|
Chinookan Tribes
The Chinookan languages were a small family of languages spoken in Oregon and Washington along the Columbia River by Chinook peoples. Although the last known native speaker of any Chinookan language died in 2012, the 2009-2013 American Community Survey found 270 self-identified speakers of Upper Chinook. Family division Chinookan consisted of three languages with multiple varieties. There is some dispute over classification, and there are two ISO 639-3 codes assignedchh(Chinook, Lower Chinook) anwac(Wasco-Wishram, Upper Chinook). For example, Ethnologue 15e classifies Kiksht as Lower Chinook, while others consider it instead Upper Chinookdiscussion, and others a separate language. * Lower Chinook (also known as Chinook-proper or Coastal Chinook) † * Kathlamet (also known as Katlamat, Cathlamet) † * Upper Chinook (also known as Kiksht, Columbia Chinook) † Phonology The vowels in the Chinookan languages are /a i ɛ ə u/. Stress is marked as /á/. Morphology As in man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Canada. It flows northwest and then south into the U.S. state of Washington, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state of Oregon before emptying into the Pacific Ocean. The river is long, and its largest tributary is the Snake River. Its drainage basin is roughly the size of France and extends into seven US states and a Canadian province. The fourth-largest river in the United States by volume, the Columbia has the greatest flow of any North American river entering the Pacific. The Columbia has the 36th greatest discharge of any river in the world. The Columbia and its tributaries have been central to the region's culture and economy for thousands of years. They have been used for transportation since a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tense–aspect–mood
Tense–aspect–mood (commonly abbreviated ) or tense–modality–aspect (abbreviated as ) is a group of grammatical categories that are important to understanding spoken or written content, and which are marked in different ways by different languages. TAM covers the expression of three major components of words which lead to or assist in the correct understanding of the speaker's meaning: * Tense—the position of the state or action in time, that is, whether it is in the past, present or future. * Aspect—the extension of the state or action in time, that is, whether it is unitary (perfective), continuous or repeated (imperfective). * Mood or Modality—the reality of the state or action, that is, whether it is actual (realis), a possibility or a necessity (irrealis). For example, in English the word "walk" would be used in different ways for the different combinations of TAM: * Tense: He walked (past), He walks (present), He will walk (future). * Aspect: He walked (uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intransitive Verb
In grammar, an intransitive verb is a verb whose context does not entail a direct object. That lack of transitivity distinguishes intransitive verbs from transitive verbs, which entail one or more objects. Additionally, intransitive verbs are typically considered within a class apart from modal verbs and defective verbs. Examples In the following sentences, verbs are used without a direct object: *"Rivers flow." *"I sneezed." *"My dog ran." *"Water evaporates when it's hot." *"You've grown since I last saw you!" *"I wonder how old I will be when I die." The following sentences contain transitive verbs (they entail one or more objects): *"We watched ''a movie'' last night." *"She's making ''promises''." *"When I said that, my sister smacked ''me''." *"Santa gave ''me'' ''a present''." *"He continuously clicked ''his pen'' and it was incredibly annoying to me." Some verbs, called ambitransitive verbs, may entail objects but do not always require one. Such a verb may be used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patient (grammar)
In linguistics, a grammatical patient, also called the target or undergoer, is the participant of a situation upon whom an action is carried out or the thematic relation such a participant has with an action. Sometimes, "theme" and "patient" are used to mean the same thing. When used to mean different things, "patient" describes a receiver that changes state ("I crushed the car") and "theme" describes something that does not change state ("I have the car").A similar distinction is made here: [Baidu] |
Transitive Verb
A transitive verb is a verb that accepts one or more objects, for example, 'cleaned' in ''Donald cleaned the window''. This contrasts with intransitive verbs, which do not have objects, for example, 'panicked' in ''Donald panicked''. Transitivity is traditionally thought of as a global property of a clause, by which activity is transferred from an agent to a patient. Transitive verbs can be classified by the number of objects they require. Verbs that accept only two arguments, a subject and a single direct object, are monotransitive. Verbs that accept two objects, a direct object and an indirect object, are ''ditransitive'', or less commonly ''bitransitive''. An example of a ditransitive verb in English is the verb ''to give'', which may feature a subject, an indirect object, and a direct object: ''John gave Mary the book''. Verbs that take three objects are ''tritransitive''. In English a tritransitive verb features an indirect object, a direct object, and a prepositional ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agent (grammar)
In linguistics, a grammatical agent is the thematic relation of the cause or initiator to an event. The agent is a semantic concept distinct from the subject of a sentence as well as from the topic Topic, topics, TOPIC, topical, or topicality may refer to: Topic / Topics * Topić, a Slavic surname * ''Topics'' (Aristotle), a work by Aristotle * Topic (chocolate bar), a brand of confectionery bar * Topic (DJ), German musician * Topic (g .... Whereas the subject is determined syntactically, primarily through word order, the agent is determined through its relationship to the action expressed by the verb. For example, in the sentence "The little girl was bitten by the dog", "girl" is the subject, but "dog" is the agent. The word "agent" comes from the present participle ''agens, agentis'' ("the one doing") of the Latin verb ''agere'', to "do" or "make". Theory Typically, the situation is denoted by a Sentence (linguistics), sentence, the action by a verb in the sentence, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Future Tense
In grammar, a future tense (abbreviated ) is a verb form that generally marks the event described by the verb as not having happened yet, but expected to happen in the future. An example of a future tense form is the French ''aimera'', meaning "will love", derived from the verb ''aimer'' ("love"). The "future" expressed by the future tense usually means the future relative to the moment of speaking, although in contexts where relative tense is used it may mean the future relative to some other point in time under consideration. English does not have an inflectional future tense, though it has a variety of grammatical and lexical means for expressing future-related meanings. These include modal auxiliaries such as ''will'' and ''shall'' as well as the futurate present tense. Expressions The nature of the future, necessarily uncertain and at varying distances ahead, means that the speaker may refer to future events with the modality either of probability (what the speaker expec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Present Tense
The present tense (abbreviated or ) is a grammatical tense whose principal function is to locate a situation or event in the present time. The present tense is used for actions which are happening now. In order to explain and understand present tense, it is useful to imagine time as a line on which the past tense, the present and the future tense are positioned. The term ''present tense'' is usually used in descriptions of specific languages to refer to a particular grammatical form or set of forms; these may have a variety of uses, not all of which will necessarily refer to present time. For example, in the English sentence "My train leaves tomorrow morning", the verb form ''leaves'' is said to be in the present tense, even though in this particular context it refers to an event in future time. Similarly, in the historical present, the present tense is used to narrate events that occurred in the past. There are two common types of present tense form in most Indo-European langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Past Tense
The past tense is a grammatical tense whose function is to place an action or situation in the past. Examples of verbs in the past tense include the English verbs ''sang'', ''went'' and ''washed''. Most languages have a past tense, with some having several types in order to indicate how far back the action took place. Some languages have a compound past tense which uses auxiliary verbs as well as an imperfect tense which expresses continuous or repetitive events or actions. Some languages inflect the verb, which changes the ending to indicate the past tense, while non-inflected languages may use other words, such as "yesterday" or "last week" etc to indicate that something took place in the past. Introduction In some languages, the grammatical expression of past tense is combined with the expression of other categories such as grammatical aspect (see tense–aspect). Thus a language may have several types of past tense form, their use depending on what aspectual or other addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adverbial
In English grammar, an adverbial (abbreviated ) is a word (an adverb) or a group of words (an adverbial clause or adverbial phrase) that modifies or more closely defines the sentence or the verb. (The word ''adverbial'' itself is also used as an adjective, meaning "having the same function as an adverb".) Look at the examples below: :''Danny speaks fluently.'' (telling more about the verb) :''Lorna ate breakfast yesterday morning''. (telling when the verb's action occurred) The form of adverbials Adverbials most commonly take the form of adverbs, adverb phrases, temporal noun phrases or prepositional phrases. Many types of adverbials (for instance: reason and condition) are often expressed by clauses. :''James answered immediately''. (adverb) :''James answered in English.'' (prepositional phrase) :''James answered this morning.'' (noun phrase) :''James answered in English because he had a foreign visitor''. ( adverbial clause) An adverbial is a construction which modifies or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
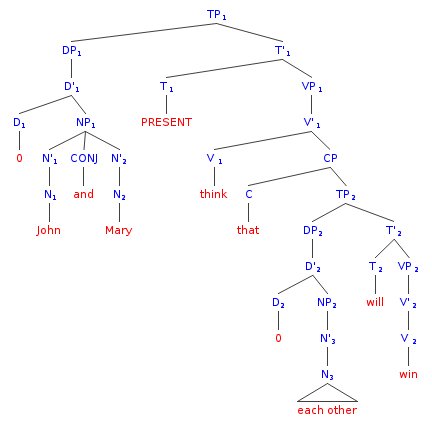
Reciprocal Pronoun
A reciprocal pronoun is a pronoun that indicates a reciprocal relationship. A reciprocal pronoun can be used for one of the participants of a reciprocal construction, i.e. a clause in which two participants are in a mutual relationship. The reciprocal pronouns of English are ''one another'' and ''each other'', and they form the category of anaphors along with reflexive pronouns (''myself'', ''yourselves'', ''themselves,'' etc.). Defining properties Semantics of reciprocal relation Reflexive pronouns are used similarly to reciprocal pronouns in the sense that they typically refer back to the subject of the sentence. (1) ''John and Mary like themselves.'' (2) ''John and Mary like each other.'' The main difference between reflexives, as in example (1), and reciprocal pronouns, as in example (2), is that reflexives are used when the subject acts upon itself, while reciprocals are used when members of a group perform the same action relative to one another. Reciprocal pronouns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflexive Pronoun
A reflexive pronoun is a pronoun that refers to another noun or pronoun (its antecedent) within the same sentence. In the English language specifically, a reflexive pronoun will end in ''-self'' or ''-selves'', and refer to a previously named noun or pronoun (''myself'', ''yourself'', ''ourselves'', ''themselves'', etc.). English intensive pronouns, used for emphasis, take the same form. In generative grammar, a reflexive pronoun is an anaphor that must be bound by its antecedent (see binding). In a general sense, it is a noun phrase that obligatorily gets its meaning from another noun phrase in the sentence. Different languages have different binding domains for reflexive pronouns, according to their structure. Origins and usage In Indo-European languages, the reflexive pronoun has its origins in Proto-Indo-European. In some languages, some distinction exists between normal object and reflexive pronouns, mainly in the third person: whether one says "I like me" or "I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |