|
Chambered Tomb
A chamber tomb is a tomb for burial used in many different cultures. In the case of individual burials, the chamber is thought to signify a higher status for the interred than a simple grave. Built from rock or sometimes wood, the chambers could also serve as places for storage of the dead from one family or social group and were often used over long periods for multiple burials. Most the chamber tombs were constructed from large stones or megaliths and covered by cairns, barrows or earth. Some chamber tombs are rock-cut monuments or wooden-chambered tombs covered with earth barrows. Grave goods are a common characteristic of chamber tomb burials. In Neolithic and Bronze Age Europe, stone-built examples of these burials are known by the generic term of megalithic tombs. Chamber tombs are often distinguished by the layout of their chambers and entrances or the shape and material of the structure that covered them, either an earth barrow or stone cairn. A wide variety of local ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WV23 By Mutnedjmet
West Virginia is a U.S. state, state in the Appalachian Mountains, Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern United States, Southeastern regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the Bureau of Labor Statistics classifies the state as a part of the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regionMid-Atlantic Home : Mid-Atlantic Information Office: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics" www.bls.gov. Archived. It is bordered by Pennsylvania to the north and east, Maryland to the east and northeast, Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, and Ohio to the northwest. West Virginia is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 10th-smallest state by area and ranks as the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 12th-least populous state, with a population of 1,793,716 residents. The capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalithic Tomb
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea. The word was first used in 1849 by the British antiquarian Algernon Herbert in reference to Stonehenge and derives from the Ancient Greek words "mega" for great and "lithos" for stone. Most extant megaliths were erected between the Neolithic period (although earlier Mesolithic examples are known) through the Chalcolithic period and into the Bronze Age. At that time, the beliefs that developed were dynamism and animism, because Indonesia experienced the megalithic age or the great stone age in 2100 to 4000 BC. So that humans ancient tribe worship certain objects that are considered to have supernatural powers. Some relics of the megalithic era are menhirs (stone monuments) and dolmens (stone tables). Types and definitions While "megalith" is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Cairn
The court cairn or court tomb is a megalithic type of chambered cairn or gallery grave. During the period, 3900–3500 BCE, more than 390 court cairns were built in Ireland and over 100 in southwest Scotland. The Neolithic (New Stone Age) monuments are identified by an uncovered courtyard connected to one or more roofed and partitioned burial chambers. Many monuments were built in multiple phases in both Ireland and Scotland and later re-used in the Early Bronze Age. Construction and design Court cairns are characterized as having an uncovered courtyard area connected to one or more covered burial chambers. The boundaries of this open area were typically lined with large standing stones. A narrow, stone lined entry extended from the main area into one or more roofed burial chambers. Courtyards were generally oval or circular in shape, with U-shaped and semi-circular courtyards being the most common layout. Large, standing stones were used to make the walls and roof of bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allée Couverte
A gallery grave is a form of megalithic tomb built primarily during the Neolithic Age in Europe in which the main gallery of the tomb is entered without first passing through an antechamber or hallway. There are at least four major types of gallery grave (complex, transepted, segmented, and wedge-shaped), and they may be covered with an earthen mound (or "tumulus") or rock mound (or "cairn"). About gallery graves Archeologist T. Douglas Price argues that the gallery grave was a form of community burial site. Those placed in a gallery grave were most likely members of the same family or hamlet, and probably were intended to reinforce the sense of community. Gallery graves may be straight, or they may form an ell. In some cases, a burial chamber exists at the end of the gallery. The walls of gallery graves were built of orthostats, slab-like stones set upright in the earth. They were roofed with multiple flat stones, although the burial chamber (if one existed) was usually roofed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallery Grave
A gallery grave is a form of megalithic tomb built primarily during the Neolithic Age in Europe in which the main gallery of the tomb is entered without first passing through an antechamber or hallway. There are at least four major types of gallery grave (complex, transepted, segmented, and wedge-shaped), and they may be covered with an earthen mound (or "tumulus") or rock mound (or "cairn"). About gallery graves Archeologist T. Douglas Price argues that the gallery grave was a form of community burial site. Those placed in a gallery grave were most likely members of the same family or hamlet, and probably were intended to reinforce the sense of community. Gallery graves may be straight, or they may form an ell. In some cases, a burial chamber exists at the end of the gallery. The walls of gallery graves were built of orthostats, slab-like stones set upright in the earth. They were roofed with multiple flat stones, although the burial chamber (if one existed) was usually roofed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamber Tumulus
A Chamber Tumulus is a large megalithic construct found in certain early neolithic societies. They have been uncovered along the Atlantic coastline in northern Europe, in countries such as France, Spain, Portugal and Ireland. These megaliths have also been found in southern Scandinavia, primarily in Scania and Falbygden. In Denmark there are numerous older megaliths, less advanced that the versions elsewhere, thought to be monuments marking communal burial places. The chamber tumuli predate the ancient Egyptian pyramids, dating back to circa 6000-3000 B.C., depending on place of construction. Before the large farming reforms of the 19th century there were supposed to have been at least 10,000 of the older megaliths in Denmark. The more sophisticated later version does not appear in Denmark. The practice of building these monuments is conjectured to have originated in Ireland or on the Atlantic coast of France where the oldest and largest versions of the monuments has been risen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corbelled Tomb
A corbelled tomb is a generic term given to burial tombs with corbel In architecture, a corbel is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal jutting from a wall to carry a superincumbent weight, a type of bracket. A corbel is a solid piece of material in the wall, whereas a console is a piece applied to the s ...led roofs rather than simple slabs, which generally denote an earlier type of construction. In Europe they include the Mycenean tholos tomb type. Burial monuments and structures Archaeology of death {{struct-type-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
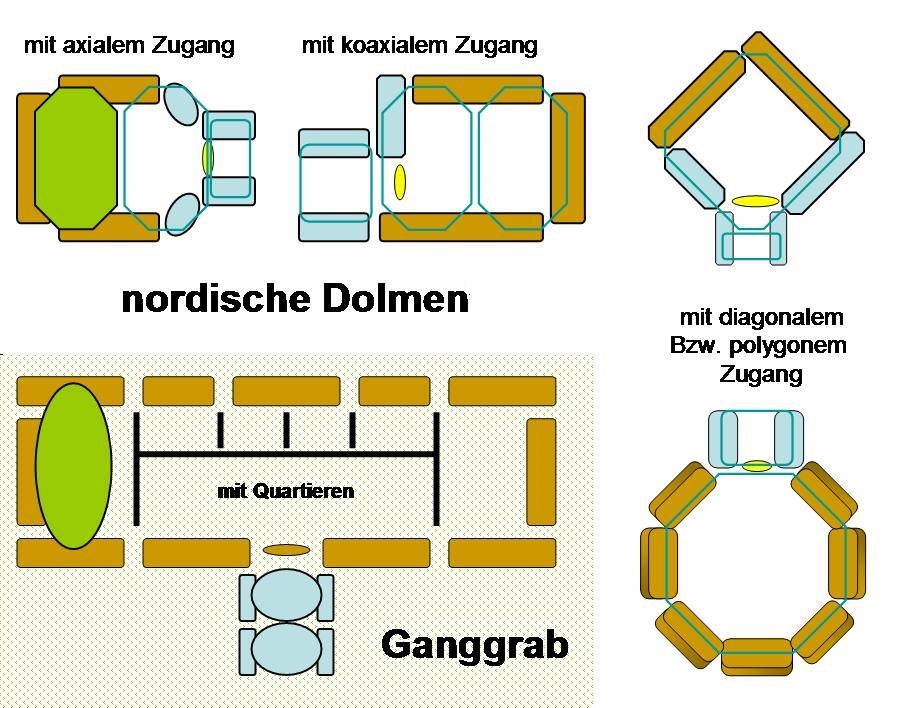
Rectangular Dolmen
A rectangular dolmen (german: Rechteckdolmen), extended dolmen (German: ''erweiteter Dolmen'') or enlarged dolmen is a specific type of megalith, rectangular in shape, with upright sidestones and, usually, two capstones. The term rectangular dolmen was coined by Ekkehard Aner and is used especially in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein, where dolmens with this type of ground plan primarily occur. A more precise term, however, is extended dolmen, used by Ewald Schuldt and Ernst Sprockhoff, because these types of dolmen also occur with trapezoidal ground plans (e.g. the Gnewitz). Neolithic monuments are an expression of the culture and ideology of neolithic communities. Their emergence and function are a hallmark of social development. Capstones and passageway Whilst the simple dolmen as a rule only had one capstone (but could have two), the rectangular dolmen, which differs primarily in the orientation of its support stones (standing) from the simple dolmen (lying), usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygonal Dolmen
A polygonal dolmen (german: Polygonaldolmen) is a megalithic architectural structure and often depicted as the archetypal dolmen. Description Five to nine supporting stones, or orthostats, shape the ground plan of the polygonal chamber. A single, sometimes especially large capstone covers them. An externally built entrance passage, whilst obligatory, has often not survived. In Dithmarschen the rectangular and polygonal dolmens of Albersdorf are particularly important. The Brutkamp is one of the most impressive examples of this type. Typologically viewed, the chamber of Hemmelmark, Rendsburg-Eckernförde, stands out, with its unusual dimensions of 2.8 × 2.25 metres and the division of sub-chambers by vertical slabs. Polygonal dolmen occur more rarely within stone enclosures ( Schülldorf) and more frequently in round barrows (e.g. Dannewerk, Eckernförde, Haßmoor and Süderende). Neolithic monuments are expressions of the culture and ideology of Neolithic communities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Dolmen
The great dolmen or grand dolmen (german: Großdolmen, da, Stordysse) is a type of megalithic site of the Funnelbeaker culture (TBK) that occurs in Nordic megalith architecture, primarily in the east of what is now German Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, and which has two different types of entrance. Neolithic monuments are features of the culture and ideology of Neolithic communities. Their evolution and function act as indicators of social development.J. Müller In: Varia neolithica VI 2009 p. 15 The type of site, called ''Stordysse'' in Danish, does not follow the criteria listed below. In Germany, dolmens with three or more capstones are described as great dolmens and are divided into: * Great dolmens with an antechamber (''Vorraum'') * Great dolmens with a porch (''Windfang'') The porch dolmen is mainly found on the island of Rügen and on the mainland opposite the island. The antechamber dolmen is found southeast of that, between Demmin and the island of Usedom. Several variant, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Dolmen
The simple dolmen (german: Urdolmen, literally "ancient dolmen") or primeval dolmen is an early form of dolmen or megalithic tomb that occurs especially in Northern Europe. The term was defined by archaeologist, Ernst Sprockhoff, and utilised by Ewald Schuldt in publicising his excavation of 106 megalithic sites in the north German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. The simple dolmen emerged in the early days of the development of megalithic monuments of the Funnelbeaker culture (TBK) and around 3,500 BC they appeared across almost the entire region covered by the stone cult structures of Nordic megalith architecture, but not in the Netherlands, in Lower Saxony west of the River Weser nor east of the River Oder and only once in Sweden (Lejeby Laholm). Neolithic monuments are an expression of the culture and ideology of neolithic communities. Their emergence and function serve as indicators of social development. Distinction between simple dolmens and stone cists In many cases t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunebed
A dolmen () or portal tomb is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of two or more upright megaliths supporting a large flat horizontal capstone or "table". Most date from the early Neolithic (40003000 BCE) and were sometimes covered with earth or smaller stones to form a tumulus (burial mound). Small pad-stones may be wedged between the cap and supporting stones to achieve a level appearance.Murphy (1997), 43 In many instances, the covering has eroded away, leaving only the stone "skeleton". The Korean Peninsula is home to the world's highest concentration of dolmens,UNESCO World Heritage List. "Gochang, Hwasun and Ganghwa Dolmen Sites." https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/977 including "cemeteries" consisting of 30–100 examples located in close proximity to each other; with over 35,000 dolmens, Korea alone (for unknown reasons) accounts for approximately 40% of the global total. History It remains unclear when, why and by whom the earliest dolmens were mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |