|
Church Of St. George Of Samatya
Saint George of Samatya or Surp Kevork (Armenian language, Armenian: ''Սամաթիոյ Սուրբ Գէորգ Եկեղեցի''; Turkish language, Turkish name: ''Sulu Manastır'', meaning: "Water Monastery") is an Armenian Apostolic Church, Armenian church in Istanbul, Turkey. The edifice, built between 1866 and 1887, has been erected above the substructure of a Byzantine church and monastery built in the eleventh century. The complex, dedicated to St. Mary Peribleptos ( el, , ''Monì tis Theotókou tis Perivléptou'') was one of the most important Greek Orthodox Church, Greek Orthodox monasteries in Constantinople.Janin (1953), p. 227. After the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Conquest of Constantinople, conquest of the city in 1453 it was ceded to the Armenian People, Armenian community in Istanbul, and became for a period the seat of the Armenian Patriarch of Constantinople, Armenian Patriarchate of Constantinople.Müller-Wiener (1977) pg. 200 Location The church is located in Istanbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
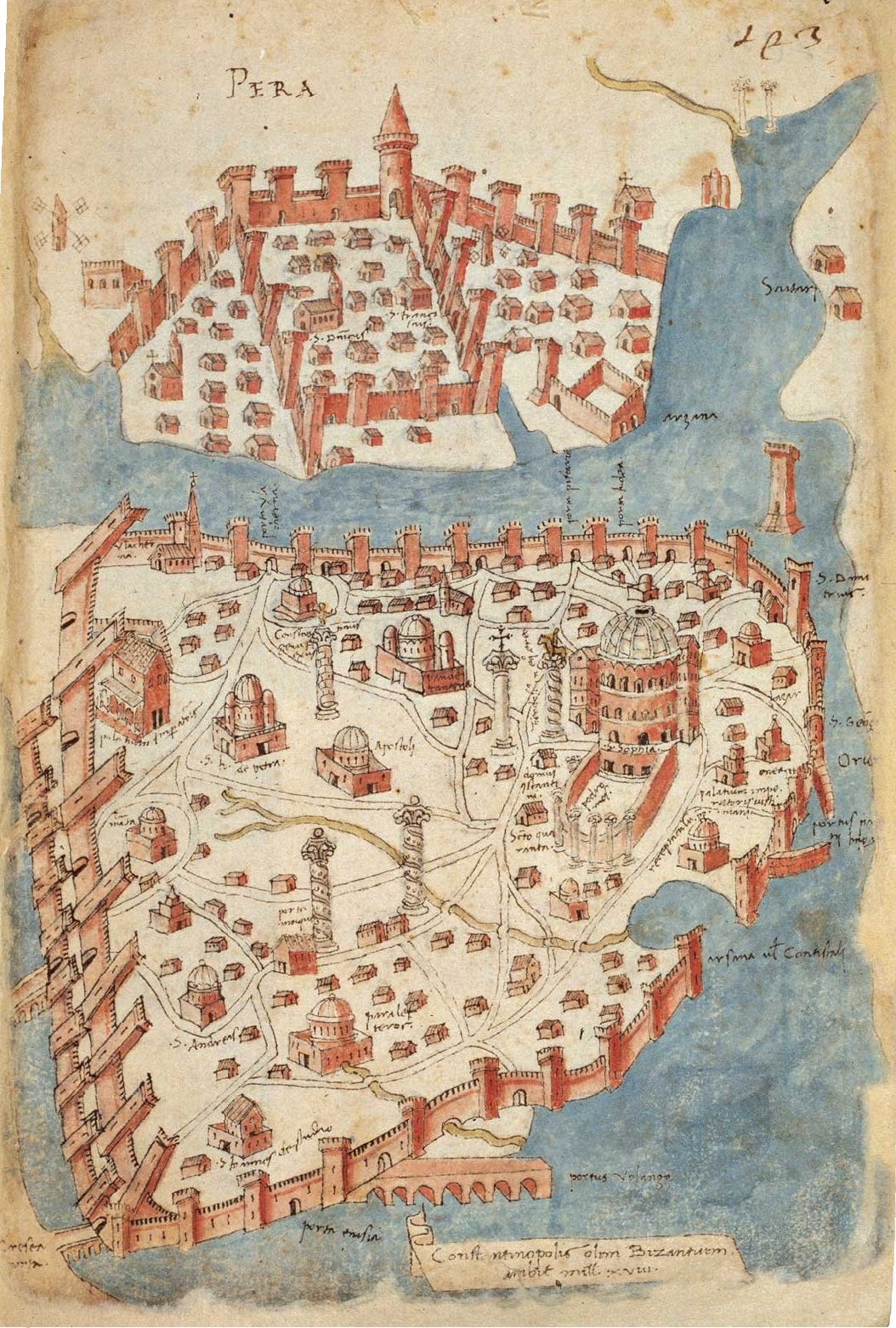
Samatya
Samatya ( el, Ψαμάθεια, pr. ''Psamatheia''; hy, Սամաթիա) is a quarter of the Fatih district of Istanbul. It is located along the Marmara Sea, and borders to the west on the neighborhood of Yedikule (the "Castle of the Seven Towers"). Etymology The name originates from the Greek word ''psamathion'' (), meaning "sandy", because of the great quantity of sand found in the quarter. History About 383 AD, the first monastic institution was established in Constantinople, at Psamatheia, at that time still outside the walled city.Tsai, Kathryn (Dr). ''A Timeline of Eastern Church History''. Divine Ascent Press, CA, 2004. p.73. Up to recent times, Samatya was mostly inhabited by Armenians, who were settled here in 1458 by Sultan Mehmet II,Müller-Wiener (1977), p. 200 and who own there the church of '' Surp Kevork'', also called ''Sulu Manastiri'' (Water's monastery) – previously an Eastern Orthodox church which dates back to before the Ottoman conquest, and by Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalmatius Of Constantinople
Saint Dalmatius, Dalmatus, or Dalmatos ( grc-gre, Δαλμάτος; died AD 440) was archimandrite of the Dalmatian Monastery in Constantinople. He also held the title ''Archimandrite of the Monasteries'', making him the city's chief monk. Dalmatius served in the second company of Guards under Theodosius the Great. He was married with a family. Experiencing a call to monastic life, he received instruction from Isaac of Dalmatia. Like most of the city's monks, he was an opponent of the Nestorian heresy, and he played an important role in the downfall of Nestorius. Following Cyril of Alexandria's instructions, Dalmatius led an army of monks to the palace of Theodosius II, and shouted abuse against him, because he had sided with the Nestorians and annulled the First Council of Ephesus. Because this was the first time Dalmatius had left his monastery in 48 years, the emperor was astonished to see the holy man abroad and granted his request to hear Cyril's case, which led ultimately to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodora Doukaina Vatatzina
Theodora Doukaina Komnene Palaiologina ( el, Θεοδώρα Δούκαινα Κομνηνή Παλαιολογίνα; – 4 March 1303), usually known simply as Theodora Palaiologina, was the Empress consort of the Byzantine emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos. Family Theodora Vatatzaina ( el, Θεοδώρα Βατάτζη) was a daughter of John Doukas (born 1215) and his wife Eudokia Angelina. Her paternal grandfather was ''sebastokrator'' Isaac Doukas Vatatzes (died 1261), the older brother of the Nicaean emperor John III Doukas Vatatzes (). Theodora's maternal grandfather was ''protostrator'' John Komnenos Angelos; his name indicates he was a member of the Angelos family, but his exact relations to the reigning members of the family are not known. Her grandmother's name is not known. Marriage Acropolites mentions that the father of Theodora died in young manhood. Her mother died in the early 1250s. Leaving Theodora to be raised by her great-uncle John III who was said to have "l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly popular in the Ancient Roman world. Mosaic today includes not just murals and pavements, but also artwork, hobby crafts, and industrial and construction forms. Mosaics have a long history, starting in Mesopotamia in the 3rd millennium BC. Pebble mosaics were made in Tiryns in Mycenean Greece; mosaics with patterns and pictures became widespread in classical times, both in Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome. Early Christian basilicas from the 4th century onwards were decorated with wall and ceiling mosaics. Mosaic art flourished in the Byzantine Empire from the 6th to the 15th centuries; that tradition was adopted by the Norman Kingdom of Sicily in the 12th century, by the eastern-influenced Republic of Venice, and among the Rus. Mosaic fell ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael VIII Palaiologos
Michael VIII Palaiologos or Palaeologus ( el, Μιχαὴλ Δούκας Ἄγγελος Κομνηνὸς Παλαιολόγος, Mikhaēl Doukas Angelos Komnēnos Palaiologos; 1224 – 11 December 1282) reigned as the co-emperor of the Empire of Nicaea from 1259 to 1261, and as Byzantine emperor from 1261 until his death in 1282. Michael VIII was the founder of the Palaiologan dynasty that would rule the Byzantine Empire until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453. He recovered Constantinople from the Latin Empire in 1261 and transformed the Empire of Nicaea into a restored Byzantine Empire. His reign saw considerable recovery of Byzantine power, including the enlargement of the Byzantine army and navy. It would also include the reconstruction of the city of Constantinople, and the increase of its population. Additionally, he re-established the University of Constantinople, which led to what is regarded as the Palaiologan Renaissance between the 13th and 15th centuries. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Empire
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzantine Empire as the Western-recognized Roman Empire in the east, with a Catholic emperor enthroned in place of the Eastern Orthodox Roman emperors. The Fourth Crusade had originally been called to retake the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem but a sequence of economic and political events culminated in the Crusader army sacking the city of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire. Originally, the plan had been to restore the deposed Byzantine Emperor Isaac II Angelos, who had been usurped by Alexios III Angelos, to the throne. The crusaders had been promised financial and military aid by Isaac's son Alexios IV, with which they had planned to continue to Jerusalem. When the crusaders reached Constantinople the situation quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benedictine
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG , caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal , abbreviation = OSB , formation = , motto = (English: 'Pray and Work') , founder = Benedict of Nursia , founding_location = Subiaco Abbey , type = Catholic religious order , headquarters = Sant'Anselmo all'Aventino , num_members = 6,802 (3,419 priests) as of 2020 , leader_title = Abbot Primate , leader_name = Gregory Polan, OSB , main_organ = Benedictine Confederation , parent_organization = Catholic Church , website = The Benedictines, officially the Order of Saint Benedict ( la, Ordo Sancti Benedicti, abbreviated as OSB), are a monastic religious order of the Catholic Church following the Rule of Saint Benedict. They are also sometimes called the Black Monks, in reference to the colour of their religious habits. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, links=no), was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic in parts of present-day Italy (mainly Northern Italy, northeastern Italy) that existed for 1100 years from AD 697 until AD 1797. Centered on the Venetian Lagoon, lagoon communities of the prosperous city of Venice, it incorporated numerous Stato da Màr, overseas possessions in modern Croatia, Slovenia, Montenegro, Greece, Albania and Cyprus. The republic grew into a Economic history of Venice, trading power during the Middle Ages and strengthened this position during the Renaissance. Citizens spoke the still-surviving Venetian language, although publishing in (Florentine) Italian became the norm during the Renaissance. In its early years, it prospered on the salt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid Sultanate, the strongest Muslim state of the time. However, a sequence of economic and political events culminated in the Crusader army's 1202 siege of Zara and the 1204 sack of Constantinople, the capital of the Greek Christian-controlled Byzantine Empire, rather than Egypt as originally planned. This led to the partitioning of the Byzantine Empire by the Crusaders. The Republic of Venice contracted with the Crusader leaders to build a dedicated fleet to transport their invasion force. However, the leaders greatly overestimated the number of soldiers who would embark from Venice, since many sailed from other ports, and the army that appeared could not pay the contracted price. In lieu of payment, the Venetian Doge Enrico Dandolo proposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candlemas
Candlemas (also spelled Candlemass), also known as the Feast of the Presentation of Jesus Christ, the Feast of the Purification of the Blessed Virgin Mary, or the Feast of the Holy Encounter, is a Christian holiday commemorating the presentation of Jesus at the Temple. It is based upon the account of the presentation of Jesus in Luke 2:22–40. In accordance with Leviticus 12, a woman was to be purified by presenting a lamb as a burnt offering, and either a young pigeon or dove as sin offering, 33 days after a boy's circumcision. It falls on 2 February, which is traditionally the 40th day (postpartum period) of and the conclusion of the Christmas–Epiphany season. While it is customary for Christians in some countries to remove their Christmas decorations on Twelfth Night (Epiphany Eve), those in other Christian countries historically remove them after Candlemas. On Candlemas, many Christians (especially Eastern Orthodox, Roman Catholics, Lutherans, Anglicans and Methodists) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexios I Komnenos
Alexios I Komnenos ( grc-gre, Ἀλέξιος Κομνηνός, 1057 – 15 August 1118; Latinized Alexius I Comnenus) was Byzantine emperor from 1081 to 1118. Although he was not the first emperor of the Komnenian dynasty, it was during his reign that the Komnenos family came to full power and initiated a hereditary succession to the throne. Inheriting a collapsing empire and faced with constant warfare during his reign against both the Seljuq Turks in Asia Minor and the Normans in the western Balkans, Alexios was able to curb the Byzantine decline and begin the military, financial, and territorial recovery known as the Komnenian restoration. His appeals to Western Europe for help against the Turks was the catalyst that sparked the First Crusade. Biography Alexios was the son of John Komnenos and Anna Dalassene,Kazhdan 1991, p. 63 and the nephew of Isaac I Komnenos (emperor 1057–1059). Alexios' father declined the throne on the abdication of Isaac, who was thu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros III Botaneiates
Nikephoros III Botaneiates, Latinized as Nicephorus III Botaniates ( el, Νικηφόρος Βοτανειάτης, 1002–1081), was Byzantine emperor from 7 January 1078 to 1 April 1081. He was born in 1002, and became a general during the reign of Byzantine Emperor Constantine IX Monomachos, serving in the Pecheneg revolt of 1048–1053. His actions in guiding his forces away from the Pechenegs following the Battle of Zygos Pass, in which they suffered eleven days of harassment before finally reaching the Byzantine city of Adrianople, attracted the attention of fellow officers, and he received the title of ''magistros'' as a reward. Nikephoros served in the revolt of Isaac I Komnenos against the Byzantine Emperor Michael VI Bringas, leading forces at the decisive Battle of Petroe. Under the Emperor Constantine X Doukas he was made '' doux'' of Thessalonica, where he remained until 1065, when he was reassigned as ''doux'' of Antioch. While ''doux'' of Antioch, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |