|
Château De Calmont D'Olt
The Château de Calmont d'Olt is a castle situated in France, in the Aveyron ''département'' in the ''commune'' of Espalion. Perched atop a basalt dyke at an altitude of 535 m, it overlooks from 100 m the town of Espalion and the valley of the Lot. It provides a panoramic view of the Aubrac highlands. History Flint fragments and a polished stone axe are evidence of occupation of the site for 5,000 years. The ''ministerium Calvomantese'' was first mentioned in 883, in documents from the Abbey at Conques. It has always had a military significance, commanding the road from Rodez to Aubrac and, more widely, the crossing of the River Lot on the Toulouse-Lyon route. The building of the castle was begun in the 11th century built and continued until the Hundred Years' War with the building of a second curtain with eight towers in 1400. Beyond this date, there was no further development. Abandoned by its owners in the 16th century, the castle fell to ruin. The castle, in its present st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Château Calmont Dolt 01
A château (; plural: châteaux) is a manor house or residence of the lord of the manor, or a fine country house of nobility or gentry, with or without fortifications, originally, and still most frequently, in French-speaking regions. Nowadays a ''château'' may be any stately residence built in a French style; the term is additionally often used for a winegrower's estate, especially in the Bordeaux wine regions, Bordeaux region of France. Definition The word château is a French word that has entered the English language, where its meaning is more specific than it is in French. The French word ''château'' denotes buildings as diverse as a medieval fortress, a Renaissance palace and a fine 19th-century country house. Care should therefore be taken when translating the French word ''château'' into English, noting the nature of the building in question. Most French châteaux are "palaces" or fine "English country house, country houses" rather than "castles", and for these, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monument Historique
''Monument historique'' () is a designation given to some national heritage sites in France. It may also refer to the state procedure in France by which National Heritage protection is extended to a building, a specific part of a building, a collection of buildings, a garden, a bridge, or other structure, because of their importance to France's architectural and historical cultural heritage. Both public and privately owned structures may be listed in this way, as well as movable objects. As of 2012 there were 44,236 monuments listed. The term "classification" is reserved for designation performed by the French Ministry of Culture for a monument of national-level significance. Monuments of lesser significance may be "inscribed" by various regional entities. Buildings may be given the classification (or inscription) for either their exteriors or interiors. A monument's designation could be for a building's décor, its furniture, a single room, or even a staircase. An example is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fencing
Fencing is a group of three related combat sports. The three disciplines in modern fencing are the foil, the épée, and the sabre (also ''saber''); winning points are made through the weapon's contact with an opponent. A fourth discipline, singlestick, appeared in the 1904 Olympics but was dropped after that and is not a part of modern fencing. Fencing was one of the first sports to be played in the Olympics. Based on the traditional skills of swordsmanship, the modern sport arose at the end of the 19th century, with the Italian school having modified the historical European martial art of classical fencing, and the French school later refining the Italian system. There are three forms of modern fencing, each of which uses a different kind of weapon and has different rules; thus the sport itself is divided into three competitive scenes: foil, épée, and sabre. Most competitive fencers choose to specialize in one weapon only. Competitive fencing is one of the five activitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In modern times, it is mainly a competitive sport and recreational activity. A person who practices archery is typically called an archer, bowman, or toxophilite. History Origins and ancient archery The oldest known evidence of the bow and arrow comes from South African sites such as Sibudu Cave, where the remains of bone and stone arrowheads have been found dating approximately 72,000 to 60,000 years ago.Backwell L, d'Errico F, Wadley L.(2008). Middle Stone Age bone tools from the Howiesons Poort layers, Sibudu Cave, South Africa. Journal of Archaeological Science, 35:1566–1580. Backwell L, Bradfield J, Carlson KJ, Jashashvili T, Wadley L, d'Errico F.(2018). The antiquity of bow-and-arrow technology: evidence from Middle Stone Age layers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
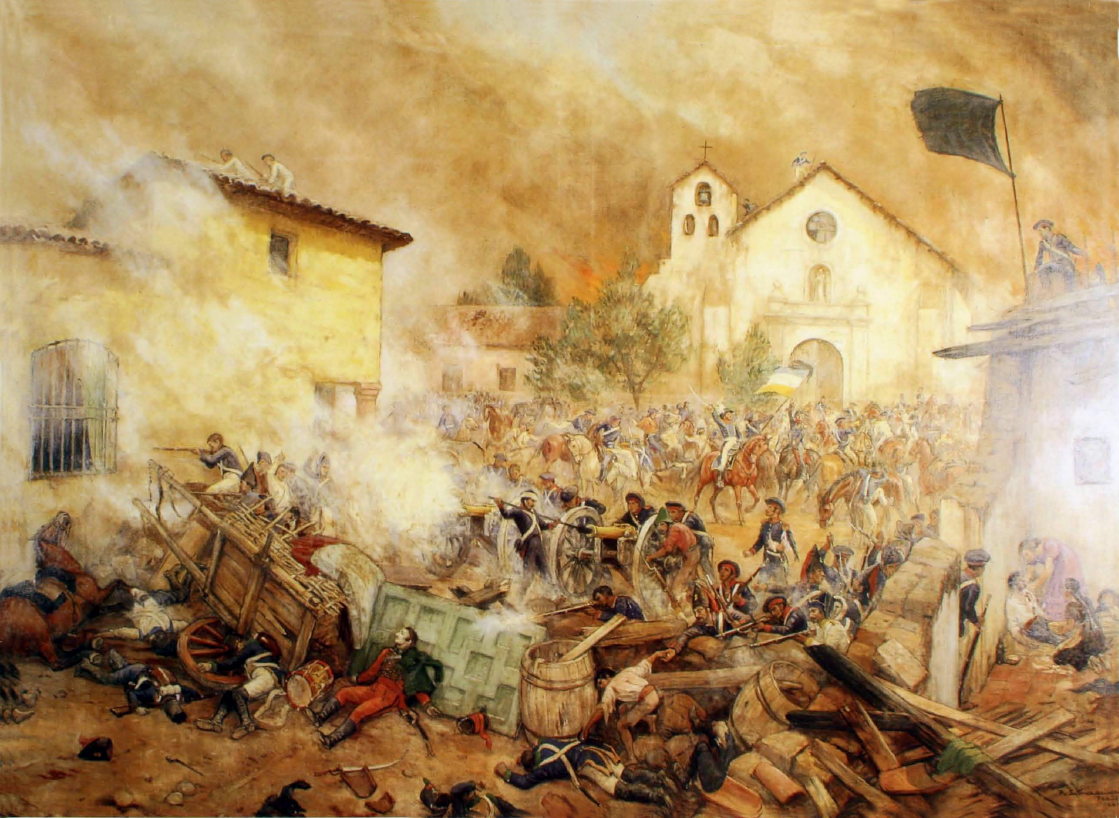
Siege Of Toulouse (1217–1218)
The siege of Toulouse occurred from 22 September 1217 to 25 July 1218 during the Albigensian Crusade. It was third of a series of sieges of the city during the height of Crusader efforts to put down Catharism (and the local Languedocian nobility). It ended in the repulsion of the Crusaders and the death of their leader, Simon IV de Montfort. Background In 1211 Simon IV de Montfort conducted his first siege of Toulouse, one that featured no siege engines is widely considered a tactical blunder and was ultimately unsuccessful. Two years later at the Battle of Muret much of Toulouse's military forces were defeated along with its Count Raymond VI, Count of Toulouse. Though Simon was practically the Count of Toulouse by 1214, it was not Pope Innocent III's decision following the Fourth Council of the Lateran in November 1215 that it was made official. Simultaneously Raymond VI and his son, Raymond VII, began to plot a double pronged invasion into Languedoc to take their territo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrus De Eboli
Peter of Eboli or Petrus de EbuloIn current medieval Latin; more correctly ''Petrus Eburensis''. (flourished ) was a didactic versifier and chronicler who wrote in Latin. A monk from Eboli (Campania, then part of the Kingdom of Naples), Peter became a court poet to Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor and King of Sicily. His flattering verse ''Liber ad honorem Augusti, sive de rebus Siculis'' (''Book to honor the Emperor, or The Affairs of Sicily''), probably written in Palermo, was his first work; it was dedicated to Henry VI, King of Sicily by right of his wife Constance, the Norman heiress and mother of the heir who would be "in every way blessed" according to Peter— Frederick II, ''stupor mundi''— whose birth is described in terms reshaped from Virgil's fourth Eclogue, which Christians read as foretelling the coming of Christ. The book celebrates in glowing terms the victory of Henry over his opponent, the illegitimate usurper Tancred, who, though a doughty fighter, was of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
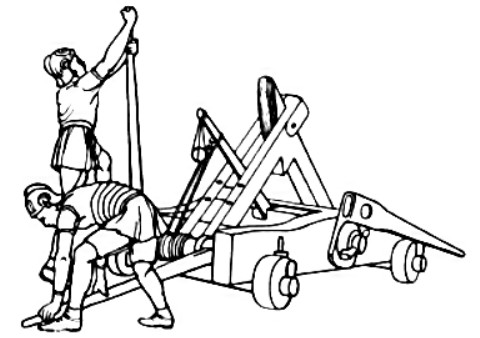
Pierrière
A trebuchet (french: trébuchet) is a type of catapult that uses a long arm to throw a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder. The design of a trebuchet allows it to launch projectiles of greater weights and further distances than that of a traditional catapult. There are two main types of trebuchet. The first is the traction trebuchet, or mangonel, which uses manpower to swing the arm. It first appeared in China in the 4th century BC. Carried westward by the Avars, the technology was adopted by the Byzantines in the late 6th century AD and by their neighbors in the following centuries. The later, and often larger and more powerful, counterweight trebuchet, also known as the counterpoise trebuchet, uses a counterweight to swing the arm. It appeared in both Christian and Muslim lands around the Mediterranean in the 12th century, and was carried back to China by the Mongols in the 13th century. Etymology and terminology It is uncert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trébuchet
A trebuchet (french: trébuchet) is a type of catapult that uses a long arm to throw a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder. The design of a trebuchet allows it to launch projectiles of greater weights and further distances than that of a traditional catapult. There are two main types of trebuchet. The first is the traction trebuchet, or mangonel, which uses manpower to swing the arm. It first appeared in China in the 4th century BC. Carried westward by the Pannonian Avars, Avars, the technology was adopted by the Byzantine Empire, Byzantines in the late 6th century AD and by their neighbors in the following centuries. The later, and often larger and more powerful, counterweight trebuchet, also known as the counterpoise trebuchet, uses a counterweight to swing the arm. It appeared in both Christian and Muslim lands around the Mediterranean in the 12th century, and was carried back to China by the Mongols in the 13th century. Etymolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trebuchet
A trebuchet (french: trébuchet) is a type of catapult that uses a long arm to throw a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder. The design of a trebuchet allows it to launch projectiles of greater weights and further distances than that of a traditional catapult. There are two main types of trebuchet. The first is the traction trebuchet, or mangonel, which uses manpower to swing the arm. It first appeared in China in the 4th century BC. Carried westward by the Avars, the technology was adopted by the Byzantines in the late 6th century AD and by their neighbors in the following centuries. The later, and often larger and more powerful, counterweight trebuchet, also known as the counterpoise trebuchet, uses a counterweight to swing the arm. It appeared in both Christian and Muslim lands around the Mediterranean in the 12th century, and was carried back to China by the Mongols in the 13th century. Etymology and terminology It is uncer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
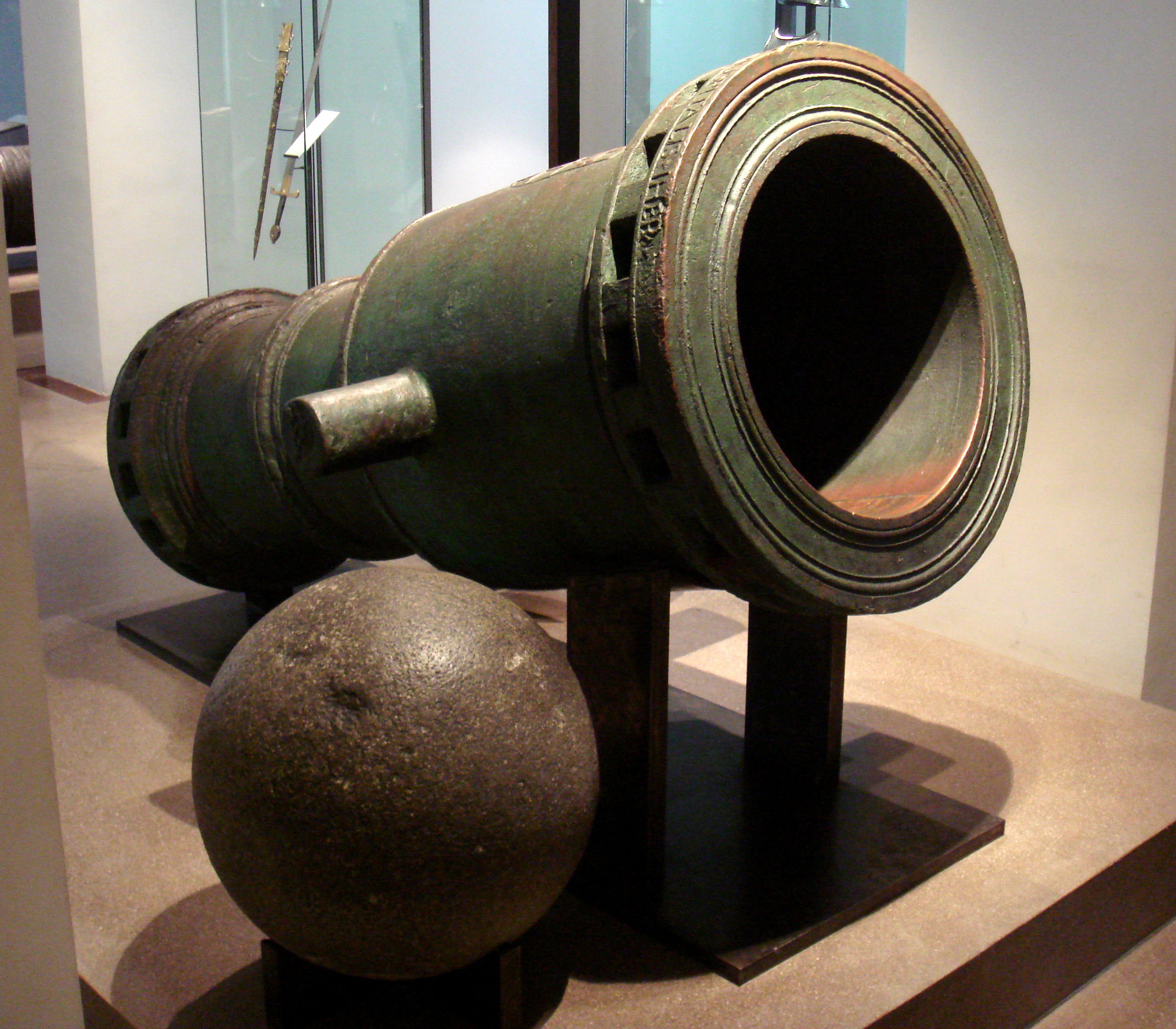
Bombard (weapon)
The bombard is a type of cannon or mortar which was used throughout the Middle Ages and the early modern period. Bombards were mainly large calibre, muzzle-loading artillery pieces used during sieges to shoot round stone projectiles at the walls of enemy fortifications, enabling troops to break in. Most bombards were made of iron and used gunpowder to launch the projectiles. There are many examples of bombards, including Mons Meg, the Dardanelles Gun, and the handheld bombard. The weapon provided the name to the Royal Artillery rank of bombardier and the word bombardment. Terminology The term "bombard" was first used to describe guns of any kind from the early to mid-14th century, but it was later applied primarily to large cannons during the 14th to 15th centuries. Despite its strong association with large cannons, there is no standard size for bombards, and the term has been applied to cannons only a meter in length as well as cannons several meters long weighing up to 20 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege engine, constructed to protect assailants and ladders while approaching the defensive walls of a fortification. The tower was often rectangular with four wheels with its height roughly equal to that of the wall or sometimes higher to allow archers to stand on top of the tower and shoot arrows into the fortification. Because the towers were wooden and thus flammable, they had to have some non-flammable covering of iron or fresh animal skins. Used since the 11th century BC by the Babylonians and Assyrians in the ancient Near East, the 4th century BC in Europe and also in antiquity in the Far East, siege towers were of unwieldy dimensions and, like trebuchets, were therefore mostly constructed on site of the siege. Taking considerable time t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition warfare, attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. The art of conducting and resisting sieges is called siege warfare, siegecraft, or poliorcetics. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to Surrender (military), surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block the provision of supplies and the reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as "Investment (military), investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |