|
Chocolate Agar
Chocolate agar (CHOC) or chocolate blood agar (CBA) is a nonselective, Growth medium#Enriched media, enriched growth medium used for isolation of pathogenic bacteria. It is a variant of the blood agar plate, containing red blood cells that have been Lysis, lysed by slowly heating to 80°C. Chocolate agar is used for growing fastidious respiratory bacteria, such as ''Haemophilus influenzae'' and ''Neisseria meningitidis''. In addition, some of these bacteria, most notably ''H. influenzae'', need growth factors such as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (factor V or NAD) and hemin (factor X), which are inside red blood cells; thus, a prerequisite to growth for these bacteria is the presence of red blood cell lysates. The heat also inactivates enzymes which could otherwise degrade NAD. The agar is named for its color and contains no chocolate products. Variants Chocolate agar with the addition of bacitracin becomes selective for the genus ''Haemophilus''. Another variant of ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chocolate Agar 1
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cocoa beans that can be a liquid, solid, or paste, either by itself or to flavor other foods. Cocoa beans are the processed seeds of the cacao tree (''Theobroma cacao''); unprocessed, they taste intensely bitter. In making chocolate, these seeds are usually fermented to develop the flavor. They are then dried, cleaned, and roasted. The shell is removed to reveal nibs, which are ground to chocolate liquor: unadulterated chocolate in rough form. The liquor can be processed to separate its two components, cocoa solids and cocoa butter, or shaped and sold as unsweetened baking chocolate. By adding sugar, sweetened chocolates are produced, which can be sold simply as dark chocolate (a.k.a., plain chocolate), or, with the addition of milk, can be made into milk chocolate. Making milk chocolate with cocoa butter and without cocoa solids produces white chocolate. In some chocolates, other ingredients such as vegetable oils, emulsifier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cocoa beans that can be a liquid, solid, or paste, either by itself or to flavoring, flavor other foods. Cocoa beans are the processed seeds of the cacao tree (''Theobroma cacao''); unprocessed, they taste intensely bitter. In making chocolate, these seeds Cocoa bean fermentation, are usually fermented to develop the flavor. They are then dried, cleaned, and roasted. The shell is removed to reveal nibs, which are ground to chocolate liquor: unadulterated chocolate in rough form. The liquor can be processed to separate its two components, cocoa solids and cocoa butter, or shaped and sold as unsweetened baking chocolate. By adding sugar, sweetened chocolates are produced, which can be sold simply as dark chocolate (a.k.a., plain chocolate), or, with the addition of milk, can be made into milk chocolate. Making milk chocolate with cocoa butter and without cocoa solids produces white chocolate. In some chocolates, other ingredients ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agar
Agar ( or ), or agar-agar, is a jelly-like substance consisting of polysaccharides obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from " ogonori" and " tengusa". As found in nature, agar is a mixture of two components, the linear polysaccharide agarose and a heterogeneous mixture of smaller molecules called agaropectin. It forms the supporting structure in the cell walls of certain species of algae and is released on boiling. These algae are known as agarophytes, belonging to the Rhodophyta (red algae) phylum. The processing of food-grade agar removes the agaropectin, and the commercial product is essentially pure agarose. Agar has been used as an ingredient in desserts throughout Asia and also as a solid substrate to contain culture media for microbiological work. Agar can be used as a laxative; an appetite suppressant; a vegan substitute for gelatin; a thickener for soups; in fruit preserves, ice cream, and other desserts; as a clarifying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopotassium Phosphate
Monopotassium phosphate (MKP) (also, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, KDP, or monobasic potassium phosphate) is the inorganic compound with the formula KH2PO4. Together with dipotassium phosphate (K2HPO4.(H2O)x) it is often used as a fertilizer, food additive, and buffering agent. The salt often cocrystallizes with the dipotassium salt as well as with phosphoric acid. Single crystals are paraelectric at room temperature. At temperatures below , they become ferroelectric. Structure Monopotassium phosphate can exist in several polymorphs. At room temperature it forms paraelectric crystals with tetragonal symmetry. Upon cooling to it transforms to a ferroelectric phase of orthorhombic symmetry, and the transition temperature shifts up to when hydrogen is replaced by deuterium. Heating to changes its structure to monoclinic. When heated further, MKP decomposes, by loss of water, to potassium metaphosphate, , at . Manufacturing Monopotassium phosphate is produced by the actio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipotassium Phosphate
Dipotassium phosphate (also dipotassium hydrogen orthophosphate or potassium phosphate dibasic) is the inorganic compound with the formula K2HPO4.(H2O)x (x = 0, 3, 6). Together with monopotassium phosphate (KH2PO4.(H2O)x), it is often used as a fertilizer, food additive, and buffering agent. It is a white or colorless solid that is soluble in water. It is produced commercially by partial neutralization of phosphoric acid with two equivalents of potassium chloride: : H3PO4 + 2 KCl → K2HPO4 + 2 HCl Uses As a food additive, dipotassium phosphate is used in imitation dairy creamers, dry powder beverages, mineral supplements, and starter cultures. It functions as an emulsifier, stabilizer and texturizer; it is also a buffering agent, and chelating agent especially for the calcium in milk products. As a food additive, dipotassium phosphate is generally recognized as safe by the United States Food and Drug Administration, and is commonly used (in conjunction with other inorganic sal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as Salt#Edible salt, edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs as the mineral halite. In its edible form, it is commonly used as a condiment and curing (food preservation), food preservative. Large quantities of sodium chloride are used in many industrial processes, and it is a major source of sodium and chlorine compounds used as feedstocks for further Chemical synthesis, chemical syntheses. Another major application of sodium chloride is deicing of roadways in sub-freezing weather. Uses In addition to the many familiar domestic uses of salt, more dominant applications of the approximately 250 million tonnes per year production (2008 data) include chemicals and de-icing.Westphal, Gisbert ''et al.'' (2002) "Sodium Chloride" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim . Chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corn Starch
Cornflour, cornstarch, maize starch, or corn starch (American English) is the starch derived from corn (maize) grain. The starch is obtained from the endosperm of the seed, kernel. Corn starch is a common food ingredient, often used to thicken sauces or soups, and to make corn syrup and other sugars. Corn starch is versatile, easily modified, and finds many uses in industry such as adhesives, in paper products, as an anti-sticking agent, and textile manufacturing. It has medical uses as well, such as to supply glucose for people with glycogen storage disease. Like many products in dust form, it can be hazardous in large quantities due to its flammable, flammability—see dust explosion. When mixed with a fluid, corn starch can rearrange itself into a non-Newtonian fluid. For example, adding water transforms corn starch into a material commonly known as Non-Newtonian fluid#Oobleck, oobleck while adding oil transforms corn starch into an electrorheological fluid, electrorheolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
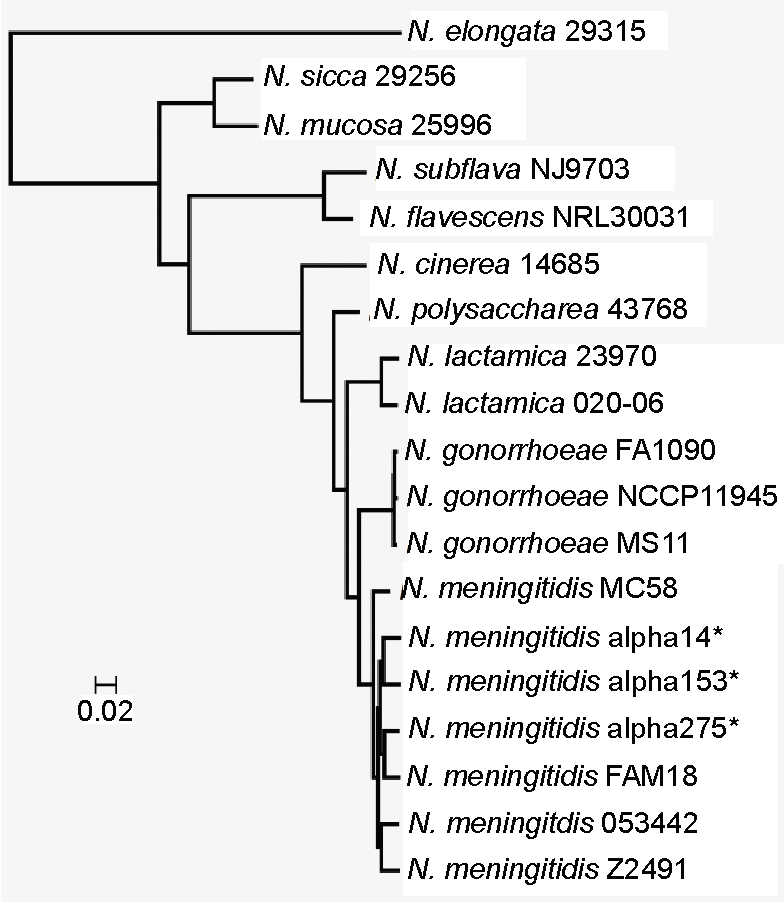
Neisseria
''Neisseria'' is a large genus of bacteria that colonize the mucous membranes of many animals. Of the 11 species that colonize humans, only two are pathogens: '' N. meningitidis'' and '' N. gonorrhoeae''. ''Neisseria'' species are Gram-negative bacteria included among the Pseudomonadota, a large group of Gram-negative forms. ''Neisseria'' diplococci resemble coffee beans when viewed microscopically. Pathogenesis and classification Pathogens Species of this genus (family Neisseriaceae) of parasitic bacteria grow in pairs and occasionally fours, and thrive best at 98.6 °F (37 °C) in the animal body or serum media. The genus includes: * '' N. gonorrhoeae'' (also called the gonococcus) causes gonorrhea. * '' N. meningitidis'' (also called the meningococcus) is one of the most common causes of bacterial meningitis and the causative agent of meningococcal septicaemia. The immune system's neutrophils are restricted in function due to the ability of ''Neisseria'' to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thayer–Martin Agar
Thayer–Martin agar (or Thayer–Martin medium, or VPN agar) is a Mueller–Hinton agar with 5% chocolate sheep blood and antibiotics. It is used for culturing and primarily isolating pathogenic ''Neisseria'' bacteria, including ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' and ''Neisseria meningitidis'', as the medium inhibits the growth of most other microorganisms. When growing ''Neisseria meningitidis'', one usually starts with a normally sterile body fluid (blood or CSF), so a plain chocolate agar is used. Thayer–Martin agar was initially developed in 1964, with an improved formulation published in 1966. Components It usually contains the following combination of antibiotics, which make up the VPN acronym: *Vancomycin, which is able to kill most Gram-positive organisms, although some Gram-positive organisms such as ''Lactobacillus'' and ''Pediococcus'' are intrinsically resistant *Colistin, Polymyxin, also known as colistin, which is added to kill most Gram-negative organisms except ''Neisse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemophilus
''Haemophilus'' is a genus of Gram-negative, pleomorphic, coccobacilli bacteria belonging to the family Pasteurellaceae. While ''Haemophilus'' bacteria are typically small coccobacilli, they are categorized as pleomorphic bacteria because of the wide range of shapes they occasionally assume. These organisms inhabit the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, mouth, vagina, and intestinal tract. The genus includes commensal organisms along with some significant pathogenic species such as '' H. influenzae''—a cause of sepsis and bacterial meningitis in young children—and '' H. ducreyi'', the causative agent of chancroid. All members are either aerobic or facultatively anaerobic. This genus has been found to be part of the salivary microbiome. Metabolism Most members of the genus ''Haemophilus'' require at least one of these blood factors for growth: hemin (sometimes called 'X-factor') and/or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD; sometimes called 'V-fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacitracin
Bacitracin is a polypeptide antibiotic. It is a mixture of related cyclic peptides produced by '' Bacillus licheniformis'' bacteria, that was first isolated from the variety "Tracy I" ( ATCC 10716) in 1945. These peptides disrupt Gram-positive bacteria by interfering with cell wall and peptidoglycan synthesis. Bacitracin is primarily used as a topical preparation, as it can cause kidney damage when used internally. It is generally safe when used topically, but in rare cases may cause hypersensitivity, allergic or anaphylactic reactions, especially in people allergic to neomycin. In 2022, it was the 323rd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 100,000 prescriptions. Medical uses Bacitracin is used in human medicine as a polypeptide antibiotic and is "approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in chickens and turkeys," though use in animals contributes to antibiotic resistance. As bacitracin zinc salt, in combination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemin
Hemin (haemin; ferric chloride heme) is an iron-containing porphyrin with chlorine that can be formed from a heme group, such as heme B found in the hemoglobin of human blood. Chemistry Hemin is protoporphyrin IX containing a ferric iron (Fe3+) ion with a coordinating chloride ligand. Chemically, hemin differs from the related heme-compound hematin chiefly in that the coordinating ion is a chloride ion in hemin, whereas the coordinating ion is a hydroxide ion in hematin. The iron ion in haem is ferrous (Fe2+), whereas it is ferric (Fe3+) in both hemin and hematin. Hemin is endogenously produced in the human body, for example during the turnover of old red blood cells. It can form inappropriately as a result of hemolysis or vascular injury. Several proteins in human blood bind to hemin, such as hemopexin and serum albumin. Pharmacological use A lyophilised form of hemin is used as a pharmacological agent in certain cases for the treatment of porphyria attacks, particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |