|
Cephalopods Described In 1884
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, whereas in the Nautiloidea, the external shell remains. About 800 living species of cephalopods have been identified. Tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cambrian
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) * Tardiness * Tardiness (scheduling) In scheduling, tardiness is a measure of a delay in exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonoidea
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish) than they are to shelled nautiloids such as the living ''Nautilus'' species. The earliest ammonites appeared during the Devonian, with the last species vanishing during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Ammonites are excellent index fossils, and linking the rock layer in which a particular species or genus is found to specific geologic time periods is often possible. Their fossil shells usually take the form of planispirals, although some helically spiraled and nonspiraled forms (known as heteromorphs) have been found. The name "ammonite", from which the scientific term is derived, was inspired by the spiral shape of their fossilized shells, which somewhat resemble tightly coiled rams' horns. Pliny the Elder ( 79 AD nea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
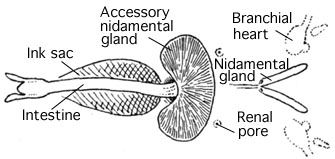
Cephalopod Ink
Cephalopod ink is a dark-coloured or luminous ink released into water by most species of cephalopod, usually as an escape mechanism. All cephalopods, with the exception of the Nautilidae and the Cirrina (deep-sea octopuses), are able to release ink to confuse predators. The ink is released from the ink sacs (located between the gills) and is dispersed more widely when its release is accompanied by a jet of water from the siphon. Its dark color is caused by its main constituent, melanin. Each species of cephalopod produces slightly differently coloured inks; generally, octopuses produce black ink, squid ink is blue-black, and cuttlefish ink is a shade of brown. A number of other aquatic molluscs have similar responses to attack, including the gastropod clade known as sea hares. Types of ink shapes The shapes taken by ink releases are classified as six types: * pseudomorphs; * pseudomorph series; * ink ropes; * clouds/smokescreens; * diffuse puffs; * mantle fills. Inking be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular Hydrostat
A muscular hydrostat is a biological structure found in animals. It is used to manipulate items (including food) or to move its host about and consists mainly of muscles with no skeletal support. It performs its hydraulic movement without fluid in a separate compartment, as in a hydrostatic skeleton. A muscular hydrostat, like a hydrostatic skeleton, relies on the fact that water is effectively incompressible at physiological pressures. In contrast to a hydrostatic skeleton, where muscle surrounds a fluid-filled cavity, a muscular hydrostat is composed mainly of muscle tissue. Since muscle tissue itself is mainly made of water and is also effectively incompressible, similar principles apply. Muscular anatomy Muscles provide the force to move a muscular hydrostat. Since muscles are only able to produce force by contracting and becoming shorter, different groups of muscles have to work against each other, with one group relaxing and lengthening as the other group provides the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tentacle
In zoology, a tentacle is a flexible, mobile, and elongated organ present in some species of animals, most of them invertebrates. In animal anatomy, tentacles usually occur in one or more pairs. Anatomically, the tentacles of animals work mainly like muscular hydrostats. Most forms of tentacles are used for grasping and feeding. Many are sensory organs, variously receptive to touch, vision, or to the smell or taste of particular foods or threats. Examples of such tentacles are the eyestalks of various kinds of snails. Some kinds of tentacles have both sensory and manipulatory functions. A tentacle is similar to a cirrus, but a cirrus is an organ that usually lacks the tentacle's strength, size, flexibility, or sensitivity. A nautilus has cirri, but a squid has tentacles. Invertebrates Molluscs Many molluscs have tentacles of one form or another. The most familiar are those of the pulmonate land snails, which usually have two sets of tentacles on the head: when extended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod Arm
All cephalopods possess flexible limbs extending from their heads and surrounding their cephalopod beak, beaks. These appendages, which function as muscular hydrostats, have been variously termed arms, legs or tentacles. Description In the scientific literature, a cephalopod ''arm'' is often treated as distinct from a ''Tentacle#Tentacles in invertebrates, tentacle'', though the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, often with the latter acting as an umbrella term for cephalopod limbs. Generally, arms have suckers along most of their length, as opposed to tentacles, which have suckers only near their ends.Young, R.E., M. Vecchione & K.M. Mangold 1999Cephalopoda Glossary Tree of Life web project. Barring a few exceptions, octopuses have eight arms and no tentacles, while squid and cuttlefish have eight arms (or two "legs" and six "arms") and two tentacles.Norman, M. 2000. ''Cephalopods: A World Guide''. ConchBooks, Hackenheim. p. 15. "There is some confusion around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilateral Symmetry
Symmetry in biology refers to the symmetry observed in organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. External symmetry can be easily seen by just looking at an organism. For example, take the face of a human being which has a plane of symmetry down its centre, or a pine cone with a clear symmetrical spiral pattern. Internal features can also show symmetry, for example the tubes in the human body (responsible for transporting gases, nutrients, and waste products) which are cylindrical and have several planes of symmetry. Biological symmetry can be thought of as a balanced distribution of duplicate body parts or shapes within the body of an organism. Importantly, unlike in mathematics, symmetry in biology is always approximate. For example, plant leaves – while considered symmetrical – rarely match up exactly when folded in half. Symmetry is one class of patterns in nature whereby there is near-repetition of the pattern element, either by reflection or rotation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nautilus
The nautilus (, ) is a pelagic marine mollusc of the cephalopod family Nautilidae. The nautilus is the sole extant family of the superfamily Nautilaceae and of its smaller but near equal suborder, Nautilina. It comprises six living species in two genera, the type of which is the genus ''Nautilus''. Though it more specifically refers to species ''Nautilus pompilius'', the name chambered nautilus is also used for any of the Nautilidae. All are protected under CITES Appendix II. Depending on species, adult shell diameter is between 4 and 10 inches. Nautilidae, both extant and extinct, are characterized by involute or more or less convolute shells that are generally smooth, with compressed or depressed whorl sections, straight to sinuous sutures, and a tubular, generally central siphuncle.Kümmel, B. 1964. Nautiloidae-Nautilida, in the Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology, Geological Society of America and Univ of Kansas Press, Teichert and Moore eds. Having survived relatively u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuttlefish
Cuttlefish or cuttles are marine molluscs of the order Sepiida. They belong to the class Cephalopoda which also includes squid, octopuses, and nautiluses. Cuttlefish have a unique internal shell, the cuttlebone, which is used for control of buoyancy. Cuttlefish have large, W-shaped pupils, eight arms, and two tentacles furnished with denticulated suckers, with which they secure their prey. They generally range in size from , with the largest species, the giant cuttlefish (''Sepia apama''), reaching in mantle length and over in mass. Cuttlefish eat small molluscs, crabs, shrimp, fish, octopus, worms, and other cuttlefish. Their predators include dolphins, sharks, fish, seals, seabirds, and other cuttlefish. The typical life expectancy of a cuttlefish is about 1–2 years. Studies are said to indicate cuttlefish to be among the most intelligent invertebrates. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octopus
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a beaked mouth at the center point of the eight limbs. The soft body can radically alter its shape, enabling octopuses to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their eight appendages behind them as they swim. The siphon is used both for respiration and for locomotion, by expelling a jet of water. Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse of all invertebrates. Octopuses inhabit various regions of the ocean, including coral reefs, pelagic waters, and the seabed; some live in the intertidal zone and others at abyssal depths. Most species grow quickly, mature ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius (cephalopod), gladius or pen, made of chitin. Squid diverged from other cephalopods during the Jurassic and occupy a similar role to teleost fish as open water predators of similar size and behaviour. They play an important role in the open water food web. The two long tentacles are used to grab prey and the eight arms to hold and control it. The beak then cuts the food into suitable size chunks for swallowing. Squid are rapid swimmers, moving by Aquatic locomotion#Jet propulsion, jet propulsion, and largely locate their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)






.jpg)
.jpg)
