|
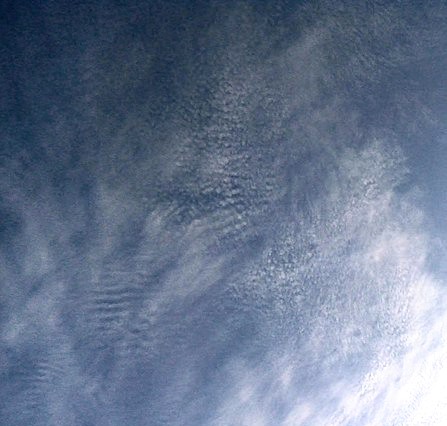
Cirrocumulus Cloud
Cirrocumulus is one of the three main genus-types of high-altitude tropospheric clouds, the other two being cirrus and cirrostratus. They usually occur at an altitude of . Like lower-altitude cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, cirrocumulus signifies convection. Unlike other high-altitude tropospheric clouds like cirrus and cirrostratus, cirrocumulus includes a small amount of liquid water droplets, although these are in a supercooled Supercooling, also known as undercooling, is the process of lowering the temperature of a liquid or a gas below its melting point without it becoming a solid. It achieves this in the absence of a seed crystal or nucleus around which a crystal ... state. Ice crystals are the predominant component, and typically, the ice crystals cause the supercooled water drops in the cloud to rapidly freeze, transforming the cirrocumulus into cirrostratus. This process can also produce precipitation in the form of a virga consisting of ice or snow. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virga
In meteorology, a virga, also called a dry storm, is an observable streak or shaft of precipitation falling from a cloud that evaporates or sublimates before reaching the ground. A shaft of precipitation that does not evaporate before reaching the ground is a precipitation shaft. At high altitudes the precipitation falls mainly as ice crystals before melting and finally evaporating; this is often due to compressional heating, because the air pressure increases closer to the ground. It is very common in deserts and temperate climates. In North America, it is commonly seen in the Western United States and the Canadian Prairies. It is also very common in the Middle East, Australia, and North Africa. Virgae can cause varying weather effects, because as rain is changed from liquid to vapor form, it removes significant amounts of heat from the air due to water's high heat of vaporization. Precipitation falling into these cooling downdrafts may eventually reach the ground. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
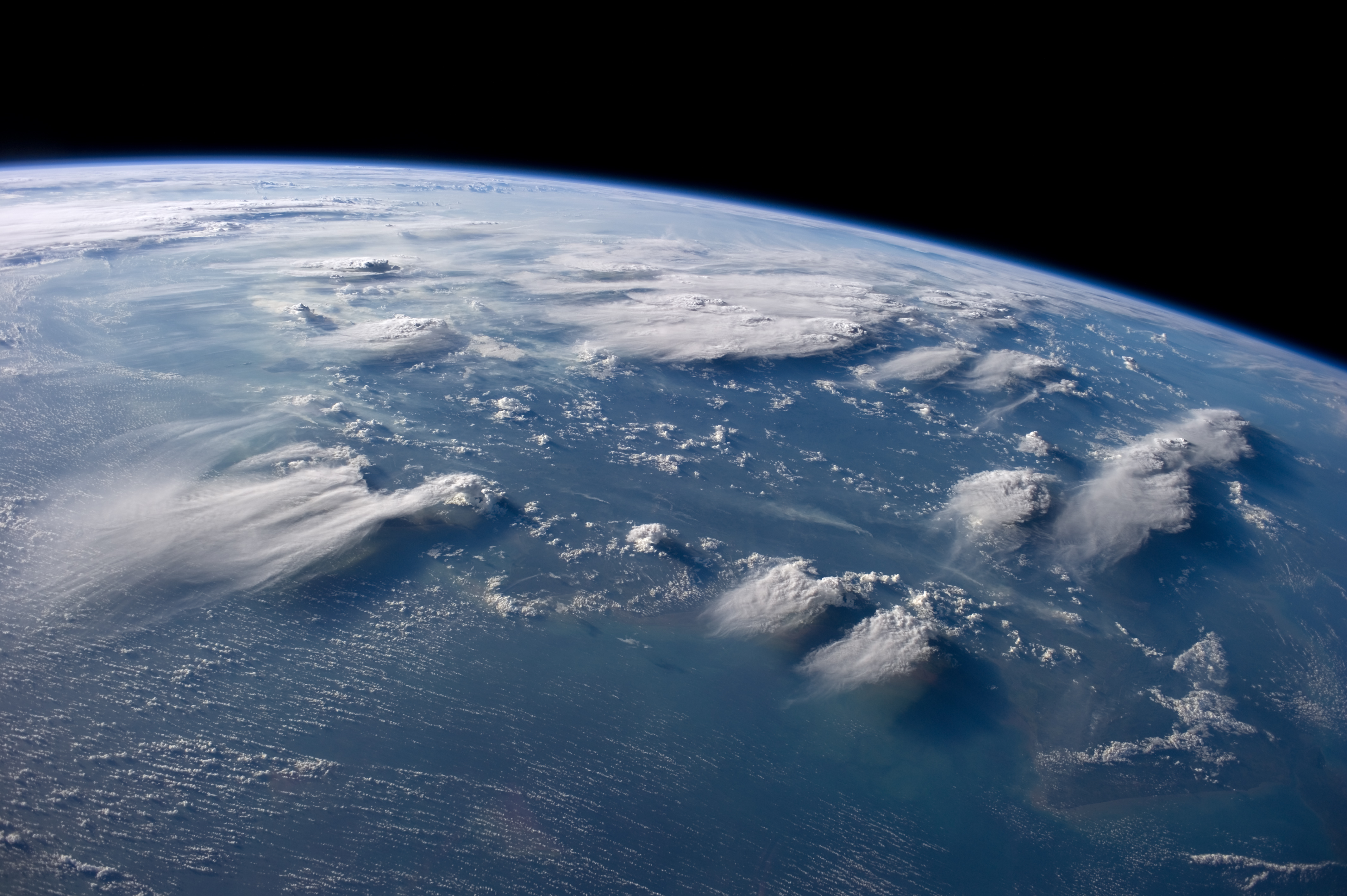
Cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may compose the droplets and crystals. On Earth, clouds are formed as a result of saturation of the air when it is cooled to its dew point, or when it gains sufficient moisture (usually in the form of water vapor) from an adjacent source to raise the dew point to the ambient temperature. They are seen in the Earth's homosphere, which includes the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere. Nephology is the science of clouds, which is undertaken in the cloud physics branch of meteorology. There are two methods of naming clouds in their respective layers of the homosphere, Latin and common name. Genus types in the troposphere, the atmospheric layer closest to Earth's surface, have Latin names because of the universal adoption of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
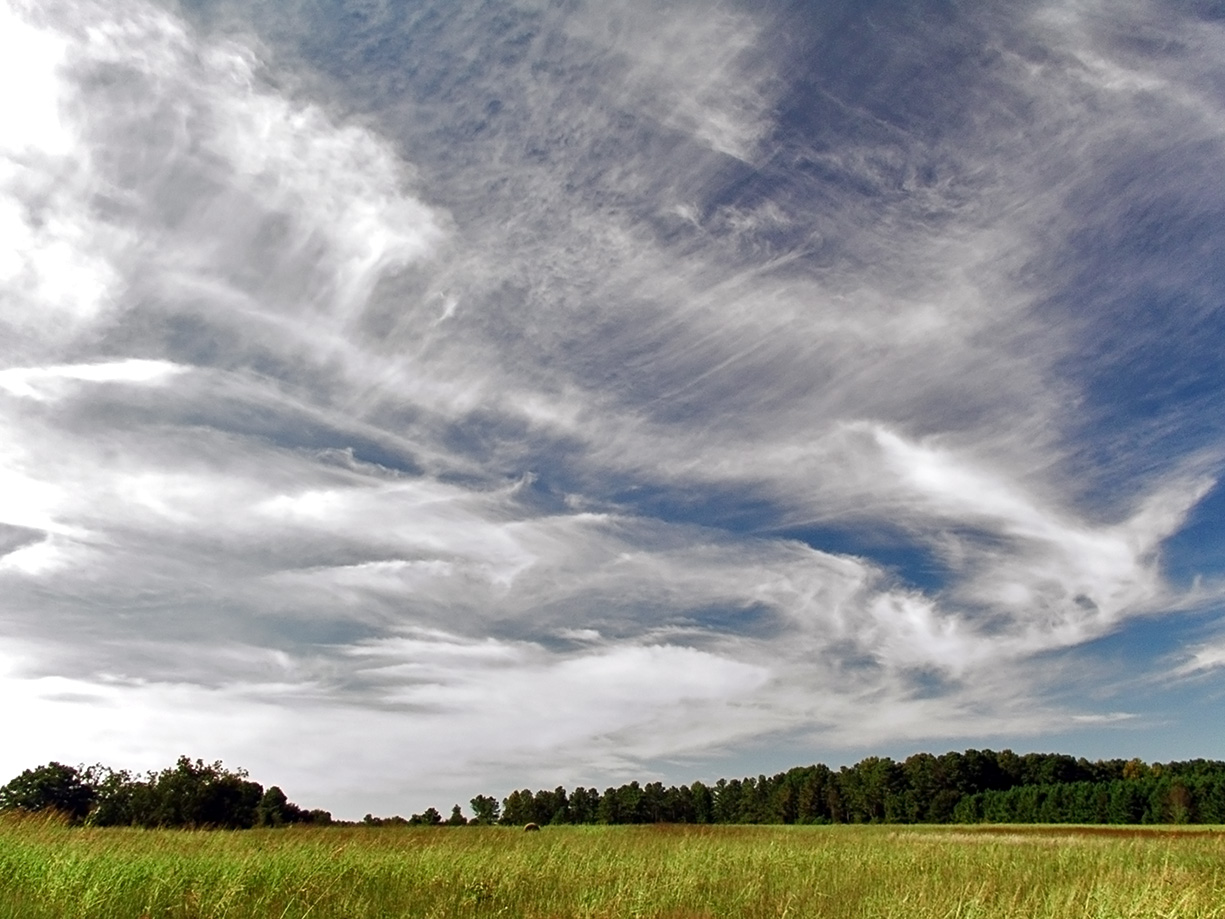
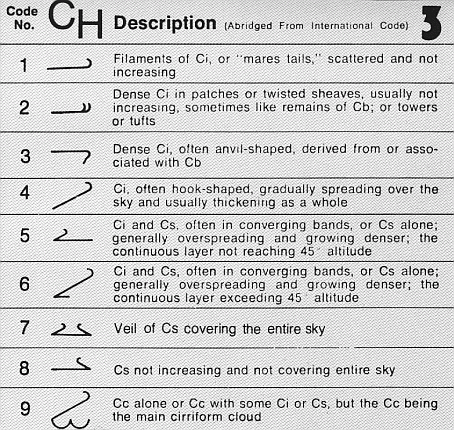
Cirrus Cloud
Cirrus ( cloud classification symbol: Ci) is a genus of high cloud made of ice crystals. Cirrus clouds typically appear delicate and wispy with white strands. Cirrus are usually formed when warm, dry air rises, causing water vapor deposition onto rocky or metallic dust particles at high altitudes. Globally, they form anywhere between above sea level, with the higher elevations usually in the tropics and the lower elevations in more polar regions. Cirrus clouds can form from the tops of thunderstorms and tropical cyclones and sometimes predict the arrival of rain or storms. Although they are a sign that rain and maybe storms are on the way, cirrus themselves drop no more than falling streaks of ice crystals. These crystals dissipate, melt, and evaporate as they fall through warmer and drier air and never reach ground. Cirrus clouds warm the earth, potentially contributing to climate change. A warming earth will likely produce more cirrus clouds, potentially resulting in a self ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrostratus Cloud
Cirrostratus is a high-level, very thin, generally uniform ''stratiform'' genus-type of cloud. It is made out of ice-crystals, which are pieces of frozen water. It is difficult to detect and it can make halos. These are made when the cloud takes the form of thin cirrostratus nebulosus. The cloud has a fibrous texture with no halos if it is thicker cirrostratus fibratus. On the approach of a frontal system, the cirrostratus often begins as nebulous and turns to fibratus. If the cirrostratus begins as fragmented of clouds in the sky it often means the front is weak. Cirrostratus is usually located above 5.5 km (18,000 ft). Its presence indicates a large amount of moisture in the upper troposphere. Clouds resembling cirrostratus occasionally form in polar regions of the lower stratosphere. Polar stratospheric clouds can take on this appearance when composed of tiny supercooled droplets of water or nitric acid. Cirrostratus clouds sometimes signal the approach of a warm fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Convection
Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air masses lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes. Overview There are a few general archetypes of atmospheric instability that are used to explain convection (or lack thereof). A necessary (but not sufficient) condition for convection is that the environmental lapse rate (the rate of decrease of temperature with height) is steeper than the lapse rate experienced by a rising parcel of air. When this condition is met, upward-displaced air parcels can become buoyant and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercooled
Supercooling, also known as undercooling, is the process of lowering the temperature of a liquid or a gas below its melting point without it becoming a solid. It achieves this in the absence of a seed crystal or nucleus around which a crystal structure can form. The supercooling of water can be achieved without any special techniques other than chemical demineralization, down to −48.3 °C (−55 °F). Droplets of supercooled water often exist in stratus and cumulus clouds. An aircraft flying through such a cloud sees an abrupt crystallization of these droplets, which can result in the formation of ice on the aircraft's wings or blockage of its instruments and probes. Animals utilize supercooling to survive in extreme temperatures. There are many mechanisms that aid in maintaining a liquid state, such as the production of antifreeze proteins, which bind to ice crystals to prevent water molecules from binding and spreading the growth of ice. The winter flounder is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mackerel Sky
A mackerel sky is a common term for clouds made up of rows of cirrocumulus or altocumulus clouds displaying an undulating, rippling pattern similar in appearance to fish scales; this is caused by high altitude atmospheric waves. Cirrocumulus appears almost exclusively with cirrus some way ahead of a warm front and is a reliable forecaster that the weather is about to change. When these high clouds progressively invade the sky and the barometric pressure begins to fall, precipitation associated with the disturbance is likely about 6 to 12 hours away. A thickening and lowering of cirrocumulus into middle-étage altostratus or altocumulus is a good sign that the warm front or low front has moved closer and it may start raining within less than six hours. The old rhymes "Mackerel sky, not twenty-four hours dry" and " Mares' tails and mackerel scales make lofty ships to carry low sails" both refer to this long-recognized phenomenon. Other phrases in weather lore take mackerel skies a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
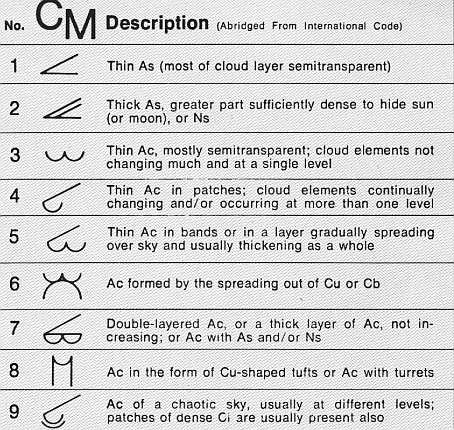
Altocumulus
Altocumulus (From Latin ''Altus'', "high", ''cumulus'', "heaped") is a middle-altitude cloud genus that belongs mainly to the ''stratocumuliform'' physical category characterized by globular masses or rolls in layers or patches, the individual elements being larger and darker than those of cirrocumulus and smaller than those of stratocumulus. However, if the layers become tufted in appearance due to increased airmass instability, then the altocumulus clouds become more purely ''cumuliform'' in structure. Like other cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, altocumulus signifies convection. A sheet of partially conjoined altocumulus perlucidus is sometimes found preceding a weakening warm front, where the altostratus is starting to fragment, resulting in patches of altocumulus perlucidus between the areas of altostratus. Altocumulus is also commonly found between the warm and cold fronts in a depression, although this is often hidden by lower clouds. Towering altocumulus, known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrocumulus Clouds July 2010
Cirrocumulus is one of the three main genus-types of high-altitude tropospheric clouds, the other two being cirrus and cirrostratus. They usually occur at an altitude of . Like lower-altitude cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, cirrocumulus signifies convection. Unlike other high-altitude tropospheric clouds like cirrus and cirrostratus, cirrocumulus includes a small amount of liquid water droplets, although these are in a supercooled state. Ice crystals are the predominant component, and typically, the ice crystals cause the supercooled water drops in the cloud to rapidly freeze, transforming the cirrocumulus into cirrostratus. This process can also produce precipitation in the form of a virga consisting of ice or snow. Thus, cirrocumulus clouds are usually short-lived., p.21 They usually only form as part of a short-lived transitional phase within an area of cirrus clouds and can also form briefly as a result of the breaking up of part of a cumulonimbus anvil. Properly, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrocumulus Stratiformis
Cirrocumulus stratiformis is a type of cirrocumulus cloud. The name ''cirrocumulus stratiformis'' is derived from Latin, meaning "stretched out". Cirrocumulus stratiformis occurs as very small cirrocumulus clouds that cover a large part of the sky. This type of cloud always occurs in thin layers. There can be spaces or rifts between the individual cloudlets in the layer. See also *List of cloud types The list of cloud types groups all genera as ''high'' (cirro-, cirrus), ''middle'' (alto-), ''multi-level'' (nimbo-, cumulo-, cumulus), and ''low'' (strato-, stratus). These groupings are determined by the altitude level or levels in the troposphe ... References External linksInternational Cloud Atlas – Cirrocumulus stratiformis Cirrus Cumulus {{Cloud-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrocumulus Lenticularis
Cirrocumulus lenticularis is a type of cirrocumulus cloud. The name ''cirrocumulus lenticularis'' is derived from Latin, meaning "like a lentil". Cirrocumulus lenticularis are smooth clouds that have the appearance of a lens or an almond. They usually form at the crests of atmospheric waves, which would otherwise be invisible. This species of cirrocumulus can often be quite elongated and normally has very distinguished boundaries. Cirrocumulus lenticularis forms when stable air is forced upward; this is usually due to orographic features, but can occur away from mountains as well. Irisation can occasionally occur with these clouds. See also * Altocumulus lenticularis * Stratocumulus lenticularis *List of cloud types The list of cloud types groups all genera as ''high'' (cirro-, cirrus), ''middle'' (alto-), ''multi-level'' (nimbo-, cumulo-, cumulus), and ''low'' (strato-, stratus). These groupings are determined by the altitude level or levels in the troposphe ... References E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |