|
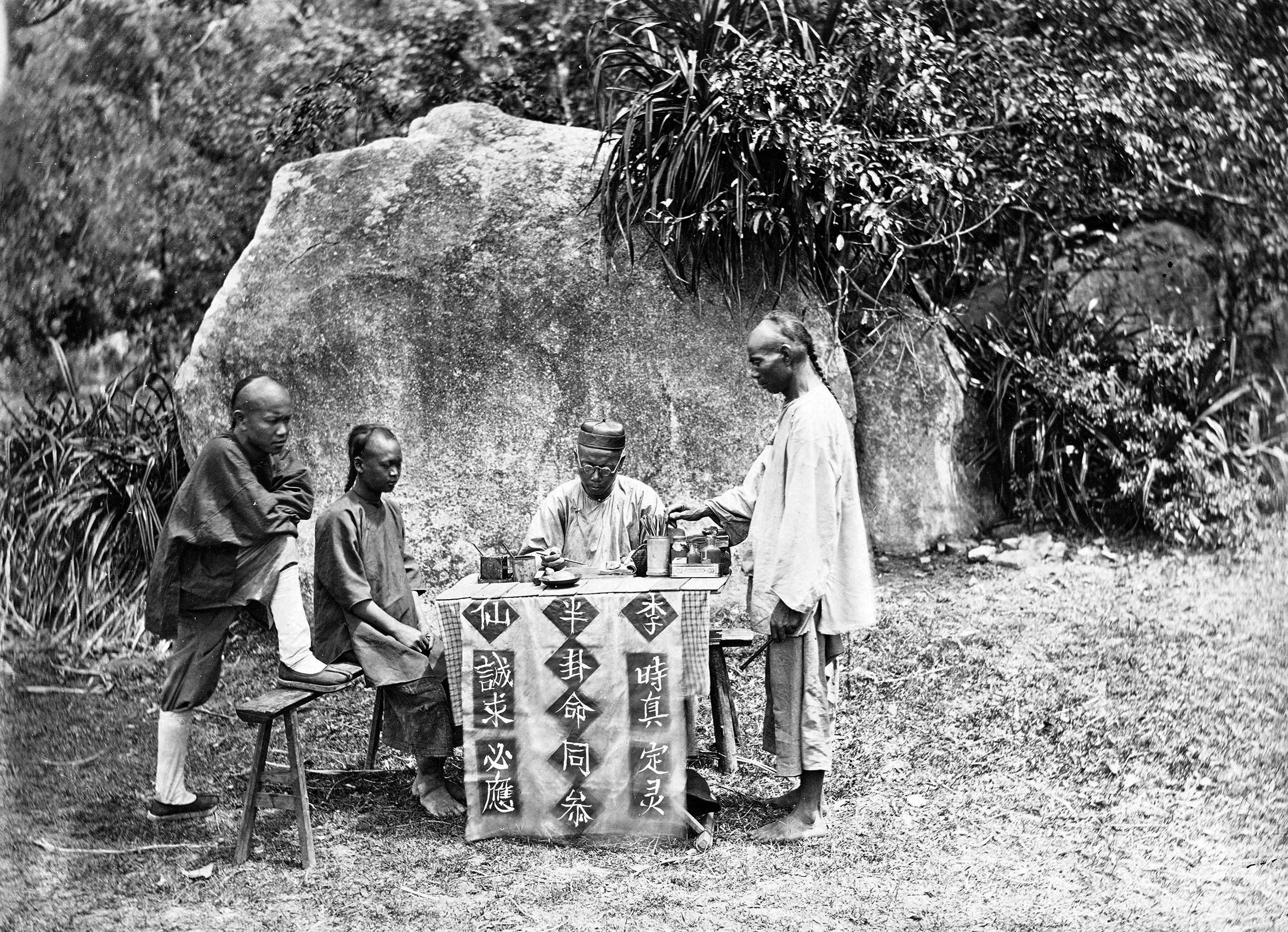
Chinese Fortune Telling
Chinese fortune telling, better known as ''Suan ming'' () has utilized many varying divination techniques throughout the dynastic periods. There are many methods still in practice in Mainland China, Taiwan, Hong Kong and other Chinese-speaking regions such as Malaysia and Singapore today. Over time, some of these concepts have moved into Korean, Japanese, and Vietnamese culture under other names. For example, ''"Saju"'' in Korea is the same as the Chinese four pillar (Chinese: 四柱八字) method. History The oldest accounts about practice of divination describe it as a measure for "solving doubts" (e.g. "Examination of doubts" 稽疑 part of the ''Great Plan'' :zh:洪範). Two well known methods of divination included ''bǔ'' 卜 (on the tortoise shells) and ''shì'' 筮 (on the stalks of milfoil shī 蓍). Those methods were sanctioned by the royal practice since Shang and Zhou dynasties. Divination of the ''xiang'' 相 type (by appearance – of the human body parts, anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guan Lu
Guan Lu (209–256), courtesy name Gongming, was a diviner who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty and Three Kingdoms period of China. Stories Putting the dead to rest At one time, Wang Ji heard of Guan Lu's fame and invited him to visit him. One of Wang Ji's other guests said that his wife was suffering from severe headaches while his son felt pain in his heart. Wang Ji then asked Guan Lu to find out why. Guan Lu used the casting lots method and told them that there were two dead bodies buried in the west corner of the main hall and that a wall had been built across them. One of them held a spear while the other carried a bow and arrows. The spearman died from a gash in his head while the archer died after being stabbed in the heart. Wang Ji then ordered his men to start digging and they found two badly decomposed bodies fitting exactly the description given by Guan Lu. Guan Lu then instructed them to rebury the bodies three miles outside the walls. After that, the woman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Constellation
Traditional Chinese astronomy has a system of dividing the celestial sphere into asterisms or constellations, known as "officials" (Chinese ''xīng guān''). The Chinese asterisms are generally smaller than the constellations of Hellenistic tradition. The Song dynasty (13th-century) Suzhou planisphere shows a total of 283 asterisms, comprising a total of 1,565 individual stars. The asterisms are divided into four groups, the Twenty-Eight Mansions (, ''Èrshíbā Xiù'') along the ecliptic, and the Three Enclosures of the northern sky. The southern sky was added as a fifth group in the late Ming Dynasty based on European star charts, comprising an additional 23 asterisms. The Three Enclosures (, ''Sān Yuán'') include the Purple Forbidden Enclosure, which is centered on the north celestial pole and includes those stars which could be seen year-round,Needham, J.Astronomy in Ancient and Medieval China. ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London''. Series A, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astrology
Chinese astrology is based on the traditional astronomy and calendars. Chinese astrology came to flourish during the Han Dynasty (2nd century BC to 2nd century AD). Chinese astrology has a close relation with Chinese philosophy (theory of the three harmonies: heaven, earth, and human), and uses the principles of yin and yang and concepts that are not found in Western astrology, such as the '' wuxing'' (five phases), the ten Heavenly Stems, the twelve Earthly Branches, the lunisolar calendar (moon calendar and sun calendar), and the time calculation after year, month, day, and '' shichen'' (, double hour). History and background Chinese astrology was elaborated during the Zhou dynasty (1046–256 BC) and flourished during the Han dynasty (2nd century BC to 2nd century AD). During the Han period, the familiar elements of traditional Chinese culture—the yin-yang philosophy, the theory of the five elements, the concepts of heaven and earth, and Confucian morality—were brought t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zi Wei Dou Shu
Zi Wei Dou Shu (Chinese: ), commonly referred to in English as Purple Star Astrology, is a form of fortune-telling in Chinese culture. The study of destiny (Chinese: , ming xue) is one of the five arts of Chinese metaphysics. Along with the Bazi chart, Zi Wei Dou Shu is one of the most renowned fortune-telling methods used in this study. Much like western astrology, Zi Wei Dou Shu claims to use the position of the cosmos at the time of one's birth to make determinations about personality, career and marriage prospects, and more. History Traditionally, Zi Wei Dou Shu is considered to have been created by a Taoist named Lu Chun Yang () during the Tang Dynasty. It was further developed by Chen Xi Yi () during the Song Dynasty and later on by Luo Hong Xian () during the Ming Dynasty to its present-day form. Its exact origin, however, is still debated among different schools. Unlike the more commonly known Four Pillars of Destiny system of birth-chart divination, Zi Wei Dou Shu is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
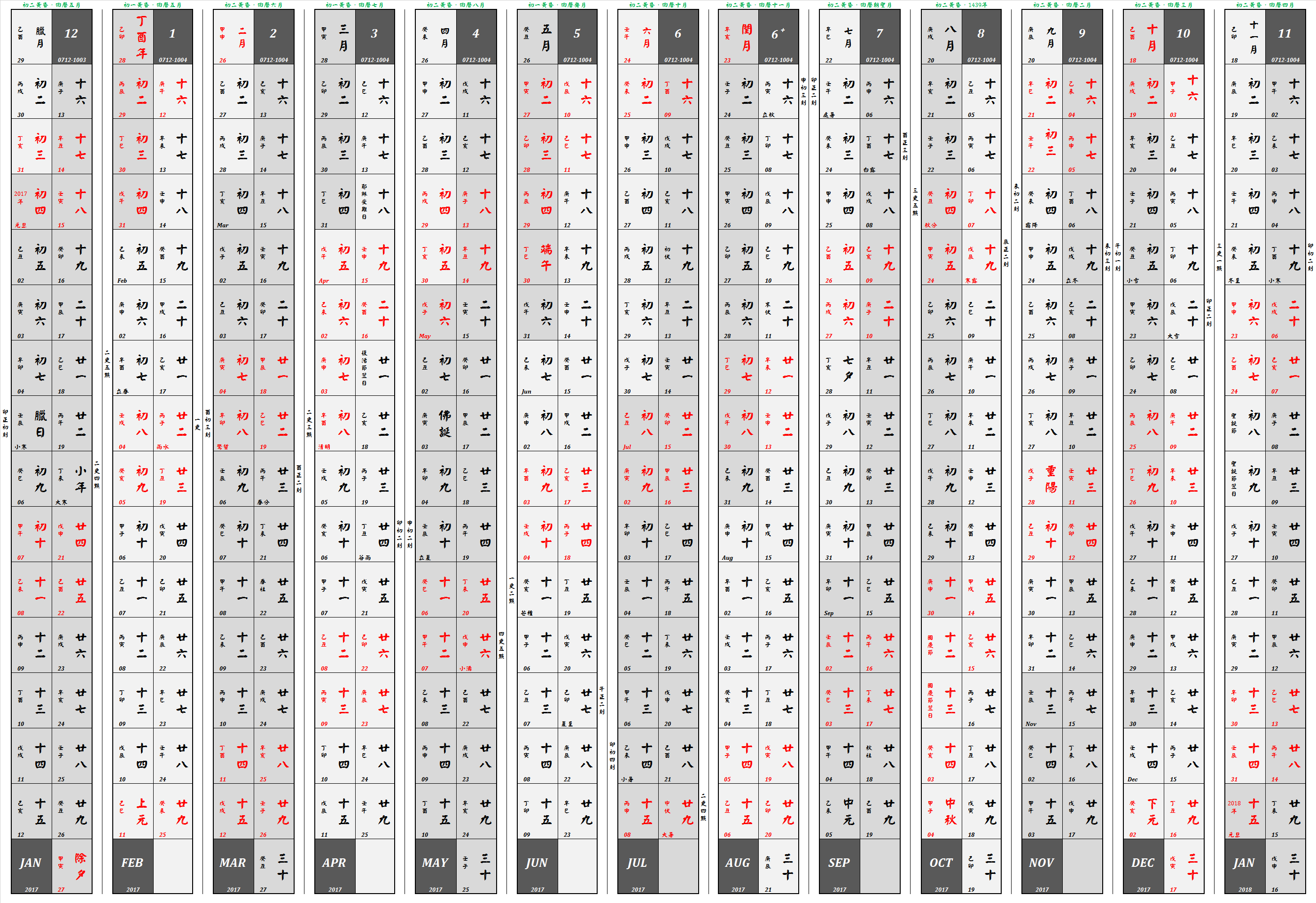
Chinese Calendar
The traditional Chinese calendar (also known as the Agricultural Calendar ��曆; 农历; ''Nónglì''; 'farming calendar' Former Calendar ��曆; 旧历; ''Jiùlì'' Traditional Calendar ��曆; 老历; ''Lǎolì'', is a lunisolar calendar which identifies years, months, and days according to astronomical phenomena. In China, it is defined by the Chinese national standard GB/T 33661–2017, "Calculation and Promulgation of the Chinese Calendar", issued by the Standardization Administration of China on May 12, 2017. Although modern-day China uses the Gregorian calendar, the traditional Chinese calendar governs holidays, such as the Chinese New Year and Lantern Festival, in both China and overseas Chinese communities. It also provides the traditional Chinese nomenclature of dates within a year which people use to select auspicious days for weddings, funerals, moving or starting a business. The evening state-run news program ''Xinwen Lianbo'' in the P.R.C. continues to anno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Characters
Chinese characters () are logograms developed for the writing of Chinese. In addition, they have been adapted to write other East Asian languages, and remain a key component of the Japanese writing system where they are known as ''kanji''. Chinese characters in South Korea, which are known as ''hanja'', retain significant use in Korean academia to study its documents, history, literature and records. Vietnam once used the '' chữ Hán'' and developed chữ Nôm to write Vietnamese before turning to a romanized alphabet. Chinese characters are the oldest continuously used system of writing in the world. By virtue of their widespread current use throughout East Asia and Southeast Asia, as well as their profound historic use throughout the Sinosphere, Chinese characters are among the most widely adopted writing systems in the world by number of users. The total number of Chinese characters ever to appear in a dictionary is in the tens of thousands, though most are graphic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incense Stick
Incense is aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremony. It may also be used as a simple deodorant or insect repellent. Incense is composed of aromatic plant materials, often combined with essential oils. The forms taken by incense differ with the underlying culture, and have changed with advances in technology and increasing number of uses. Incense can generally be separated into two main types: "indirect-burning" and "direct-burning". Indirect-burning incense (or "non-combustible incense") is not capable of burning on its own, and requires a separate heat source. Direct-burning incense (or "combustible incense") is lit directly by a flame and then fanned or blown out, leaving a glowing ember that smoulders and releases a smoky fragrance. Direct-burning incense is either a paste formed around a bamboo stick, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, but it probably comes from the Dutch or Portuguese language, which originally borrowed it from Malay or Kannada. In bamboo, as in other grasses, the internodal regions of the stem are usually hollow and the vascular bundles in the cross-section are scattered throughout the stem instead of in a cylindrical arrangement. The dicotyledonous woody xylem is also absent. The absence of secondary growth wood causes the stems of monocots, including the palms and large bamboos, to be columnar rather than tapering. Bamboos include some of the fastest-growing plants in the world, due to a unique rhizome-dependent system. Certain species of bamboo can grow within a 24-hour period, at a rate of almost an hour (equivalent to 1 mm every 90 seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kau Cim
''Kau Chim'' or ''Kau Cim'', also known as Lottery poetry (), is a fortune telling practice that originated in China in which the querent (person asking the question) requests answers from a sacred oracle lot. The practice is often performed in a Taoist or Buddhist temple in front of an altar. Kau Chim is often referred to as Chien Tung or Chinese Fortune Sticks by westerners. In the US, a version has been sold since 1915 under the name Chi Chi Sticks. Kau Chim is also sometimes known as "The Oracle of Kuan Yin" in Buddhist traditions. It is widely available in Thai temples, known as Siam Si ( th, เซียมซี). The similar practice is also found in Japan, named O-mikuji. Tools * ''Chim bucket'' (): A long cylindrical bamboo cup or tube. * ''Kau Chim sticks'' (): The flat sticks which are stored in the tube. Generally made of bamboo, they resemble wide, flat incense sticks, and are often painted red at one end. A single number, both in Arabic numerals and in Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmistry
Palmistry is the Pseudoscience, pseudoscientific practice of fortune-telling through the study of the Hand#Areas, palm. Also known as palm reading, chiromancy, chirology or cheirology, the practice is found all over the world, with numerous cultural variations. Those who practice palmistry are generally called ''palmists'', ''hand readers'', ''hand analysts'', or ''chirologists''. There are many—and often conflicting—interpretations of various lines and palmar features across various teachings of palmistry. Palmistry is practiced by the Hindus, Hindu Brahmins, and is also indirectly referenced in the Book of Job. The contradictions between different interpretations, as well as the lack of evidence for palmistry's predictions, have caused palmistry to be viewed as a pseudoscience by academics. History Ancient palmistry Palmistry is a practice common to many different places on the Eurasian landmass; it has been practiced in the cultures of Sumeria, Babylonia, Arabia, Canaan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheiromancy
Palmistry is the Pseudoscience, pseudoscientific practice of fortune-telling through the study of the Hand#Areas, palm. Also known as palm reading, chiromancy, chirology or cheirology, the practice is found all over the world, with numerous cultural variations. Those who practice palmistry are generally called ''palmists'', ''hand readers'', ''hand analysts'', or ''chirologists''. There are many—and often conflicting—interpretations of various lines and palmar features across various teachings of palmistry. Palmistry is practiced by the Hindus, Hindu Brahmins, and is also indirectly referenced in the Book of Job. The contradictions between different interpretations, as well as the lack of evidence for palmistry's predictions, have caused palmistry to be viewed as a pseudoscience by academics. History Ancient palmistry Palmistry is a practice common to many different places on the Eurasian landmass; it has been practiced in the cultures of Sumeria, Babylonia, Arabia, Canaan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |