|
Chua K'a
Chua K'a is a three-part bodywork approach developed by Oscar Ichazo. It is based on the observation that tension in the body corresponds to specific fears; therefore, removing the tension via bodywork can remove the psychological trauma, a concept similar to other Mind–body_interventions. History Chua K'a Bodywork was first introduced by Oscar Ichazo to a group of Chilean students and then to a group of Americans in Arica, Chile in the 1960s. In teaching the method, Ichazo referred to an old legend about Mongolian warriors, who were said to have a way of removing pain and tension from their bodies that enabled them to return to battle without fear. The same perspective would apply to Chua K'a in that the pain of tension and the accompanying psychic fear would be eliminated, allowing the individual to be able to approach and live life without the limitations of these physical and mental distractions. There is no documentation or reference to Chua K'a that predates Ichazo. Purpose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodywork (alternative Medicine)
In alternative medicine, bodywork is any therapeutic or personal development technique that involves working with the human body in a form involving manipulative therapy, breath work, or energy medicine. Bodywork techniques also aim to assess or improve posture, promote awareness of the " bodymind connection" which is an approach that sees the human body and mind as a single integrated unit, or to manipulate the electromagnetic field alleged to surround the human body and affect health. Forms Some of the best known forms of non-touch bodywork methods include: reiki, yoga, pranayama, as well as other non-touch methods: breathwork respiration techniques, therapeutic touch, the Bates method for sight training, qigong, and t'ai chi. The better known forms of manipulative bodywork include the Bowen technique, chiropractic, reflexology, Rolfing, postural integration, shiatsu, and the Trager approach. There are also some methods that use light touch (not tissue work) to retra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscar Ichazo
Oscar Ichazo (July 24, 1931 in Bolivia – March 26, 2020 in Kihei, Hawaii, USA) was a Bolivian and American philosopher and the originator of Integral Philosophy. In 1968, Ichazo founded the Arica School in Chile. An American headquarters was later established in New York. Arica School The Arica School, also known as the Arica Institute (which is its incorporated educational organization) or simply as Arica, is a Human Potential Movement group founded by Ichazo in 1968. The school is named after the city of Arica, Chile, where Ichazo once lived and where he led an intensive months-long training in 1970 and 1971 before settling in the United States where the Arica Institute (incorporated in 1971) has since been headquartered. The Arica School can be considered, as '' Ramparts'' magazine put it in 1973, "A body of techniques for cosmic consciousness-raising and an ideology to relate to the world in an awakened way." Origins The Arica School's origins began in 1956 when groups o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mind–body Interventions
Mind–body interventions (MBI) or mind-body training (MBT) are health and fitness interventions that are intended to work on a physical and mental level such as yoga, tai chi, and Pilates. The category was introduced in September 2000 by the United States National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH), a government agency, and encompasses alternative medicine interventions.US National Library of Medicine. National Institutes of Health Collection Development Manual. Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 8 October 2003Online Version.Retrieved 31 July 2015. It excludes scientifically validated practices such as cognitive behavioral therapy. Cochrane reviews have found that studies in this area are small and have low scientific validity. Since 2008, authors documenting research conducted on behalf of the NCCIH have used terms ''mind and body practices'' and ''mind-body medicine'' interchangeably with ''mind-body intervention'' to denote therapies, as well as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arica, Chile
Arica ( ; ) is a commune and a port city with a population of 222,619 in the Arica Province of northern Chile's Arica y Parinacota Region. It is Chile's northernmost city, being located only south of the border with Peru. The city is the capital of both the Arica Province and the Arica and Parinacota Region. Arica is located at the bend of South America's western coast known as the Arica Bend or Arica Elbow. At the location of the city are two valleys that dissect the Atacama Desert converge: Azapa and Lluta. These valleys provide citrus and olives for export. Arica is an important port for a large inland region of South America. The city serves a free port for Bolivia and manages a substantial part of that country's trade.In addition it is the end station of the Bolivian oil pipeline beginning in Oruro. The city's strategic position is enhanced by being next to the Pan-American Highway, being connected to both Tacna in Peru and La Paz in Bolivia by railroad and being serve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arica Institute
Oscar Ichazo (July 24, 1931 in Bolivia – March 26, 2020 in Kihei, Hawaii, USA) was a Bolivian and American philosopher and the originator of Integral Philosophy. In 1968, Ichazo founded the Arica School in Chile. An American headquarters was later established in New York. Arica School The Arica School, also known as the Arica Institute (which is its incorporated educational organization) or simply as Arica, is a Human Potential Movement group founded by Ichazo in 1968. The school is named after the city of Arica, Chile, where Ichazo once lived and where he led an intensive months-long training in 1970 and 1971 before settling in the United States where the Arica Institute (incorporated in 1971) has since been headquartered. The Arica School can be considered, as '' Ramparts'' magazine put it in 1973, "A body of techniques for cosmic consciousness-raising and an ideology to relate to the world in an awakened way." Origins The Arica School's origins began in 1956 when groups of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Tissues
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macrophages. The subcutaneous tissue is derived from the mesoderm, but unlike the dermis, it is not derived from the mesoderm's dermatome region. It consists primarily of loose connective tissue, and contains larger blood vessels and nerves than those found in the dermis. It is a major site of fat storage in the body. In arthropods, a hypodermis can refer to an epidermal layer of cells that secretes the chitinous cuticle. The term also refers to a layer of cells lying immediately below the epidermis of plants. Structure * Fibrous bands anchoring the skin to the deep fascia * Collagen and elastin fibers attaching it to the dermis * Fat is absent from the eyelids, clitoris, penis, much of pinna, and scrotum * Blood vessels on route to the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided into two layers, the superficial area adjacent to the epidermis called the papillary region and a deep thicker area known as the reticular dermis.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology'' (10th ed.). Saunders. Pages 1, 11–12. . The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis through a basement membrane. Structural components of the dermis are collagen, elastic fibers, and extrafibrillar matrix.Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). ''Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology'' (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. Page 8–9. . It also contains mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and thermoreceptors that provide the sense of heat. In addition, hair foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypodermis
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macrophages. The subcutaneous tissue is derived from the mesoderm, but unlike the dermis, it is not derived from the mesoderm's dermatome region. It consists primarily of loose connective tissue, and contains larger blood vessels and nerves than those found in the dermis. It is a major site of fat storage in the body. In arthropods, a hypodermis can refer to an epidermal layer of cells that secretes the chitinous cuticle. The term also refers to a layer of cells lying immediately below the epidermis of plants. Structure * Fibrous bands anchoring the skin to the deep fascia * Collagen and elastin fibers attaching it to the dermis * Fat is absent from the eyelids, clitoris, penis, much of pinna, and scrotum * Blood vessels on route to the der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascia
A fascia (; plural fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; from Latin: "band") is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches to, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organs. Fascia is classified by layer, as superficial fascia, deep fascia, and ''visceral'' or ''parietal'' fascia, or by its function and anatomical location. Like ligaments, aponeuroses, and tendons, fascia is made up of fibrous connective tissue containing closely packed bundles of collagen fibers oriented in a wavy pattern parallel to the direction of pull. Fascia is consequently flexible and able to resist great unidirectional tension forces until the wavy pattern of fibers has been straightened out by the pulling force. These collagen fibers are produced by fibroblasts located within the fascia. Fasciae are similar to ligaments and tendons as they have collagen as their major component. They differ in their location and function: ligam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
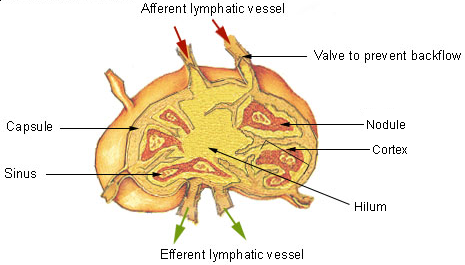
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph (the Latin word ''lympha'' refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha") back towards the heart, for re-circulation. Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system, the lymphatic system is open. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma from the blood. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered blood is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymphatic system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres. The other main function is that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dantian
Dantian, dan t'ian, dan tien or tan t'ien is loosely translated as "elixir field", "sea of qi", or simply "energy center". Dantian are the "qi focus flow centers", important focal points for meditative and exercise techniques such as qigong, martial arts such as t'ai chi ch'uan, and in traditional Chinese medicine. Overview Historically the first detailed description of the lower Dantian is in the '' Laozi zhongjing'' 老子中經 from the 3rd century CE, which refers to the elixir-of-life field where "essence" and "spirit" are stored; it is related to regeneration and sexual energy, menstruation and semen.Laozi zhongjing (Central Scripture of Laozi), sec. 17. Translation published in Fabrizio Pregadio, "Early Daoist Meditation and the Origins of Inner Alchemy," in Benjamin Penny, ed., Daoism in History: Essays in Honour of Liu Ts'un-yan, 139–40 (London: Routledge, 2006). http://www.goldenelixir.com/taoism/texts_laozi_zhongjing.html Traditionally, a dantian is considered to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karma
Karma (; sa, कर्म}, ; pi, kamma, italic=yes) in Sanskrit means an action, work, or deed, and its effect or consequences. In Indian religions, the term more specifically refers to a principle of cause and effect, often descriptively called the principle of karma, wherein intent and actions of an individual (cause) influence the future of that individual (effect): Good intent and good deeds contribute to good karma and happier rebirths, while bad intent and bad deeds contribute to bad karma and bad rebirths. As per some scripture, there is no link of rebirths with karma. The concept of karma is closely associated with the idea of rebirth in many schools of Indian religions (particularly Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikhism), as well as Taoism.Eva Wong, Taoism, Shambhala Publications, , pp. 193 In these schools, karma in the present affects one's future in the current life, as well as the nature and quality of future lives—one's '' saṃsāra''. This concept ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |