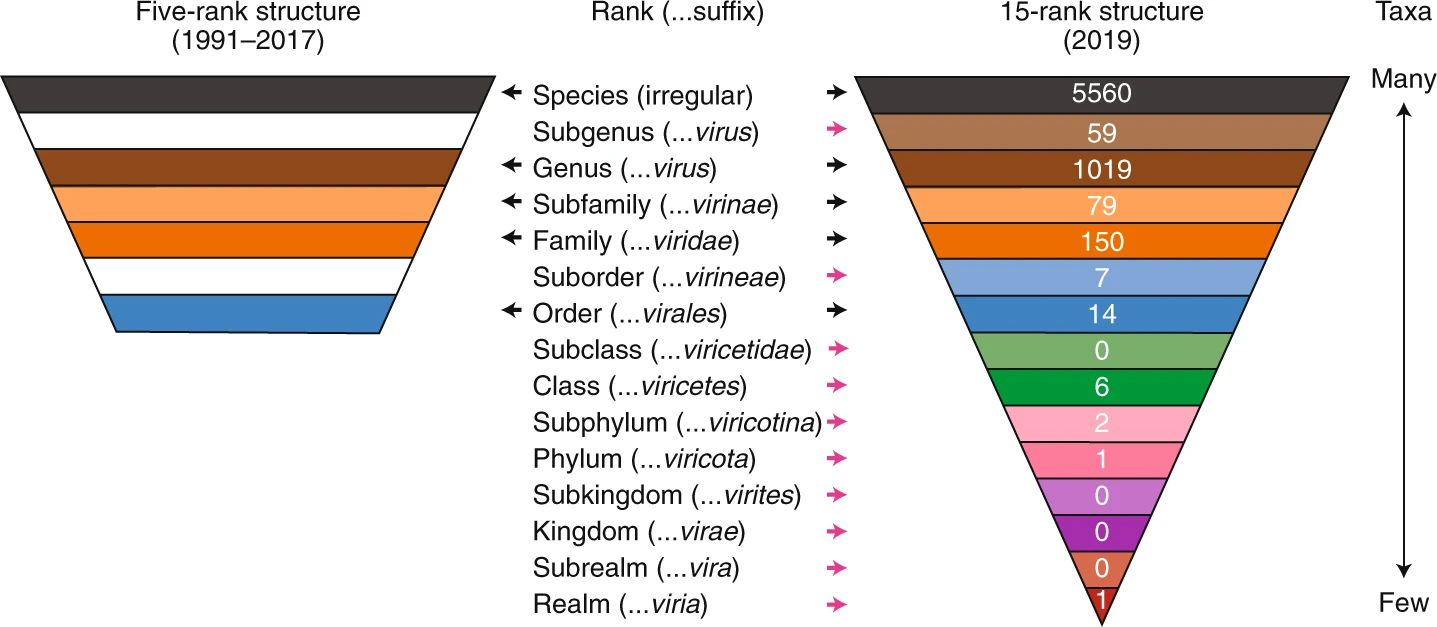
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms. Viruses are classified by phenotypic characteristics, such as morphology, nucleic acid type, mode of replication, host organisms, and the type of disease they cause. The formal taxonomic classification of viruses is the responsibility of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) system, although the Baltimore classification system can be used to place viruses into one of seven groups based on their manner of mRNA synthesis. Specific naming conventions and further classification guidelines are set out by the ICTV. A catalogue of all the world's known viruses has been proposed and, in 2013, some preliminary efforts were underway. Definitions Species definition Species form the basis for any biological classification system. Before 1982, it was thought that viruses could not be made to fit Ernst Mayr' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afraegle
''Afraegle'' is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Rutaceae. Its native range is Western and Western Central Tropical Africa. . Species: * '' Afraegle mildbraedii'' Engl. * ''Afraegle paniculata ''Afraegle'' is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Rutaceae. Its native range is Western and Western Central Tropical Africa Although tropical Africa is mostly familiar to the West for its rainforests, this biogeographic re ...'' (Schumach. & Thonn.) Engl. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q8191106 Aurantioideae Aurantioideae genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphis Gossypii
''Aphis gossypii'' is a tiny insect, an aphid ("greenfly") in the superfamily Aphidoidea in the order Hemiptera. It is a true bug and sucks sap from plants. It is a widely distributed pest of a variety of agricultural crops in the families Cucurbitaceae, Rutaceae and Malvaceae. Common names include cotton aphid, melon aphid and melon and cotton aphid. Distribution It is not known where this species originated, but it is now found in tropical and temperate regions throughout the world except extreme northern areas. It is common in North and South America, Central Asia, Africa, Australia, Brazil, East Indies, Mexico and Hawaii and in most of Europe. It is cosmopolitan in habitat. It thrives outdoors in southern Europe but survives only under glass in northern Europe. In the former Soviet Union it is found up to 54°N. Morphology The wingless female cotton aphid has an ovoid body about two millimetres long in varying shades of green. The legs are yellow, as are the antennae whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phloem
Phloem (, ) is the living biological tissue, tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis and known as ''photosynthates'', in particular the sugar sucrose, to the rest of the plant. This transport process is called translocation. In trees, the phloem is the innermost layer of the bark (botany), bark, hence the name, derived from the Ancient Greek word (''phloiós''), meaning "bark". The term was introduced by Carl Nägeli in 1858. Structure Phloem tissue consists of conducting Cell (biology), cells, generally called sieve elements, Ground tissue#Parenchyma, parenchyma cells, including both specialized companion cells or albuminous cells and unspecialized cells and supportive cells, such as fibres and sclereids. Conducting cells (sieve elements) Sieve elements are the type of cell that are responsible for transporting sugars throughout the plant. At maturity they lack a Cell nucleus, nucleus and have very few organelles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Citrus Aphid 5194050
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model used to project colors onto television screens and computer monitors, brown combines red and green. The color brown is seen widely in nature, wood, soil, human hair color, eye color and skin pigmentation. Brown is the color of dark wood or rich soil. According to public opinion surveys in Europe and the United States, brown is the least favorite color of the public; it is often associated with plainness, the rustic, feces, and poverty. More positive associations include baking, warmth, wildlife, and the autumn. Etymology The term is from Old English , in origin for any dusky or dark shade of color. The first recorded use of ''brown'' as a color name in English was in 1000. The Common Germanic adjectives ''*brûnoz and *brûnâ'' meant b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican Lime
The Key lime or acid lime (''Citrus'' × ''aurantiifolia'' or ''C. aurantifolia'') is a citrus hybrid ('' C. hystrix'' × '' C. medica'') native to tropical Southeast Asia. It has a spherical fruit, in diameter. The Key lime is usually picked while it is still green, but it becomes yellow when ripe. The Key lime is smaller, seedier, has higher acidity, stronger aroma, and thinner rind than the Persian lime (''Citrus × latifolia''). It is valued for its characteristic flavor. The name comes from its association with the Florida Keys, where it is best known as the flavoring ingredient in Key lime pie. It is also known as West Indian lime, bartender's lime, Omani lime, or Mexican lime, the last classified as a distinct race with a thicker skin and darker green colour. Philippine varieties have various names, including ''dayap'' and ''bilolo''. Etymology The English word ''lime'' was derived, via Spanish then French, from the Arabic word ''līma'', which is, in turn, a deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CTV Stem Pitting
CTV may refer to: Television * Connected TV, or Smart TV, a TV set with integrated internet North America and South America * CTV Television Network, a Canadian television network owned by Bell Media ** CTV 2, a secondary Canadian television network owned by Bell Media **CTV Atlantic, a system of four television stations in the Canadian Maritime provinces ** CTV Comedy Channel ** CTV Drama Channel ** CTVglobemedia, now owned by Canadian telecom giant Bell Canada as Bell Media ** CTV Life Channel ** CTV News ** CTV News Channel (Canadian TV channel) ** CTV Sci-Fi Channel * C TV, a Trinidad and Tobago broadcast television station * Citizens Television, an American public access network in Connecticut * CTV: The Comedy Network, former name of Comedy Central, an American television channel Asia * China Television, a Taiwanese television company, established 1968 ** CTV Main Channel ** CTV News Channel (Taiwan) ** CTV Classic * CTV (Japan) or Chūkyō Television Broadcastin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buntan
The pomelo ( ), ''Citrus maxima'', is the largest citrus fruit from the family Rutaceae and the principal ancestor of the grapefruit. It is a natural, non-hybrid, citrus fruit, native to Southeast Asia. Similar in taste to a sweet grapefruit, the pomelo is commonly consumed and used for festive occasions throughout Southeast Asia. As with the grapefruit, phytochemicals in the pomelo have the potential for drug interactions. Etymology and common names According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the etymology of the word "pomelo" is uncertain. It may be derived from Dutch ''pompelmoes''. Its botanical name, ''Citrus maxima'', means "the biggest citrus". In English, the word "pomelo" (also spelled pummelo, pumelo, pomello, pommelo) has become the more common name, although "pomelo" has historically been used for grapefruit. After introduction to Barbados by 'Captain Shaddock' of the East India Company (apparently Philip Chaddock, who visited the island in the late 1640s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amanatsu
or is a yellowish orange citrus hybrid fruit, a group of cultivars of ''Citrus natsudaidai'', which were discovered in 1740 in the Yamaguchi prefecture of Japan. Names ''Amanatsu'' means "sweet summer" in Japanese. In Japan, the fruit is known as , but also colloquially the ''amanatsu'', , , and . Description Natsumikan is about the size of grapefruit and oblate in shape. The fruit contains 12 segments and about 30 seeds. The rough textured fruit is easy to peel and is commonly eaten fresh. It is also used for wide variety of products ranging from marmalades to alcoholic beverages. Cultivation Natsumikan is grown commercially in Japan, notably in Yamaguchi, Kumamoto and Ehime prefecture. The city of Hagi is famous for its natsumikans, particularly when used in natsumikan juice and ice cream. Yamaguchi Prefecture takes such pride in their natsumikan industry that the typically white crash barriers of Japan were changed to a befitting orange. Genetics The natsumikan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CTV Leaf Chlorosis
CTV may refer to: Television * Connected TV, or Smart TV, a TV set with integrated internet North America and South America * CTV Television Network, a Canadian television network owned by Bell Media ** CTV 2, a secondary Canadian television network owned by Bell Media **CTV Atlantic, a system of four television stations in the Canadian Maritime provinces ** CTV Comedy Channel ** CTV Drama Channel ** CTVglobemedia, now owned by Canadian telecom giant Bell Canada as Bell Media ** CTV Life Channel ** CTV News ** CTV News Channel (Canadian TV channel) ** CTV Sci-Fi Channel * C TV, a Trinidad and Tobago broadcast television station * Citizens Television, an American public access network in Connecticut * CTV: The Comedy Network, former name of Comedy Central, an American television channel Asia * China Television, a Taiwanese television company, established 1968 ** CTV Main Channel ** CTV News Channel (Taiwan) ** CTV Classic * CTV (Japan) or Chūkyō Television Broadcastin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosids
The rosids are members of a large clade (monophyletic group) of flowering plants, containing about 70,000 species, more than a quarter of all angiosperms. The clade is divided into 16 to 20 orders, depending upon circumscription and classification. These orders, in turn, together comprise about 140 families. Fossil rosids are known from the Cretaceous period. Molecular clock estimates indicate that the rosids originated in the Aptian or Albian stages of the Cretaceous, between 125 and 99.6 million years ago. Today's forests are highly dominated by rosid species, which in turn helped with diversification in many other living lineages. Additionally, rosid herbs and shrubs are also a significant part of arctic/alpine, temperate floras, aquatics, desert plants, and parasites. Name The name is based upon the name "Rosidae", which had usually been understood to be a subclass. In 1967, Armen Takhtajan showed that the correct basis for the name "Rosidae" is a description of a group of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passiflora
''Passiflora'', known also as the passion flowers or passion vines, is a genus of about 550 species of flowering plants, the type genus of the family Passifloraceae. They are mostly tendril-bearing vines, with some being shrubs or trees. They can be woody or herbaceous. Passion flowers produce regular and usually showy flowers with a distinctive corona. There can be as many as eight coronal series, as in the case of ''P. xiikzodz''. The flower is pentamerous and ripens into an indehiscent fruit with numerous seeds. List of species Distribution ''Passiflora'' has a largely neotropic distribution, unlike other genera in the family Passifloraceae, which includes more Old World species (such as the genus ''Adenia''). The vast majority of ''Passiflora'' are found in Mexico, Central America, the United States and South America, although there are additional representatives in Southeast Asia and Oceania. New species continue to be identified: for example, '' P. xishuangbannaensis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_001.jpg)