|
Circuit Riding
In the United States, circuit riding was the practice of a judge, sometimes referred to as a circuit rider, traveling to a judicial district to preside over court cases there. A defining feature of American federal courts for over a century after the founding of the United States, circuit riding has since been mostly abolished. The term, however, lives on in the name " circuit court", a colloquialism commonly used to refer to the United States courts of appeals. History Shortly after the ratification of the United States Constitution in 1788, Congress passed the Judiciary Act of 1789, creating the U.S. circuit courts. These circuit courts did not have appointed judges; rather, two Supreme Court Justices and a local U.S. district court judge would preside over cases. This created the practice of circuit riding, wherein Supreme Court justices would travel to designated meeting places in their assigned circuit to hear cases. Circuit riding in the early United States was often an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Judicial Center
The Federal Judicial Center is the education and research agency of the United States federal courts. It was established by in 1967, at the recommendation of the Judicial Conference of the United States. According to , the main areas of responsibility for the center include: #conducting and promoting "research and study of the operation of the courts of the United States," and to act to encourage and coordinate the same by others; #developing "recommendations for improvement of the administration and management of .S.courts," and presenting these to the Judicial Conference of the U.S.; and # through all means available, see to conducting programs for the "continuing education and training for personnel" of the U.S. judiciary, for all employees in the justice system, from judges through probation officers and mediators. In addition to these major provisions, §620 (b)(4)(5)(6) sets forth the additional provisions that the FJC will (i) provide staff and assistance to the Jud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Britannica
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into article (publishing), articles or entries that are arranged Alphabetical order, alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionary, dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on ''factual information'' concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on Linguistics, linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammar, grammatical forms.Béjoint, Henri (2000)''Modern Lexicography'', pp. 30–31. Oxford University Press. Encyclopedias have existed for around 2,000 years and have evolved considerably during that time as regards language (written in a major inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
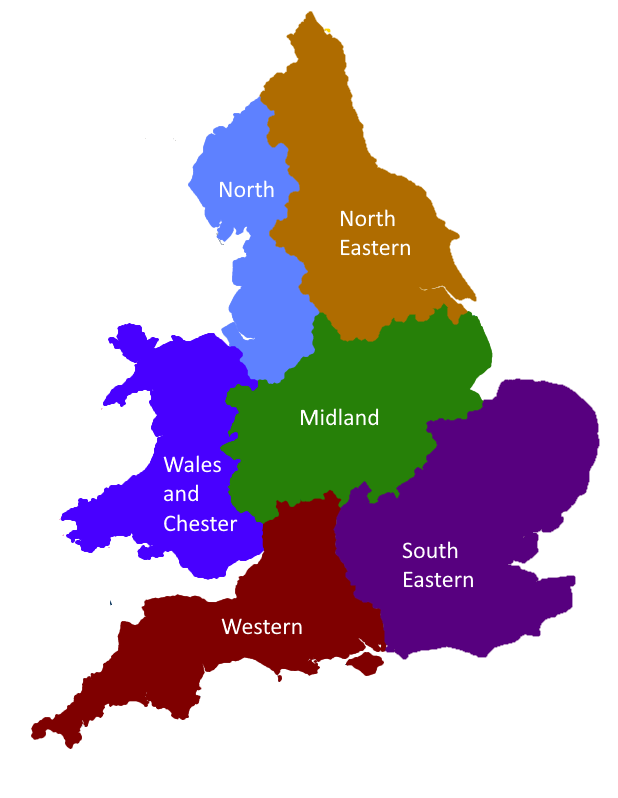
Circuit Court
Circuit courts are court systems in several common law jurisdictions. It may refer to: * Courts that literally sit 'on circuit', i.e., judges move around a region or country to different towns or cities where they will hear cases; * Courts that sit within a judicial circuit, i.e., an administrative division of a country's judiciary; or * A higher-level trial court, e.g., for felony or indictment offences. History Origin in England The term "circuit court" is derived from the English custom of itinerant courts whose judges periodically travelled on pre-set paths - or circuits - to hear cases from different areas. Establishment The first formal circuits were defined in 1293, when a statute was enacted which established four assize circuits. It was long assumed that these circuits originated with the eyre in common pleas during the reign of Henry II, but during the late 1950s, legal historians such as Ralph Pugh recognized that the eyre's "connection with later circuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
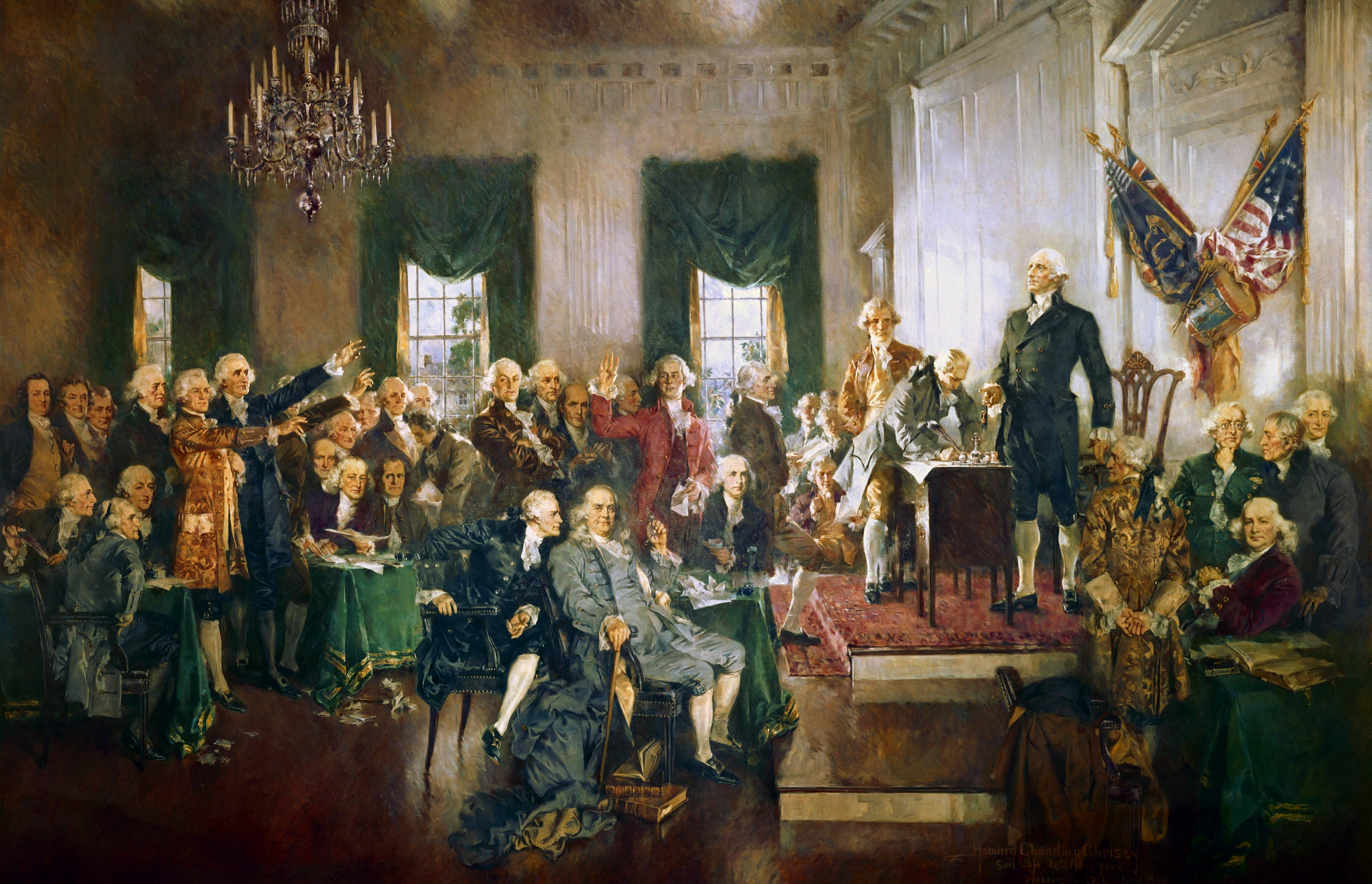
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, on March 4, 1789. Originally including seven articles, the Constitution delineates the frame of the Federal government of the United States, federal government. The Constitution's first three articles embody the doctrine of the separation of powers, in which the federal government is divided into three branches: the United States Congress, legislative, consisting of the bicameralism, bicameral Congress (Article One of the United States Constitution, Article I); the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive, consisting of the President of the United States, president and subordinate officers (Article Two of the United States Constitution, Article II); and the Federal judiciary of the United States, judicial, consisting of the Supreme Court of the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives, and an Upper house, upper body, the United States Senate, U.S. Senate. They both meet in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C. Members of Congress are chosen through direct election, though vacancies in the Senate may be filled by a Governor (United States), governor's appointment. Congress has a total of 535 voting members, a figure which includes 100 United States senators, senators and 435 List of current members of the United States House of Representatives, representatives; the House of Representatives has 6 additional Non-voting members of the United States House of Representatives, non-voting members. The vice president of the United States, as President of the Senate, has a vote in the Senate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judiciary Act Of 1789
The Judiciary Act of 1789 (ch. 20, ) was a United States federal statute enacted on September 24, 1789, during the first session of the First United States Congress. It established the federal judiciary of the United States. Article Three of the United States Constitution, Article III, Article Three of the United States Constitution#Section 1: Federal courts, Section 1 of the United States Constitution, Constitution prescribed that the "judicial power of the United States, shall be vested in one Supreme Court of the United States, Supreme Court, and such inferior Courts" as Congress saw fit to establish. It made no provision for the composition or procedures of any of the courts, leaving this to Congress to decide. The existence of a separate federal judiciary had been controversial during the debates over History of the United States Constitution#1788_ratification, the ratification of the Constitution. Anti-Administration Party (United States), Anti-Federalists had denounced th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Court Of The United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all Federal tribunals in the United States, U.S. federal court cases, and over State court (United States), state court cases that turn on questions of Constitution of the United States, U.S. constitutional or Law of the United States, federal law. It also has Original jurisdiction of the Supreme Court of the United States, original jurisdiction over a narrow range of cases, specifically "all Cases affecting Ambassadors, other public Ministers and Consuls, and those in which a State shall be Party." In 1803, the Court asserted itself the power of Judicial review in the United States, judicial review, the ability to invalidate a statute for violating a provision of the Constitution via the landmark case ''Marbury v. Madison''. It is also able to strike down presidential directives for violating either the Constitution or s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federalist Party
The Federalist Party was a conservativeMultiple sources: * * * * * * * * and nationalist American political party and the first political party in the United States. It dominated the national government under Alexander Hamilton from 1789 to 1801. The party was defeated by the Democratic-Republican Party in 1800, and it became a minority party while keeping its stronghold in New England. It made a brief resurgence by opposing the War of 1812, then collapsed with its last presidential candidate in 1816 United States presidential election, 1816. Remnants lasted for a few years afterwards. The party appealed to businesses who favored banks, national over state government, and manufacturing an army and navy. In world affairs, the party preferred Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and strongly opposed involvement in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. The party favored centralization, Early federalism in the United States, federalism, modernization, industriali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judiciary Act Of 1891
The Judiciary Act of 1891 (), also known as the Circuit Court of Appeals Act of 1891, or the Evarts Act after its primary sponsor, Senator William M. Evarts, created the United States courts of appeals and reassigned the jurisdiction of most routine appeals from the district and circuit courts to these appellate courts. Therefore, it is also called the Circuit Courts of Appeals Act. The Act created nine new courts that were originally known as the "United States circuit courts of appeals;" the name was changed to its current form in 1948. Each court was composed of two circuit judges and one district judge. The new courts had jurisdiction over most appeals of lower court decisions. The Supreme Court could review either legal issues that a court of appeals certified or decisions of court of appeals by writ of certiorari. The change resulted in an immediate reduction in the Supreme Court's workload (from 623 cases filed in 1890 to 379 in 1891 and 275 in 1892). The Act also eli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judicial Code Of 1911
The Judicial Code of 1911 () abolished the United States circuit courts and transferred their trial jurisdiction to the U.S. district courts. In 1911, the United States Congress created a single code encompassing all statutes related to the judiciary and took the opportunity to revise and unify existing laws. At the same time, Congress abolished the U.S. circuit courts as of January 1, 1912, the effective date of the statute. Established by the Judiciary Act of 1789, the circuit courts served as the most important trial courts of the federal judiciary for over a century. The circuit courts lost their limited appellate jurisdiction in the Judiciary Act of 1891, which created the United States courts of appeals, U.S. courts of appeals, but as part of the political compromise behind the 1891 Act, the circuit courts continued to serve as trial courts alongside the U.S. district courts, district courts for the next 20 years. By abolishing the circuit courts and transferring their juri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assizes
The assizes (), or courts of assize, were periodic courts held around England and Wales until 1972, when together with the quarter sessions they were abolished by the Courts Act 1971 and replaced by a single permanent Crown Court. The assizes exercised both Civil law (common law), civil and English criminal law, criminal jurisdiction, though most of their work was on the criminal side. The assizes heard the most serious cases, most notably those subject to capital punishment or, later, life imprisonment. Other serious cases were dealt with by the quarter sessions (local county courts held four times per year), while the more minor offences were dealt with summarily by justice of the peace, justices of the peace in petty sessions (also known as magistrates' court (England and Wales), magistrates' courts). The word ''assize'' refers to the sittings or sessions (Old French ''assises'') of the judges, known as "justices of assize", who were judges who travelled across the seven circu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |