|
Chromothripsis The Result Of A Single Catastrophic Event In A Cells History
Chromothripsis is a mutational process by which up to thousands of clustered chromosomal rearrangements occur in a single event in localised and confined genomic regions in one or a few chromosomes, and is known to be involved in both cancer and congenital diseases. It occurs through one massive genomic rearrangement during a single catastrophic event in the cell's history. It is believed that for the cell to be able to withstand such a destructive event, the occurrence of such an event must be the upper limit of what a cell can tolerate and survive. The chromothripsis phenomenon opposes the conventional theory that cancer is the gradual acquisition of genomic rearrangements and somatic mutations over time. The simplest model as to how these rearrangements occur is through the simultaneous fragmentation of distinct chromosomal regions (breakpoints show a non-random distribution) and then subsequent imperfect reassembly by DNA repair, DNA repair pathways or aberrant DNA replication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromothripsis The Result Of A Single Catastrophic Event In A Cells History
Chromothripsis is a mutational process by which up to thousands of clustered chromosomal rearrangements occur in a single event in localised and confined genomic regions in one or a few chromosomes, and is known to be involved in both cancer and congenital diseases. It occurs through one massive genomic rearrangement during a single catastrophic event in the cell's history. It is believed that for the cell to be able to withstand such a destructive event, the occurrence of such an event must be the upper limit of what a cell can tolerate and survive. The chromothripsis phenomenon opposes the conventional theory that cancer is the gradual acquisition of genomic rearrangements and somatic mutations over time. The simplest model as to how these rearrangements occur is through the simultaneous fragmentation of distinct chromosomal regions (breakpoints show a non-random distribution) and then subsequent imperfect reassembly by DNA repair, DNA repair pathways or aberrant DNA replication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel movements, weight loss, and fatigue. Most colorectal cancers are due to old age and lifestyle factors, with only a small number of cases due to underlying genetic disorders. Risk factors include diet, obesity, smoking, and lack of physical activity. Dietary factors that increase the risk include red meat, processed meat, and alcohol. Another risk factor is inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Some of the inherited genetic disorders that can cause colorectal cancer include familial adenomatous polyposis and hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer; however, these represent less than 5% of cases. It typically starts as a benign tumor, often in the form of a polyp, which over time becomes cancerous. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
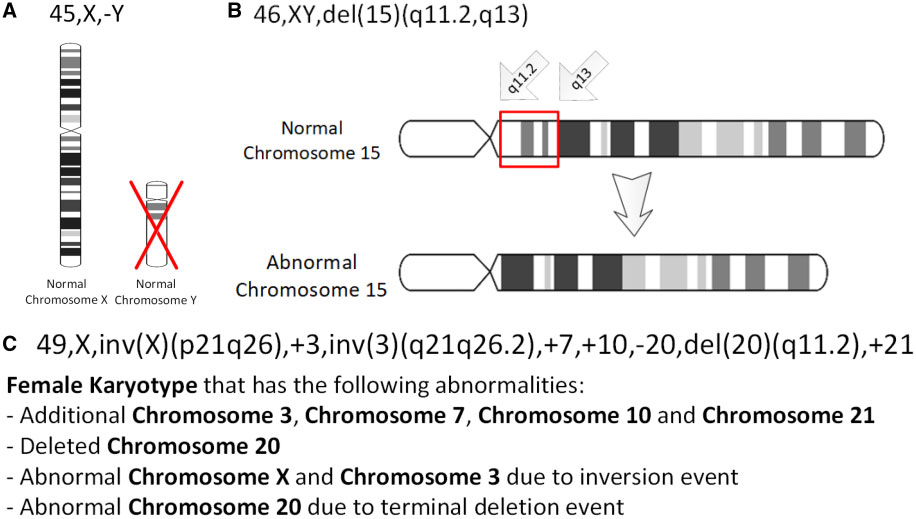
Deletion (genetics)
In genetics, a deletion (also called gene deletion, deficiency, or deletion mutation) (sign: Δ) is a mutation (a genetic aberration) in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is left out during DNA replication. Any number of nucleotides can be deleted, from a single base to an entire piece of chromosome. Some chromosomes have fragile spots where breaks occur which result in the deletion of a part of chromosome. The breaks can be induced by heat, viruses, radiations, chemicals. When a chromosome breaks, a part of it is deleted or lost, the missing piece of chromosome is referred to as deletion or a deficiency. For synapsis to occur between a chromosome with a large intercalary deficiency and a normal complete homolog, the unpaired region of the normal homolog must loop out of the linear structure into a deletion or compensation loop. The smallest single base deletion mutations occur by a single base flipping in the template DNA, followed by template DNA strand sli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
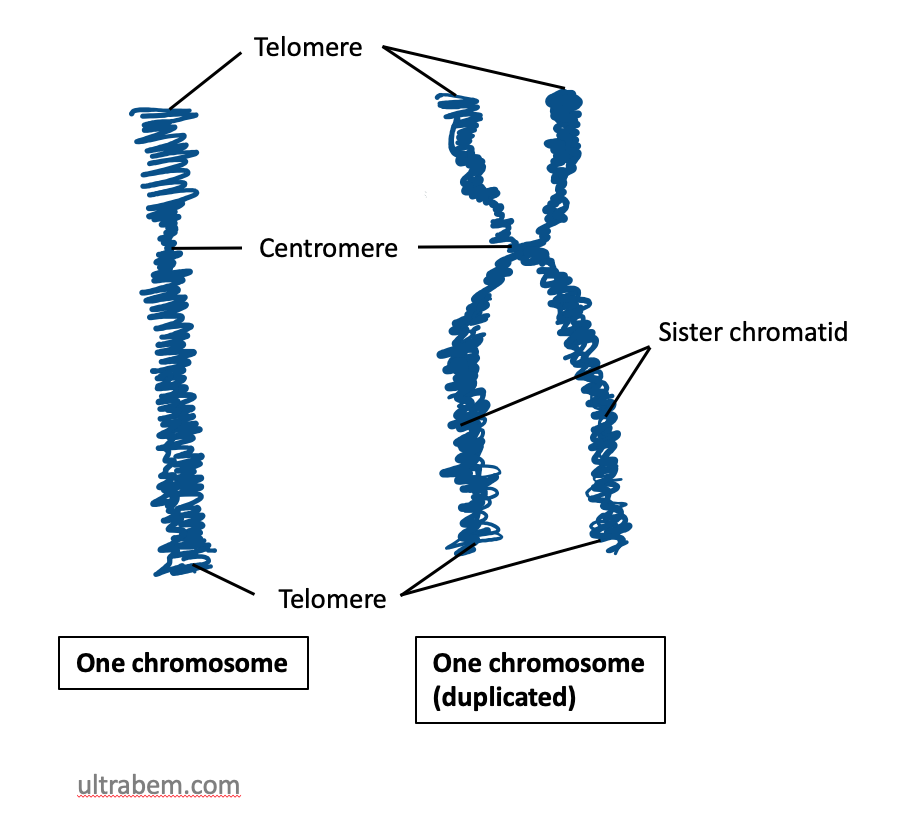
Chromosomal Region
Several chromosome regions have been defined by convenience in order to talk about gene loci. Most important is the distinction between chromosome region p and chromosome region q. The p region is represented in the shorter arm of the chromosome (p is for petit, French for small) while the q region is in the larger arm (chosen as next letter in alphabet after p). These are virtual regions that exist in all chromosomes. These are listed as follows: * Chromatids * Arms * Centromere * Kinetochore * Telomere * Sub telomere * satellite chromosome or trabant. * NOR region During cell division, the molecules that compose chromosomes ( DNA and proteins) suffer a condensation process (called the chromatin reticulum condensation) that forms a compact and small complex called a chromatid. The complexes containing the duplicated DNA molecules, the sister chromatids, are attached to each other by the centromere(where the Kinetochore assembles). If the chromosome is a submetacentric c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non Homologous End Joining And Microhomology Mediated End Joining
Non, non or NON can refer to: * ''Non'', a negatory word in French, Italian and Latin People *Non (given name) *Non Boonjumnong (born 1982), Thai amateur boxer * Rena Nōnen (born 1993), Japanese actress who uses the stage name "Non" since July 2016 * NON, a name used by musician Boyd Rice Other uses * ''Non'' (album), The Amenta * ''Non!'' (EP), Big Country * ''Non'' (book), a 2009 book by Japanese model Nozomi Sasaki * Non (comics), a villain of Superman in the DC Comics universe * non, language code for Old Norse * NON Records, an independent record label based in Amsterdam, Netherlands * Abbreviation of NATO's Allied Forces North Norway Command * "Non", a song by Phinehas from the album '' Till the End'' See also * nan (other) Nan or NAN may refer to: Places China * Nan County, Yiyang, Hunan, China * Nan Commandery, historical commandery in Hubei, China Thailand * Nan Province ** Nan, Thailand, the administrative capital of Nan Province * Nan River People ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterozygosity
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is nullizygous. The DNA sequence of a gene often varies from one individual to another. These gene variants are called alleles. While some gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
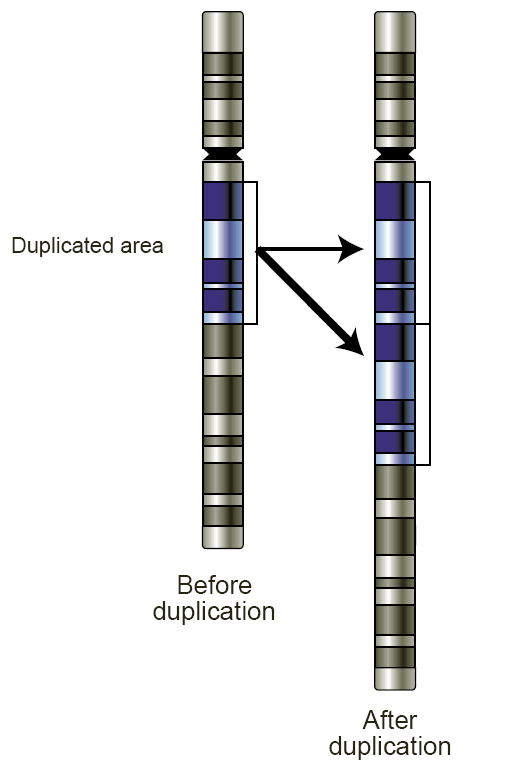
Copy-number Variation
Copy number variation (CNV) is a phenomenon in which sections of the genome are repeated and the number of repeats in the genome varies between individuals. Copy number variation is a type of structural variation: specifically, it is a type of Gene duplication, duplication or deletion (genetics), deletion event that affects a considerable number of base pairs. Approximately two-thirds of the entire human genome may be composed of repeats and 4.8–9.5% of the human genome can be classified as copy number variations. In mammals, copy number variations play an important role in generating necessary variation in the population as well as disease phenotype. Copy number variations can be generally categorized into two main groups: short repeats and long repeats. However, there are no clear boundaries between the two groups and the classification depends on the nature of the locus (genetics), loci of interest. Short repeats include mainly Tandem repeat, dinucleotide repeats (two repeat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Therefore, mitosis is also known as equational division. In general, mitosis is preceded by S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis; which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant cells), prophase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ewing Sarcoma
Ewing sarcoma is a type of cancer that forms in bone or soft tissue. Symptoms may include swelling and pain at the site of the tumor, fever, and a bone fracture. The most common areas where it begins are the legs, pelvis, and chest wall. In about 25% of cases, the cancer has already spread to other parts of the body at the time of diagnosis. Complications may include a pleural effusion or paraplegia. It is a type of small round cell sarcoma. The cause of Ewing sarcoma is unknown. Most cases appear to occur randomly. Sometimes there has been a germline mutation. The underlying mechanism often involves a genetic change known as a reciprocal translocation. Diagnosis is based on biopsy of the tumor. Treatment often includes chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, and stem cell transplant. Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are being studied. Five-year survival is about 70%. A number of factors, however, affect this estimate. James Ewing in 1920 established that the tumor is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondromyxoid Fibroma
Chondromyxoid fibroma is a rare type of cartilaginous tumor. Rarely occur in the skull or skull base. Most cases are characterised by GRM1 The glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1, also known as GRM1, is a human gene which encodes the metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGluR1) protein. Function L- glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system a ... gene fusion or promoter swapping. It can be associated with a translocation at t(1;5)(p13;p13). References External links Osseous and chondromatous neoplasia {{neoplasm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ependymoma
An ependymoma is a tumor that arises from the ependyma, a tissue of the central nervous system. Usually, in pediatric cases the location is intracranial, while in adults it is spinal. The common location of intracranial ependymomas is the fourth ventricle. Rarely, ependymomas can occur in the pelvic cavity. Syringomyelia can be caused by an ependymoma. Ependymomas are also seen with neurofibromatosis type II. Signs and symptoms Source: * severe headache * visual loss (due to papilledema) * vomiting * bilateral Babinski sign * drowsiness (after several hours of the above symptoms) * gait change (rotation of feet when walking) * impaction/constipation * back flexibility Morphology Ependymomas are composed of cells with regular, round to oval nuclei. There is a variably dense fibrillary background. Tumor cells may form gland-like round or elongated structures that resemble the embryologic ependymal canal, with long, delicate processes extending into the lumen; more frequently pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |