|
Cereceda's Conjecture
In the mathematics of graph coloring, Cereceda’s conjecture is an unsolved problem on the distance between pairs of colorings of sparse graphs. It states that, for two different colorings of a graph of degeneracy , both using at most colors, it should be possible to reconfigure one coloring into the other by changing the color of one vertex at a time, using a number of steps that is quadratic in the size of the graph. The conjecture is named after Luis Cereceda, who formulated it in his 2007 doctoral dissertation. Background The degeneracy of an undirected graph is the smallest number such that every non-empty subgraph of has at least one vertex of degree at most . If one repeatedly removes a minimum-degree vertex from until no vertices are left, then the largest of the degrees of the vertices at the time of their removal will be exactly , and this method of repeated removal can be used to compute the degeneracy of any graph in linear time. Greedy coloring the vertices in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Path 3-colorings
A path is a route for physical travel – see Trail. Path or PATH may also refer to: Physical paths of different types * Bicycle path * Bridle path, used by people on horseback * Course (navigation), the intended path of a vehicle * Desire path, created by human or animal foot traffic * Footpath, intended for use only by pedestrians * Shared-use path, intended for multiple modes such as walking, bicycling, in-line skating or others * Sidewalk, a paved path along the side of a road * Hoggin, a buff-coloured gravel & clay pathway often seen in gardens of Stately Homes, Parks etc. * Trail, an unpaved lane or road Mathematics, physics, and computing * Path (computing), in file systems, the human-readable address of a resource ** PATH (variable), in computing, a way to specify a list of directories containing executable programs * Path (graph theory), a sequence of edges of a graph that form a trail ** st-connectivity problem, sometimes known as the "path problem" * Path (topol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steady State
In systems theory, a system or a Process theory, process is in a steady state if the variables (called state variables) which define the behavior of the system or the process are unchanging in time. In continuous time, this means that for those properties ''p'' of the system, the partial derivative with respect to time is zero and remains so: : \frac = 0 \quad \text t. In discrete time, it means that the first difference of each property is zero and remains so: :p_t-p_=0 \quad \text t. The concept of a steady state has relevance in many fields, in particular thermodynamics, Steady state economy, economics, and engineering. If a system is in a steady state, then the recently observed behavior of the system will continue into the future. In stochastic systems, the probabilities that various states will be repeated will remain constant. See for example Linear difference equation#Conversion to homogeneous form for the derivation of the steady state. In many systems, a steady state i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjectures
In mathematics, a conjecture is a conclusion or a proposition that is proffered on a tentative basis without proof. Some conjectures, such as the Riemann hypothesis (still a conjecture) or Fermat's Last Theorem (a conjecture until proven in 1995 by Andrew Wiles), have shaped much of mathematical history as new areas of mathematics are developed in order to prove them. Important examples Fermat's Last Theorem In number theory, Fermat's Last Theorem (sometimes called Fermat's conjecture, especially in older texts) states that no three positive integers a, ''b'', and ''c'' can satisfy the equation ''a^n + b^n = c^n'' for any integer value of ''n'' greater than two. This theorem was first conjectured by Pierre de Fermat in 1637 in the margin of a copy of '' Arithmetica'', where he claimed that he had a proof that was too large to fit in the margin. The first successful proof was released in 1994 by Andrew Wiles, and formally published in 1995, after 358 years of effort by mathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The ACM
The ''Journal of the ACM'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering computer science in general, especially theoretical aspects. It is an official journal of the Association for Computing Machinery. Its current editor-in-chief is Venkatesan Guruswami. The journal was established in 1954 and "computer scientists universally hold the ''Journal of the ACM'' in high esteem". See also * ''Communications of the ACM ''Communications of the ACM'' is the monthly journal of the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM). It was established in 1958, with Saul Rosen as its first managing editor. It is sent to all ACM members. Articles are intended for readers with ...'' References External links * Publications established in 1954 Computer science journals Association for Computing Machinery academic journals Bimonthly journals English-language journals {{compu-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Combinatorial Theory
The ''Journal of Combinatorial Theory'', Series A and Series B, are mathematical journals specializing in combinatorics and related areas. They are published by Elsevier. ''Series A'' is concerned primarily with structures, designs, and applications of combinatorics. ''Series B'' is concerned primarily with graph and matroid theory. The two series are two of the leading journals in the field and are widely known as ''JCTA'' and ''JCTB''. The journal was founded in 1966 by Frank Harary and Gian-Carlo Rota.They are acknowledged on the journals' title pages and Web sites. SeEditorial board of JCTA Originally there was only one journal, which was split into two parts in 1971 as the field grew rapidly. An electronic, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kempe Chain
Kempe may refer to: * Kempe baronets, a title in the Baronetage of England * Kempe chain, part of the four-colour theorem * Kempe Fjord, King Christian X Land, Greenland * Kempe Glacier, Antarctica * Kempe Hill, former name of Camp Hill, West Midlands, England People with the surname * Alfred Kempe (1849–1922), English mathematician * Arnold E. Kempe (born 1927), American lawyer and politician * Carl Kempe (1884–1967), Swedish paper producer * Charles Eamer Kempe (1837–1907), English stained glass designer * C. Henry Kempe (1922–1984), American pediatrician who identified the Battered child syndrome * Kempe Gowda I (1513–69), Yelahanka chieftain, founded the city of Bangalore * Margery Kempe (c. 1373–after 1438), English autobiographer, religious pilgrim * Raymond J. Kempe (born 1931), American lawyer and politician * Rudolf Kempe (1910–76), German conductor * William Kempe (died c. 1603), English actor and morris dancer See also * Kemp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Path Graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a path graph or linear graph is a graph whose vertices can be listed in the order such that the edges are where . Equivalently, a path with at least two vertices is connected and has two terminal vertices (vertices that have degree 1), while all others (if any) have degree 2. Paths are often important in their role as subgraphs of other graphs, in which case they are called paths in that graph. A path is a particularly simple example of a tree, and in fact the paths are exactly the trees in which no vertex has degree 3 or more. A disjoint union of paths is called a linear forest. Paths are fundamental concepts of graph theory, described in the introductory sections of most graph theory texts. See, for example, Bondy and Murty (1976), Gibbons (1985), or Diestel (2005). As Dynkin diagrams In algebra, path graphs appear as the Dynkin diagrams of type A. As such, they classify the root system of type A and the Weyl group of ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big O Notation
Big ''O'' notation is a mathematical notation that describes the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards a particular value or infinity. Big O is a member of a family of notations invented by Paul Bachmann, Edmund Landau, and others, collectively called Bachmann–Landau notation or asymptotic notation. The letter O was chosen by Bachmann to stand for ''Ordnung'', meaning the order of approximation. In computer science, big O notation is used to classify algorithms according to how their run time or space requirements grow as the input size grows. In analytic number theory, big O notation is often used to express a bound on the difference between an arithmetical function and a better understood approximation; a famous example of such a difference is the remainder term in the prime number theorem. Big O notation is also used in many other fields to provide similar estimates. Big O notation characterizes functions according to their growth rates: d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid for the diameter of a sphere. In more modern usage, the length d of a diameter is also called the diameter. In this sense one speaks of diameter rather than diameter (which refers to the line segment itself), because all diameters of a circle or sphere have the same length, this being twice the radius r. :d = 2r \qquad\text\qquad r = \frac. For a convex shape in the plane, the diameter is defined to be the largest distance that can be formed between two opposite parallel lines tangent to its boundary, and the is often defined to be the smallest such distance. Both quantities can be calculated efficiently using rotating calipers. For a curve of constant width such as the Reuleaux triangle, the width and diameter are the same because all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markov Chain Mixing Time
In probability theory, the mixing time of a Markov chain is the time until the Markov chain is "close" to its steady state distribution. More precisely, a fundamental result about Markov chains is that a finite state irreducible aperiodic chain has a unique stationary distribution ''π'' and, regardless of the initial state, the time-''t'' distribution of the chain converges to ''π'' as ''t'' tends to infinity. Mixing time refers to any of several variant formalizations of the idea: how large must ''t'' be until the time-''t'' distribution is approximately ''π'' ? One variant, ''variation distance mixing time'', is defined as the smallest ''t'' such that the total variation distance of probability measures is small: :, \Pr(X_t \in A) - \pi(A), \leq 1/4 for all subsets A of states and all initial states. This is the sense in which proved that the number of riffle shuffles needed to mix an ordinary 52 card deck is 7. Mathematical theory focuses on how mixing times chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
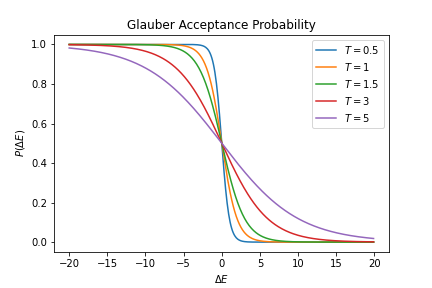
Glauber Dynamics
In statistical physics, Glauber dynamics is a way to simulate the Ising model (a model of magnetism) on a computer. It is a type of Markov Chain Monte Carlo algorithm. The algorithm In the Ising model, we have say N particles that can spin up (+1) or down (-1). Say the particles are on a 2D grid. We label each with an x and y coordinate. Glauber's algorithm becomes: # Choose a particle \sigma_ at random. # Sum its four neighboring spins. S = \sigma_ + \sigma_ + \sigma_ + \sigma_. # Compute the change in energy if the spin x, y were to flip. This is \Delta E = 2\sigma_ S (see the Hamiltonian for the Ising model). # Flip the spin with probability e^/(1 + e^) where T is the temperature . # Display the new grid. Repeat the above N times. In Glauber algorithm, if the energy change in flipping a spin is zero, \Delta E = 0, then the spin would always gets flipped with probability p(0, T) = 0.5. Glauber V.S. Metropolis–Hastings algorithm Metropolis–Hastings algorithm gives ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete Uniform Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the discrete uniform distribution is a symmetric probability distribution wherein a finite number of values are equally likely to be observed; every one of ''n'' values has equal probability 1/''n''. Another way of saying "discrete uniform distribution" would be "a known, finite number of outcomes equally likely to happen". A simple example of the discrete uniform distribution is throwing a fair dice. The possible values are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and each time the die is thrown the probability of a given score is 1/6. If two dice are thrown and their values added, the resulting distribution is no longer uniform because not all sums have equal probability. Although it is convenient to describe discrete uniform distributions over integers, such as this, one can also consider discrete uniform distributions over any finite set. For instance, a random permutation is a permutation generated uniformly from the permutations of a given length, and a unif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |