|
Children's Island
Children's Island, formerly known as "Cat Island" is an island off Marblehead, Massachusetts, and is part of the City of Salem, Massachusetts. The YMCA of the North Shore has owned and operated a children's day camp on it since 1955. The first written record of the island was in 1655 when it was granted to Governor John Endecott. It was then bought and sold several times until around the Revolutionary War when the Essex hospital was built as a smallpox inoculation site. The hospital was burned down by townspeople of Marblehead. By the end of the 19th century, the Lowell island house was established as a summer resort. This was run for about 30 years before being converted into a sanitarium for sick and crippled children until 1946. The island then lay unused until bought by the YMCA and converted into a day camp. Name The island has had numerous names including Catta, Cotta, Catt, Cat, Lowell, Pollard, and Children's; for most of history it was Cat Island. Speculation about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Children's Island From Cormorant Rock
A child ( : children) is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. The legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person younger than the age of majority. Children generally have fewer rights and responsibilities than adults. They are classed as unable to make serious decisions. ''Child'' may also describe a relationship with a parent (such as sons and daughters of any age) or, metaphorically, an authority figure, or signify group membership in a clan, tribe, or religion; it can also signify being strongly affected by a specific time, place, or circumstance, as in "a child of nature" or "a child of the Sixties." Biological, legal and social definitions In the biological sciences, a child is usually defined as a person between birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. Legally, the term ''child'' may refer to anyone below the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbridge Gerry
Elbridge Gerry (; July 17, 1744 – November 23, 1814) was an American Founding Father, merchant, politician, and diplomat who served as the fifth vice president of the United States under President James Madison from 1813 until his death in 1814. The political practice of gerrymandering is named after him. He was the second vice president to die in office. Born into a wealthy merchant family, Gerry vocally opposed British colonial policy in the 1760s and was active in the early stages of organizing the resistance in the American Revolutionary War. Elected to the Second Continental Congress, Gerry signed both the Declaration of Independence and Articles of Confederation. He was one of three men who attended the Constitutional Convention in 1787 who refused to sign the United States Constitution because it did not include a Bill of Rights at the time it was signed. After its ratification, he was elected to the inaugural United States Congress, where he was actively involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Bentley
William Bentley (June 22, 1759, Boston, Massachusetts – December 29, 1819, Salem, Massachusetts) was an American Unitarian minister, scholar, columnist, and diarist. He was a polymath who possessed the second best library in the United States (after that of Thomas Jefferson), and was an indefatigable reader and collector of information at the local national and international level. Starting in 1794, he produced a weekly news summary of world events for the local newspaper the '' Salem Gazette.'' He provided a highly sophisticated capsule of current political and cultural news, set in a broad historical context. His unsigned reports were widely copied and reproduced in the young nation's newspapers. Bentley believed in Republican enlightenment and the widest possible diffusion of knowledge. He was upset by the increasingly shrill tone of the partisan press, and the superficiality of much journalism. Career Bentley graduated from Harvard University in 1777, and worked as a sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marblehead Harbor
Marblehead Harbor is a harbor located in Marblehead, Massachusetts, 17 miles northeast of Boston. It is considered the birthplace of the Continental Navy, forerunner of the United States Navy, and of United States Marine Corps Aviation. Description Marblehead Harbor is located to the east of the town's center. To the south is an isthmus that connects the town to Marblehead Neck, which is located on the eastern side of the harbor. The harbor is home to many yachts and also a fishing community, which has increased over the years. There are 2,000 moorings and the harbor contains 14.2 miles of tidal coastline. For a number of years, the Burgess Company was located along the shores of the harbor. Fort Sewall is also located along the northwestern edge of the harbor. Military history Marblehead Harbor has a distinguished military history as well. It was the home port of the schooner ''Hannah'', the first armed vessel of the Continental Navy, and her original owner and master and most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Sewall
Fort Sewall is a historic coastal fortification in Marblehead, Massachusetts. It is located at Gale's Head, the northeastern point of the main Marblehead peninsula, on a promontory that overlooks the entrance to Marblehead Harbor. Until 1814 it was called Gale's Head Fort. History Gale's Head was first fortified in 1634, and was one of the oldest English coastal fortifications in the United States. A more permanent fortification was built in 1742 during King George's War and it served through the French and Indian War.Roberts, p. 410 Gale's Head Fort was rebuilt in 1775 during the American Revolutionary War. It was garrisoned by Colonel John Glover's Marblehead Regiment in 1775–76. After the American Revolution, the federal government took over the property during an expansion of the nation's coast defenses from 1794 to 1807, which is known as the First System of U.S. fortifications. A blockhouse was added in 1794, with further rebuilding in 1799; magazines from both of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakers Island
Bakers Island is a small, private residential island in Massachusetts Bay, in Salem, Massachusetts. It is located southeast of Great Misery Island & Little Misery Island, northeast of North Gooseberry Island and South Gooseberry Island, and far northeast of Children's Island. It is the outermost island on the main shipping channel into Salem Harbor. Bakers Island Light, located on the island's northern side, is used for navigation. The island is pear-shaped. Most of its coast is rocky ledges, except for its western coast. There are three small landlocked ponds located near one another at the center. Vegetation on the island is trees and scrub. There is a private pier on the west side. Most of the buildings are concentrated in the western and southern portions of the island. The approximately island was known as Bakers Island as early as the 1630s. Originally owned by the Massachusetts Bay Colony, it was granted to the town of Salem in 1660. John Turner was the first private ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Montagu (Royal Navy Officer)
Admiral Sir George Montagu (12 December 1750 – 24 December 1829) was a Royal Navy officer, the second son of Admiral John Montagu, and the brother of Captain James Montagu and Lieutenant-Colonel Edward Montagu. Early career In 1763 Montagu entered the Royal Academy at Portsmouth, and was then appointed to with Captain Alan Gardner (afterwards Admiral Lord Gardner), going out to the Jamaica station with the flag of Rear Admiral William Parry. He served in ''Preston'' for three years, before following Captain Gardner to HMS ''Levant''. He finally returned to England in 1770. He passed his lieutenant's examination on 2 October 1770, and on 14 January 1771 was appointed lieutenant of HMS ''Marlborough''. In February he was moved into HMS ''Captain'', going out to North America as the flagship of his father. On 9 April 1773 he was appointed commander in the 18 gun sloop , and on 15 April 1774 (Pay-book of the ''Fowey'') he was posted to . In her he continued on the North A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Lively (1756)
HMS ''Lively'' was a 20-gun post ship of the Royal Navy, launched in 1756. During the Seven Years' War she captured several vessels, most notably the French corvette ''Valeur'' in 1760. She then served during the American Revolutionary War, where she helped initiate the Battle of Bunker Hill. The French captured her in 1778, but the British recaptured her in 1781. She was sold in 1784. Seven Years' War ''Lively'' was commissioned in July 1756 under Captain Francis Wyatt. In November 1756 she captured the French privateer ''Intrépide'', of Nantes, and her prize, ''Charming Molly'', which had been sailing from Malaga to Bristol. ''Intrépide'' was armed with eight guns and 10 swivel guns, and had a crew of 75 men. ''Lively'' brought the two vessels into Plymouth. Around this time she also recaptured the merchant vessel ''Pike'', of Liverpool. ''Lively'' sailed for Jamaica on 31 January 1757. In March 1759 she was under the command of Captain Frederick Maitland, at Jamaica. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Fowey (1749)
HMS ''Fowey'' was a sixth-rate warship of the Royal Navy. Built in 1749, the ship was sunk in action with the French during the Siege of Yorktown in 1781. Mark Robinson was appointed to the Fowey, a 6th Rate of 24 guns, on the 13th June 1767, at Sheerness, and sailed via Spithead, to Plymouth, and thence to Madeira in September, and on to the East Coast of the American colonies, arriving at Charleston in 28 October 1767, relieving the Sardoine. “Pennsylvania Gazetter December 1767 Nov. 6. Captain Mark Robinson, of his Majesty ship Fowey, of 28 guns, who arrived here last week from Great Britain, is commanding officer, or Commodore of all his Majesty’s ships from Virginia to Cape Florida, including the Bahama Islands. Commodore Hood, stationed at Halifax, commands as far south as New York, and, it is said, a third Commodore will be stationed at Virginia.” The itinerary of the Fowey, with Mark Robinson in command was Charleston in 1768, Rebellion Roads (July 1768), Charl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
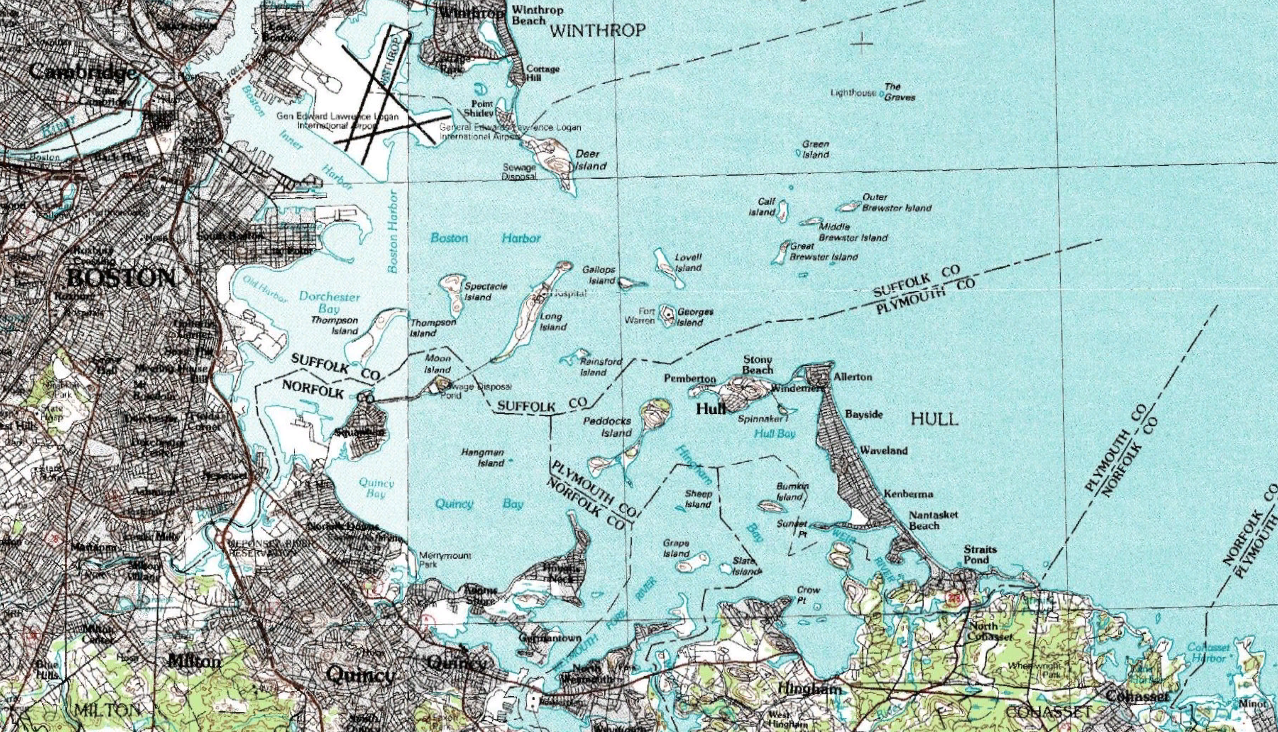
Boston Harbor
Boston Harbor is a natural harbor and estuary of Massachusetts Bay, and is located adjacent to the city of Boston, Massachusetts. It is home to the Port of Boston, a major shipping facility in the northeastern United States. History Since its discovery to Europeans by John Smith in 1614, Boston Harbor has been an important port in American history. Early on, it was recognized by Europeans as one of the finest natural harbors in the world due to its depth and natural defense from the Atlantic as a result of the many islands that dot the harbor. It was also favored due to its access to the Charles River, Neponset River and Mystic River which made travel from the harbor deeper into Massachusetts far easier. It was the site of the Boston Tea Party, as well as almost continuous building of wharves, piers, and new filled land into the harbor until the 19th century. By 1660, almost all imports came to the greater Boston area and the New England coast through the waters of Boston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston Port Act
The Boston Port Act, also called the Trade Act 1774, was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain which became law on March 31, 1774, and took effect on June 1, 1774. It was one of five measures (variously called the ''Intolerable Acts'', the ''Punitive Acts'' or the ''Coercive Acts'') that were enacted during the spring of 1774 to punish Boston for the December 16, 1773, Boston Tea Party. Background The Act was a response to the Boston Tea Party. King George III's speech of March 7, 1774 charged the colonists with attempting to injure British commerce and subvert the constitution. On March 18, Lord North brought in the Port Bill, which outlawed the use of the Port of Boston (by setting up a barricade/blockade) for "landing and discharging, loading or shipping, of goods, wares, and merchandise" until restitution was made to the King's treasury (for customs duty lost) and to the East India Company for damages suffered. In other words, it closed Boston Port to all ships, no ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston Tea Party
The Boston Tea Party was an American political and mercantile protest by the Sons of Liberty in Boston, Massachusetts, on December 16, 1773. The target was the Tea Act of May 10, 1773, which allowed the British East India Company to sell tea from China in American colonies without paying taxes apart from those imposed by the Townshend Acts. The Sons of Liberty strongly opposed the taxes in the Townshend Act as a violation of their rights. Protesters, some disguised as Indigenous Americans, destroyed an entire shipment of tea sent by the East India Company. The demonstrators boarded the ships and threw the chests of tea into the Boston Harbor. The British government considered the protest an act of treason and responded harshly. The episode escalated into the American Revolution, becoming an iconic event of American history. Since then other political protests such as the Tea Party movement have referred to themselves as historical successors to the Boston protest of 1773. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |