|
Chaperone-mediated Autophagy
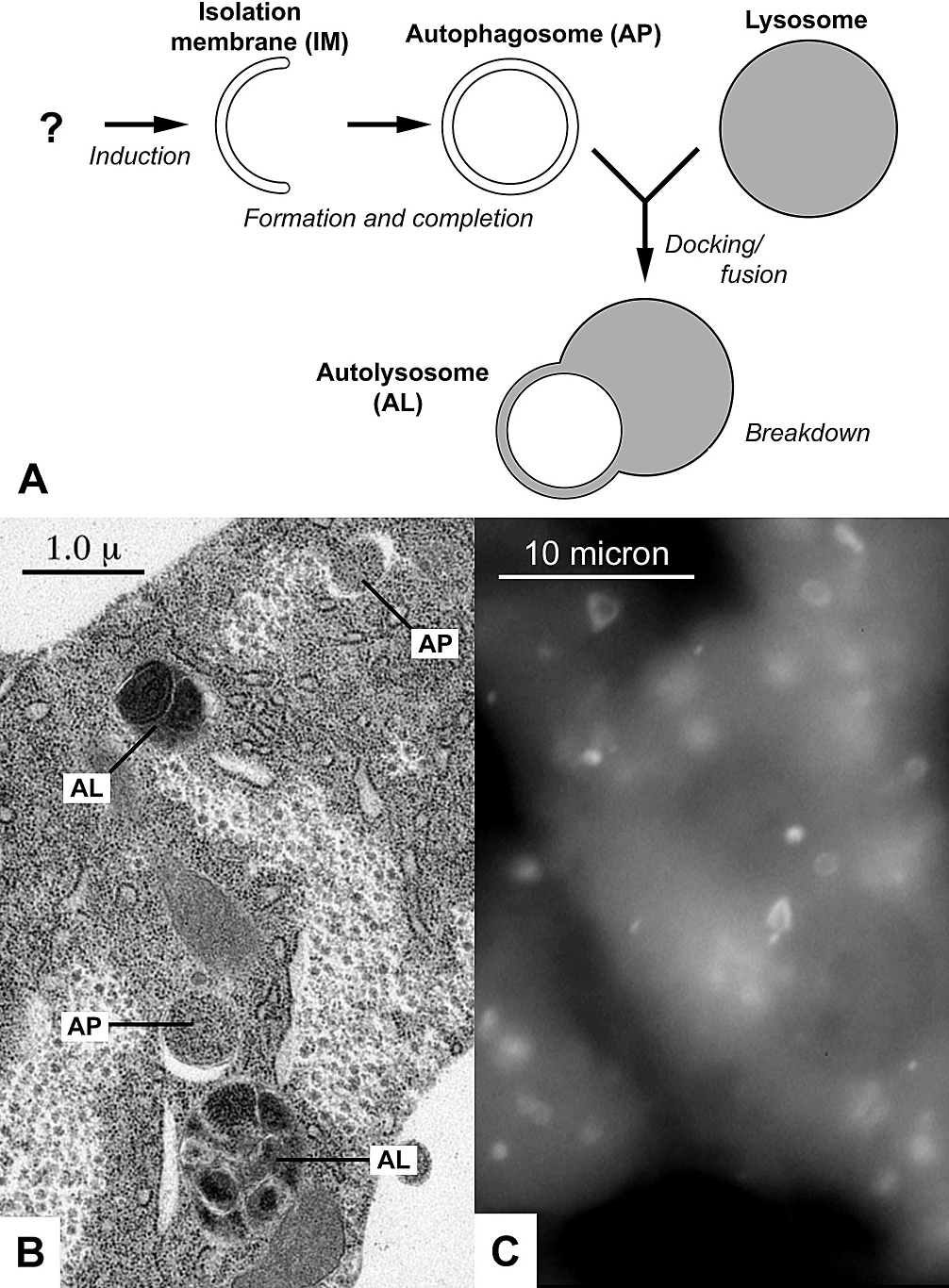
Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) refers to the chaperone-dependent selection of soluble cytosolic proteins that are then targeted to lysosomes and directly translocated across the lysosome membrane for degradation. The unique features of this type of autophagy are the selectivity on the proteins that are degraded by this pathway and the direct shuttling of these proteins across the lysosomal membrane without the requirement for the formation of additional vesicles (Figure 1). Molecular components and steps The proteins that are degraded through CMA are cytosolic proteins or proteins from other compartments once they reach the cytosol. Therefore, some of the components that participate in CMA are present in the cytosol while others are located at the lysosomal membrane (Table I). Specific selection of proteins for degradation in all forms of autophagy came to further understanding as studies discovered the role of chaperones like hsc70. Although hsc70 targets cytosolic protein to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytosolic
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells (intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments. In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is surrounded by the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. The cytosol is thus a liquid matrix around the organelles. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others take place within organelles. The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and propertie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins, and its lumenal proteins. The lumen's pH (~4.5–5.0) is optimal for the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, analogous to the activity of the stomach. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in various cell processes, including secretion, plasma membrane repair, apoptosis, cell signaling, and energy metabolism. Lysosomes act as the waste disposal system of the cell by digesting used materials in the cytoplasm, from both inside and outside the cell. Material from outside the cell is taken up through endocytosis, while material from the inside of the cell is digested through autophagy. The sizes of the organelles vary greatly—the larger ones can be more than 10 times the size of the smaller ones. They were discov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autophagy
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent regulated mechanism. It allows the orderly degradation and recycling of cellular components. Although initially characterized as a primordial degradation pathway induced to protect against starvation, it has become increasingly clear that autophagy also plays a major role in the homeostasis of non-starved cells. Defects in autophagy have been linked to various human diseases, including neurodegeneration and cancer, and interest in modulating autophagy as a potential treatment for these diseases has grown rapidly. Four forms of autophagy have been identified: macroautophagy, microautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), and crinophagy. In macroautophagy (the most thoroughly researched form of autophagy), cytoplasmic components (like mit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. Biological membranes include cell membranes (outer coverings of cells or organelles that allow passage of certain constituents); nuclear membranes, which cover a cell nucleus; and tissue membranes, such as mucosae and serosae. Synthetic membranes are made by humans for use in laboratories and industry (such as chemical plants). This concept of a membrane has been known since the eighteenth century but was used little outside of the laboratory until the end of World War II. Drinking water supplies in Europe had been compromised by the war and membrane filters were used to test for water safety. However, due to the lack of reliability, slow operation, reduced selectivity and elevated costs, membranes were not widely exploited. The first us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Components Of Chaperone-mediated Autophagy
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are typically not con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentapeptide (oligopeptide)
An oligopeptide, often just called peptide ('' oligo-'', "a few"), consists of two to twenty amino acids and can include dipeptides, tripeptides, tetrapeptides, and pentapeptides. Some of the major classes of naturally occurring oligopeptides include aeruginosins, cyanopeptolins, microcystins, microviridins, microginins, anabaenopeptins, and cyclamides. Microcystins are best studied, because of their potential toxicity impact in drinking water. A review of some oligopeptides found that the largest class are the cyanopeptolins (40.1%), followed by microcystins (13.4%). Production Oligopeptide classes are produced by nonribosomal peptides synthases (NRPS), except cyclamides and microviridins are synthesized through ribosomic pathways. Examples Examples of oligopeptides include: * Amanitins - Cyclic peptides taken from carpophores of several different mushroom species. They are potent inhibitors of RNA polymerases in most eukaryotic species, the prevent the production of mRNA and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysosome-associated Membrane Protein Type 2A
Lysosome-associated membrane protein 2 (LAMP2), also known as CD107b (Cluster of Differentiation 107b) and Mac-3, is a human gene. Its protein, LAMP2, is one of the lysosome-associated membrane glycoproteins. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of a family of membrane glycoproteins. This glycoprotein provides selectins with carbohydrate ligands. It may play a role in tumor cell metastasis. It may also function in the protection, maintenance, and adhesion of the lysosome. Alternative splicing of the gene produces three variants - LAMP-2A, LAMP-2B and LAMP-2C. LAMP-2A is the receptor for chaperone-mediated autophagy. Recently it has been determined that antibodies against LAMP-2 account for a fraction of patients who get a serious kidney disease termed focal necrotizing glomerulonephritis. LAMP-2B is associated with Danon disease. Structure and tissue distribution The gene for LAMP2 has 9 coding exons and 2 alternate last exons, 9a and 9b. When the last exon is spl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perilipin 2
Adipose differentiation-related protein, also known as perilipin 2 , ADRP or adipophilin, is a protein which belongs from PAT family of cytoplasmic lipid droplet(CLD) binding protein. In humans it is encoded by the ''ADFP'' gene. This protein surrounds the lipid droplet along with phospholipids and are involved in assisting the storage of neutral lipids within the lipid droplets. Discovery The adipose differentiation related protein (ADRP) was first characterized as an mRNA molecule that express early in adipocyte differentiation. The full length cDNA was cloned by rapid amplification of cDNA ends method and sequence analysis results in a protein with 425 amino acids that is unique and similar sequences had not previously been reported. Gene location In humans, the gene for adipose differentiation related protein is located at short p arm of chromosome 9 at region 22 band 1 from base pair 19108391 to 19127606 (GRCh38.p7) (map). Protein structure The proposed models for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perilipin 3
Mannose-6-phosphate receptor binding protein 1 (M6PRBP1) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''M6PRBP1'' gene. Its gene product, as well as the gene itself, is commonly known as TIP47. Function Mannose 6-phosphate receptors (MPRs) deliver lysosomal hydrolase from the Golgi to endosomes and then return to the Golgi complex. The protein encoded by this gene interacts with the cytoplasmic domains of both cation-independent and cation-dependent MPRs, and is required for endosome-to-Golgi transport. This protein also binds directly to the GTPase RAB9 (RAB9A), a member of the RAS oncogene family. The interaction with RAB9 has been shown to increase the affinity of this protein for its cargo. The mannose-6-phosphate receptor-binding properties of TIP47 are disputed, despite the designation of M6PRBP1 as TIP47's gene symbol. TIP47 protein is most commonly described in the scientific literature as a coat protein for lipid droplets. TIP47 belongs to the peripilin protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |