|
Christian Walls Of Madrid
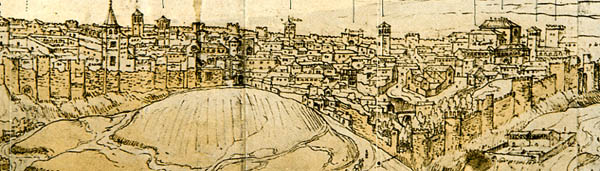
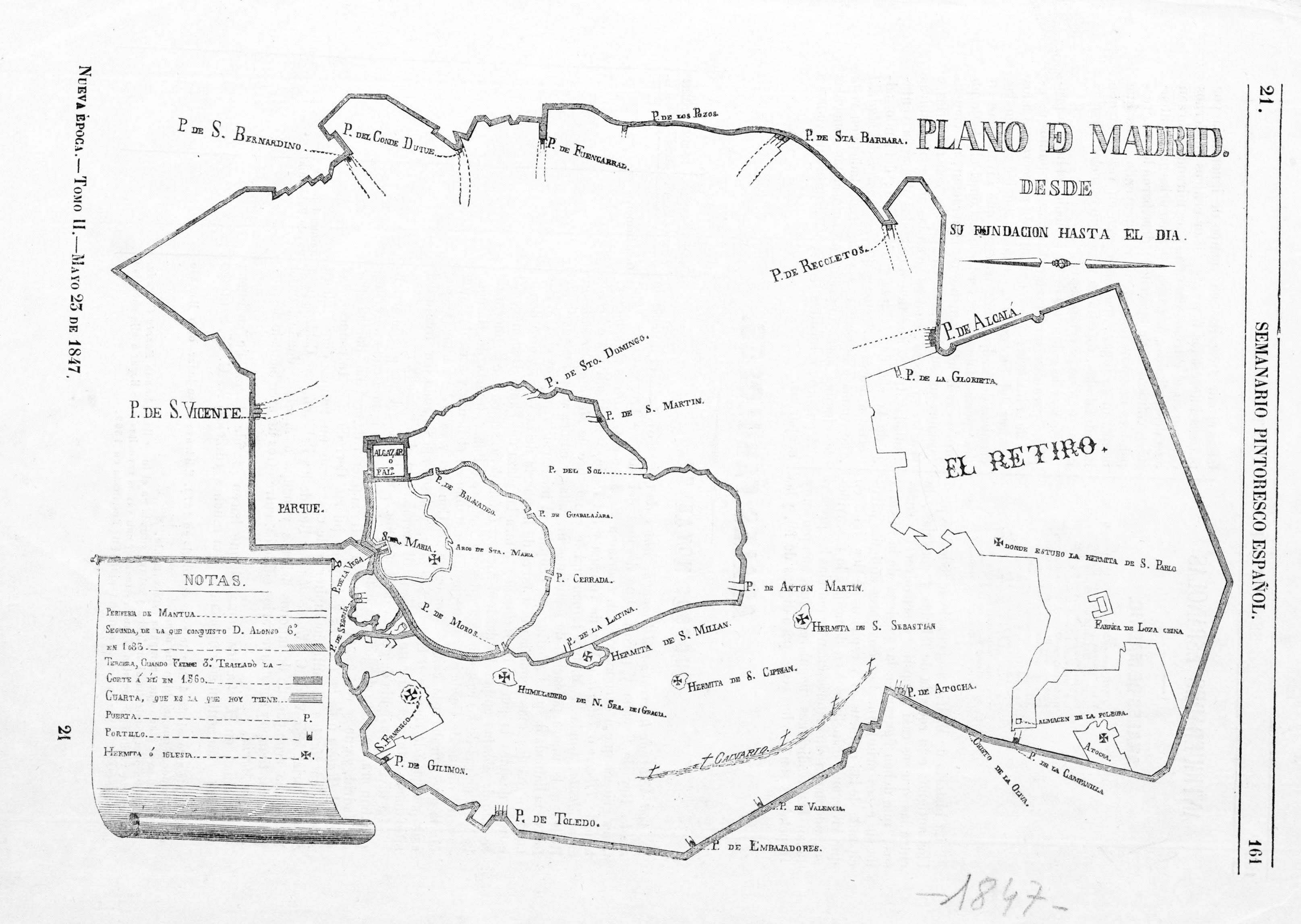
The Christian Walls of Madrid, also known as the Medieval Walls, were built in Madrid, Spain between the 11th and 12th centuries, once the city passed to the Crown of Castile. They were built as an extension of the original 9th-century Muslim Walls of Madrid to accommodate the new districts which emerged after the Reconquista (11th–13th centuries). When Philip II moved his court to Madrid from Valladolid in 1561, the walls fell into disuse and were almost entirely demolished. Some of the remains are still standing, however, and are integrated into the structure of various buildings in El Madrid de los Austrias, a name designating the Habsburgs' historic center of the city. The most important sections of the wall are in the (streets) of los Mancebos, Don Pedro, del Almendro, Escalinata, del Espejo, de Mesón de Paños, and Cava Baja; in Plaza de Isabel II; and in the underground parking garage of the Plaza de Oriente. The remains that are still standing were declared a His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muralla Cristiana De Madrid
''The Goalkeeper'' ( es, Muralla) is a 2018 Bolivian thriller film directed by Rodrigo Patiño. It was selected as the Bolivian entry for the Best Foreign Language Film at the 91st Academy Awards, but it was not nominated. Cast * Juan Carlos Aduviri as Quispe * Luis Aduviri as Aparapita * Erika Andia as Dueña del hostal. * Fernando Arze as Jorge See also * List of submissions to the 91st Academy Awards for Best Foreign Language Film * List of Bolivian submissions for the Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film Bolivia has submitted films for the Academy Award for Best International Feature Film since 1995. The award is handed out annually by the United States Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences to a feature-length motion picture produced outside ... References External links * 2018 films 2018 thriller films 2010s Spanish-language films Bolivian drama films {{2010s-thriller-film-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start fires. It occurs chiefly as nodules and masses in sedimentary rocks, such as chalks and limestones.''The Flints from Portsdown Hill'' Inside the nodule, flint is usually dark grey, black, green, white or brown in colour, and often has a glassy or waxy appearance. A thin layer on the outside of the nodules is usually different in colour, typically white and rough in texture. The nodules can often be found along s and |
Ruins In Madrid
Ruins () are the remains of a civilization's architecture. The term refers to formerly intact structures that have fallen into a state of partial or total disrepair over time due to a variety of factors, such as lack of maintenance, deliberate destruction by humans, or uncontrollable destruction by natural phenomena. The most common root causes that yield ruins in their wake are natural disasters, armed conflict, and population decline, with many structures becoming progressively derelict over time due to long-term weathering and scavenging. There are famous ruins all over the world, with notable sites originating from ancient China, the Indus Valley and other regions of ancient India, ancient Iran, ancient Israel and Judea, ancient Iraq, ancient Greece, ancient Egypt, Roman sites throughout the Mediterranean Basin, and Incan and Mayan sites in the Americas. Ruins are of great importance to historians, archaeologists and anthropologists, whether they were once individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Completed In The 12th Century
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walls Of Madrid
The Walls of Madrid () are the five successive sets of walls that surrounded the city of Madrid from the Middle Ages until the end of the 19th century. Some of the walls had a defensive or military function, while others made it easy to tax goods entering the city. Towards the end of the 19th century the demographic explosion that came with the Industrial Revolution prompted urban expansion throughout Spain. Older walls were torn down to enable the expansion of the city under the grid plan of Carlos María de Castro. Muslim Walls of Madrid The Muslim Walls of Madrid, of which some vestiges remain, are probably the oldest construction in the city. The walls were built in the 9th century, during the period of Muslim rule in the Iberian Peninsula. They were part of a fortress around which developed the urban nucleus of Madrid and started on a promontory next to the Manzanares river. To defend the ''almudaina'' or Muslim citadel of Mayrit, Umayyad Emir of Cordoba Muhammad I o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro Teixeira Albernaz
Pedro Teixeira Albernaz was a Portuguese cartographer born in 1595 in Lisbon, Kingdom of Portugal. He came from a family of cartographers including his father Luís Teixeira, uncle Domingos Teixeira, and his brother João Teixeira Albernaz I who he collaborated with. Around 1610, Pedro went to work in Spain. Pedro served as the royal cosmographer to Philip III of Spain (1598 -1621) and Philip IV (1621-1665). In the years 1622 to 1630 he worked on mapping the coasts of the Iberian Peninsula. Pedro changed his works from nautical charts to topographical survey chart throughout this time period. Pedro was appointed with his brother to make a map of Straits of Magellan and St. Vincent. Pedro died in 1662 in Madrid. Contributions His 1634 work ''La descripción de España y de las costas y puertos de sus reinos'' (''Description of Spain and of the Coasts and Ports of Her Kingdoms'') is preserved in Vienna. Teixeira's map is made of twenty individual folios. The plates for the map we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torre De Los Huesos
The Tower of Bones is an Islamic watchtower, the remains of which are exhibited in the underground parking structure in the Plaza de Oriente, in the Spanish city of Madrid. It was built in the 11th century by the Muslim population that founded the Mayrit fortress two centuries earlier, as an integral part of its defensive system. Background The tower was located outside the citadel and served to keep watch in the Arenal stream area, in the northwest of the capital, next to the place currently occupied by the Royal Palace. With the conquest of Madrid by Alfonso VI in 1083, the tower was incorporated as an albarrana tower into the Christian wall, which the Madrilenos built as an extension of the Muslim walls. In addition to protecting the Fountain of the Pear Tree Canals, which was located in what is now Plaza de Isabel II, it guaranteed the security of the , one of the four entrances to the Christian wall. This was near the confluence of Calle de la Unión and Calle Vergara, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemin De Ronde
A ''chemin de ronde'' ( French, "round path"' or "patrol path"; ), also called an allure, alure or, more prosaically, a wall-walk, is a raised protected walkway behind a castle battlement. In early fortifications, high castle walls were difficult to defend from the ground. The ''chemin de ronde'' was devised as a walkway allowing defenders to patrol the tops of ramparts, protected from the outside by the battlements or a parapet A parapet is a barrier that is an extension of the wall at the edge of a roof, terrace, balcony, walkway or other structure. The word comes ultimately from the Italian ''parapetto'' (''parare'' 'to cover/defend' and ''petto'' 'chest/breast'). Whe ..., placing them in an advantageous position for shooting or dropping. References External links * Castle architecture {{castle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fountain Of The Pear Tree Canals
The Fountain of the Pear Tree Canals ('' es, Fuente de los Caños del Peral'') is an ancient fountain discovered buried under the Plaza de Isabel II in Madrid, Spain, in 2009. The name comes from a 13th-century pear tree that shaded the source spring at the fountain's location. The fountain is also known as the '' es, Lavadero de los Caños del Peral'' (Laundry of the Pear Tree Canals). Background The fountain was documented variously in the 15th century as Hontanillas or Fontanillas and is thought to have been one of the first Turkish baths in Madrid. Water from the canals supplied the population of Madrid through a distribution system made up of water carriers. The water was also used by the “lavadores,” or clothes washers. The discovered part was built in the 17th century and was originally in length, occupying a small valley at the end of Arenal Street. It featured granite ashlars in a padded style. The fountains shared the water from the spring with the royal palace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watchtower
A watchtower or watch tower is a type of fortification used in many parts of the world. It differs from a regular tower in that its primary use is military and from a turret in that it is usually a freestanding structure. Its main purpose is to provide a high, safe place from which a sentinel or guard may observe the surrounding area. In some cases, non-military towers, such as religious towers, may also be used as watchtowers. History Military watchtowers The Romans built numerous towers as part of a system of communications, one example being the towers along Hadrian's Wall in Britain. Romans built many lighthouses, such as the Tower of Hercules in northern Spain, which survives to this day as a working building, and the equally famous lighthouse at Dover Castle, which survives to about half its original height as a ruin. In medieval Europe, many castles and manor houses, or similar fortified buildings, were equipped with watchtowers. In some of the manor houses of wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albarrana Tower
An albarrana tower ( ar, البراني, al-barrānī, lit=exterior) is a defensive tower detached from the curtain wall and connected to it by a bridge or an arcade. They were built by Muslims when they occupied the Iberian Peninsula between the 8th and the 15th centuries, especially from the 12th century during the Almohad dynasty and mainly in the south of Spain and Portugal where the Islamic influence was the longest. In Spanish, they are called ''torre albarrana''. Background The towers of typical appearance, with a square section, were built several meters in front of the curtain wall. They were accessible by a bridge walkway from the curtain wall. More often, the bridge had a removable wooden section allowing the tower to be isolated from the wall if the tower is occupied by attacking forces. The earliest Albarrana towers were often pentagonal or octagonal in plan (e.g. Badajoz, Tarifa, Seville) but a more rectangular plan became the norm. In France and the north of Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |