|
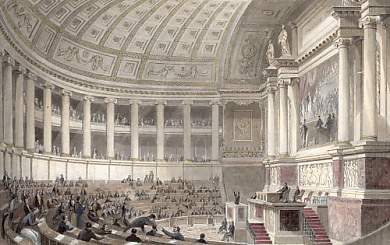
Chambre Des Députés (French Restoration)
The Chamber of Deputies (, ) was the lower house of parliament in France at various times in the 19th and 20th centuries: * 1814–1848 during the Bourbon Restoration in France, Bourbon Restoration and the July Monarchy, the Chamber of Deputies was the lower house of the French Parliament, elected by census suffrage. * 1875–1940 during the French Third Republic, the Chamber of Deputies was the legislative assembly of the French Parliament, elected by two-round system with universal male suffrage. When reunited with the Senate (France), Senate in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, the French Parliament was called the National Assembly (France), National Assembly (''Assemblée nationale'') and carried out the election of the President of France, president of the French Republic. During the Bourbon Restoration Created by the Charter of 1814 and replacing the Corps législatif, which existed under the First French Empire, the Chamber of Deputies was composed of individuals electe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chambre Des Deputes
Chambre (French for ''chamber'') may refer to: * Chambre des Pairs * Chambre des Députés * Chambre de bonne * Chambre introuvable * Valet de chambre * Chambre Ardente People with the surname * Alan Chambré * Calcot Chambre See also * Chambre des représentants (other) * Chamber (other) * {{disambiguation, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First French Empire
The First French Empire or French Empire (; ), also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 6 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815, when Napoleon was exiled to Saint Helena. Although France had already established a French colonial empire, colonial empire overseas since the early 17th century, the French state had remained a France in the early modern period, kingdom under the Bourbons and a French First Republic, republic after the French Revolution. Historians refer to Napoleon's regime as the ''First Empire'' to distinguish it from the restorationist ''Second French Empire, Second Empire'' (1852–1870) ruled by his nephew Napoleon III. On 18 May 1804 (28 Floréal year XII on the French Republican calendar), Napoleon was granted the title Emperor of the French (, ) by the French and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moderate Republicans (France, 1848–1870)
The Moderate Republicans were a large political group active from the birth of the French Second Republic (1848) to the collapse of the Second French Empire (1870). History During the Second Republic Originally, the Moderate Republicans was a group of politicians, writers and journalists close to the newspaper '' Le National''. After the February Revolution of 1848, they became the official majority group in the Provisional Government led by Louis-Eugène Cavaignac, François Arago and Dupont de l'Eure that became the official head of the government. Reputed to be the winners of the 1848 Constituent Assembly election, the Moderate Republicans were strategically allied to The Mountain, the left-wing group, against the monarchists. During this time, the Moderate Republicans were also divided in two groups, namely the Sleeping Republicans (active until the February Revolution) and the Morning-after Republicans that opportunistically endorsed the new regime. The latter were the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miscellaneous Left
Miscellaneous left (', ''DVG'') in France refers to left-wing candidates who are not members of any party or a member of party that has no elected seats. They include either small left-wing parties or dissidents expelled from their parties for running against their party's candidate. Numerous ' candidates are elected at a local level, and a smaller number at the national level. See also * Independent Democrat, a label used in the United States for an independent candidate who loosely identifies with the ideals of the Democratic Party but is not a formal member of the party *Miscellaneous centre *Miscellaneous right Miscellaneous right (', ''DVD'') in France refers to centre-right or right-wing candidates who are not members of any large party. This can include members of small right-wing parties, dissidents expelled from their party for running against thei ... References Left-wing parties in France Political parties of the French Fifth Republic Independent politicia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobin (politics)
A Jacobin (; ) was a member of the Jacobin Club, a revolutionary political movement that was the most famous political club during the French Revolution (1789–1799). The club got its name from meeting at the Dominican rue Saint-Honoré Monastery of the Jacobins. The Dominicans in France were called ''Jacobins'' (, corresponds to ''Jacques'' in French and ''James'' in English) because their first house in Paris was the Saint Jacques Monastery. The terms Jacobin and Jacobinism have been used in a variety of senses. Prior to 1793, the terms were used by contemporaries to describe the politics of Jacobins in the congresses of 1789 through 1792. With the ascendancy of Maximilien Robespierre and the Montagnards into 1793, they have since become synonymous with the policies of the Reign of Terror, with Jacobinism now meaning "Robespierrism". As Jacobinism was memorialized through legend, heritage, tradition and other nonhistorical means over the centuries, the term acquir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Guizot
François Pierre Guillaume Guizot (; 4 October 1787 – 12 September 1874) was a French historian, orator and Politician, statesman. Guizot was a dominant figure in French politics between the July Revolution, Revolution of 1830 and the Revolution of 1848. A Conservative liberalism, conservative liberal who opposed the attempt by King Charles X of France, Charles X to usurp legislative power, he worked to sustain a constitutional monarchy following the July Revolution of 1830. He then served the "citizen king" Louis-Philippe of France, Louis Philippe, as Minister of Education 1832–37, ambassador to London 1840, Foreign Minister 1840–1847, and finally Prime Minister of France from 19 September 1847 to 23 February 1848. Guizot's influence was critical in expanding public education, which under his ministry saw the creation of primary schools in every French commune. As a leader of the "Doctrinaires", committed to supporting the policies of Louis Phillipe and limitations on fur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charter Of 1830
The Charter of 1830 () instigated the July Monarchy in France. It was considered a compromise between constitutional monarchy, constitutional monarchists and republicanism, republicans. History After three days of protests in July 1830 – the July Revolution, also called the "Three Glorious Days" () – by the merchant , who were outraged to be ousted from the limited voters list by the July Ordinances, Charles X of France, Charles X was forced to abdicate. Charles X's chosen successor was his young grandson, Henri, Count of Chambord, Henri, comte de Chambord, but Henri never ascended to the throne. The line of natural hereditary succession was abolished and a member of the cadet House of Orléans, Orléans line of the Bourbon family was chosen: Louis Philippe I. On August 7, the Charter of 1814 was revised, and its preamble evoking the was eliminated. When voted on in the Chamber, it was passed by 219 votes to 33. The new charter was imposed on the king by the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illustrirte Zeitung (1843) 08 116 1 Der Sitzungssaal Der Deputirtenkammer In Paris
''Illustrirte Zeitung''The word "Illustrirt" is written in contemporary German mandatorily as "Illustriert" with an additional "e", leading to the fact that today's German-speaking readers may be irritated by the title of the historical magazine at first. () was Germany's first illustrated magazine that existed between 1843 and 1944. It was also known as ''Leipziger illustrirte Zeitung''. The magazine described itself as the Germany's illustrated magazine with an international view. History and profile ''Illustrirte Zeitung'' was founded by Johann Jakob Weber in Leipzig in 1843. The ''Illustrated London News'' and ''L'Illustration'' which was published in Paris were the two models for the magazine which were both successful commercial enterprises. The first issue of ''Illustrirte Zeitung'' was published on 1 July 1843. The magazine was a weekly news magazine which had a wide scope. It mostly covered news on daily affairs, public and social life, science and art, music, theatre a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chambre Introuvable
The ( French for "Unobtainable Chamber") was the first Chamber of Deputies elected after the Second Bourbon Restoration in 1815. It was dominated by Ultra-royalists who completely refused to accept the results of the French Revolution. The name was coined by King Louis XVIII, referring to the impossibility of cooperating with the chamber. History The elections held on 14 August 1815, under census suffrage and the impact of the " White Terror", produced a heavy Ultra-royalist majority: 350 of the 402 members were Ultra-royalists. The "Unobtainable Chamber", which was first assembled on 7 October 1815, was characterized by its zeal in favour of the aristocracy and the clergy and aimed at reestablishing the . The banned the display of tricolor flags, voted the establishment of military provost-marshal courts, and banished all of the Conventionnels who had voted for Louis XVI's execution. The chamber pursued its militant policy even in defiance of the king himself, proclai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra-royalists
The Ultra-royalists (, collectively Ultras) were a French political faction from 1815 to 1830 under the Bourbon Restoration. An Ultra was usually a member of the nobility of high society who strongly supported Roman Catholicism as the state and only legal religion of France, the Bourbon monarchy, traditional hierarchy between classes and census suffrage (privileged voting rights), while rejecting the political philosophy of popular will and the interests of the bourgeoisie along with their liberal and democratic tendencies. The Legitimists, another of the main right-wing factions identified in René Rémond's ''Les Droites en France'', were disparagingly classified with the Ultras after the 1830 July Revolution by the victors, the Orléanists, who deposed the Bourbon dynasty for the more liberal king Louis Philippe. Second White Terror Following the return of Louis XVIII to power in 1815, people suspected of having ties with the governments of the French Revolution o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterloo To Paris (2–7 July)
Waterloo most commonly refers to: * Battle of Waterloo, 1815 battle where Napoleon's French army was defeated by Anglo-allied and Prussian forces * Waterloo, Belgium Waterloo may also refer to: Other places Australia *Waterloo, New South Wales * Waterloo, Queensland *Waterloo, South Australia *Waterloo Bay, now Elliston, South Australia *Waterloo, Victoria *Waterloo, Western Australia Canada *Waterloo, Nova Scotia *Regional Municipality of Waterloo, a region in Ontario **Waterloo, Ontario, a city **Waterloo (federal electoral district) **Waterloo (provincial electoral district) **Waterloo County, Ontario (1853–1973) *Waterloo, Quebec *Waterloo Village, a neighbourhood in Saint John, New Brunswick United Kingdom England *Waterloo, Dorset, England, a suburb of Poole *Waterloo, Huddersfield, England, a suburb *Waterloo, London, England, area around Waterloo Station *Waterloo Place, London, a street in the St James's area *Waterloo, Merseyside, England **Waterloo (UK Parliamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chambre Des Représentants De France
The Chamber of Representatives () was the popularly elected lower body of the French Parliament set up under the Charter of 1815. The body had 629 members who were to serve five-year terms. The upper body was the Chamber of Peers. History Jean Denis, comte Lanjuinais served as president of this body while it existed. The Chamber of Representatives was short-lived. At the end of the Hundred Days, with the defeat of Napoleon at Waterloo, the chamber issued Napoleon a demand for abdication as Emperor of the French. On 22 June 1815 the Chamber of Representatives elected three members ( Carnot, the duc d'Otrante, and the comte Grenier) of a five-member commission, the ''Commission de gouvernement'', to constitute a new government, and on 23 June 1815 the Chamber of Representatives named Napoleon II as Emperor. The allied powers of the Seventh Coalition soon occupied Paris, and the chamber capitulated on 3 July. It soon became clear that the occupiers wished to again restore the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |