|
Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Sainte-Justine
The Centre hospitalier universitaire Sainte-Justine (CHU Sainte-Justine) is the largest mother and child centre in Canada and one of the four most important pediatric centres in North America. It is affiliated with the Université de Montréal, located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Founded in 1907 by Justine Lacoste-Beaubien and Dr Irma Levasseur, the CHU Sainte-Justine is currently the largest pediatric health centre in Canada. With its 550 beds, of which 30 are in the intensive care unit, it receives 19,000 inpatients yearly. The centre employs 520 doctors and 4500 medical students and residents. The CHU officially became a university health centre in 1995 and has since welcomed around 2500 medical students yearly. It has also been home to a research centre since 1973. In 2000, the Centre de réadaptation Marie-Enfant, the only pediatric rehabilitation centre in Quebec, became affiliated with the CHU Sainte-Justine. The institution underwent a major expansion in 2018, under th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Université De Montréal Faculty Of Medicine
The Faculty of Medicine (french: Faculté de médecine) is one of four medical schools in Quebec. The faculty is part of the Université de Montréal and is located in Montreal and Trois-Rivières. Recent accolades for the school include an endowment by Pfizer (worth $1.8 million) for a chair in atherosclerosis and being awarded a million-dollar grant for the study of leukemia. The Faculty offers a variety of undergraduate programs, graduate programs, the Doctor of Medicine, and several postgraduate medical programs. It also offers the only francophone health management training program in North America. In partnership with the Centre de pédagogie appliquée aux sciences de la santé (CPASS), the Faculty provides practicing physicians, trainers, students and researchers with colloquia, online tools and continuing professional development and health sciences education activities.http://www.cpass.umontreal.ca/developpement-professionnel-continu/autres-programmes-et-activites-sur- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
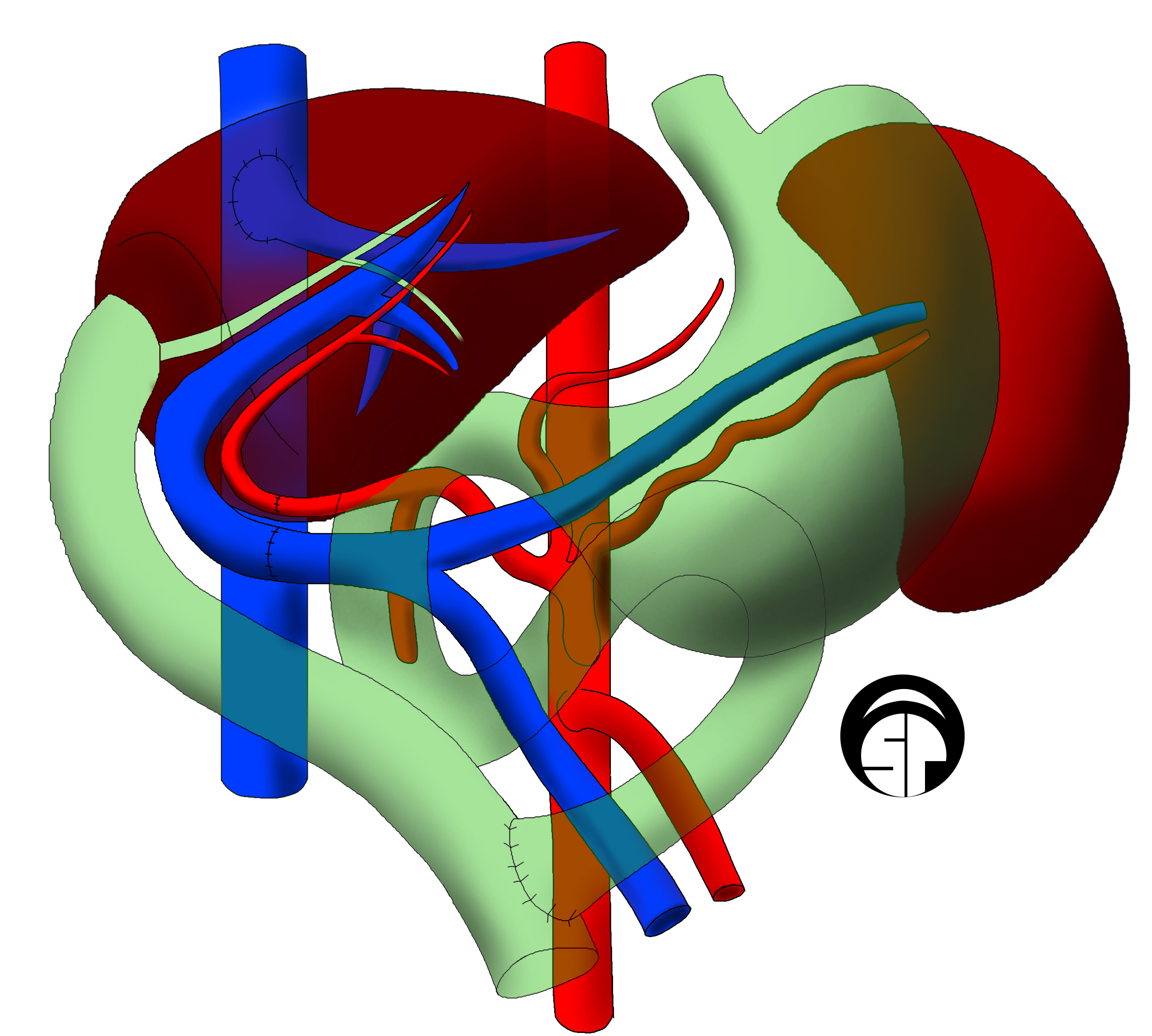
Liver Transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, although availability of donor organs is a major limitation. The most common technique is orthotopic transplantation, in which the native liver is removed and replaced by the donor organ in the same anatomic position as the original liver. The surgical procedure is complex, requiring careful harvest of the donor organ and meticulous implantation into the recipient. Liver transplantation is highly regulated, and only performed at designated transplant medical centers by highly trained transplant physicians and supporting medical team. The duration of the surgery ranges from 4 to 18 hours depending on outcome. Favorable outcomes require careful screening for eligible recipient, as well as a well-calibrated live or cadaveric donor match. Medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Victoria Hospital, Montreal
The Royal Victoria Hospital (RVH) (french: Hôpital Royal Victoria), colloquially known as the "Royal Vic" or "The Vic", is a hospital in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. It forms the biggest base hospital of the McGill University Health Centre (MUHC), which is affiliated with McGill University. The hospital was established in 1893 and was based at Pine Avenue, now known as the Legacy site, until 2015, when major hospital operations were moved to the Glen site (1001 Décarie Boulevard), named for the former Glen railway yards. The future uses of the Legacy site are now under study and it seems likely that the site, which is adjacent to its main campus, will be taken over by McGill University. History The Royal Victoria Hospital was established in 1893 in the historic Golden Square Mile through donations by two public-spirited Scottish immigrants, the cousins Donald Smith, 1st Lord Strathcona, and George Stephen, 1st Lord Mount Stephen. In 1887, they announced a joint gift of C$1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Surgery
Cardiac surgery, or cardiovascular surgery, is surgery on the heart or great vessels performed by cardiac surgeons. It is often used to treat complications of ischemic heart disease (for example, with coronary artery bypass grafting); to correct congenital heart disease; or to treat valvular heart disease from various causes, including endocarditis, Rheumatic fever, rheumatic heart disease, and atherosclerosis. It also includes heart transplantation. History 19th century The earliest operations on the pericardium (the sac that surrounds the heart) took place in the 19th century and were performed by Francisco Romero (surgeon), Francisco Romero (1801) in the city of Almería (Spain), Dominique Jean Larrey (1810), Henry Dalton (1891), and Daniel Hale Williams (1893). The first surgery on the heart itself was performed by Axel Cappelen on 4 September 1895 at Rikshospitalet in Kristiania, now Oslo. Cappelen ligature (medicine), ligated a bleeding coronary circulation, coronary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premature Birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between 28 and 32 weeks, early preterm birth occurs between 32 and 36 weeks, late preterm birth is between 34 and 36 weeks' gestation. These babies are also known as premature babies or colloquially preemies (American English) or premmies (Australian English). Symptoms of preterm labor include uterine contractions which occur more often than every ten minutes and/or the leaking of fluid from the vagina before 37 weeks. Premature infants are at greater risk for cerebral palsy, delays in development, hearing problems and problems with their vision. The earlier a baby is born, the greater these risks will be. The cause of spontaneous preterm birth is often not known. Risk factors include diabetes, high blood pressure, multiple gestation (being pregna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the surgical treatment of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nervous system. Education and context In different countries, there are different requirements for an individual to legally practice neurosurgery, and there are varying methods through which they must be educated. In most countries, neurosurgeon training requires a minimum period of seven years after graduating from medical school. United States In the United States, a neurosurgeon must generally complete four years of undergraduate education, four years of medical school, and seven years of residency (PGY-1-7). Most, but not all, residency programs have some component of basic science or clinical research. Neurosurgeons may pursue additional training in the form of a fellowship after residency, or, in some cases, as a senior resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
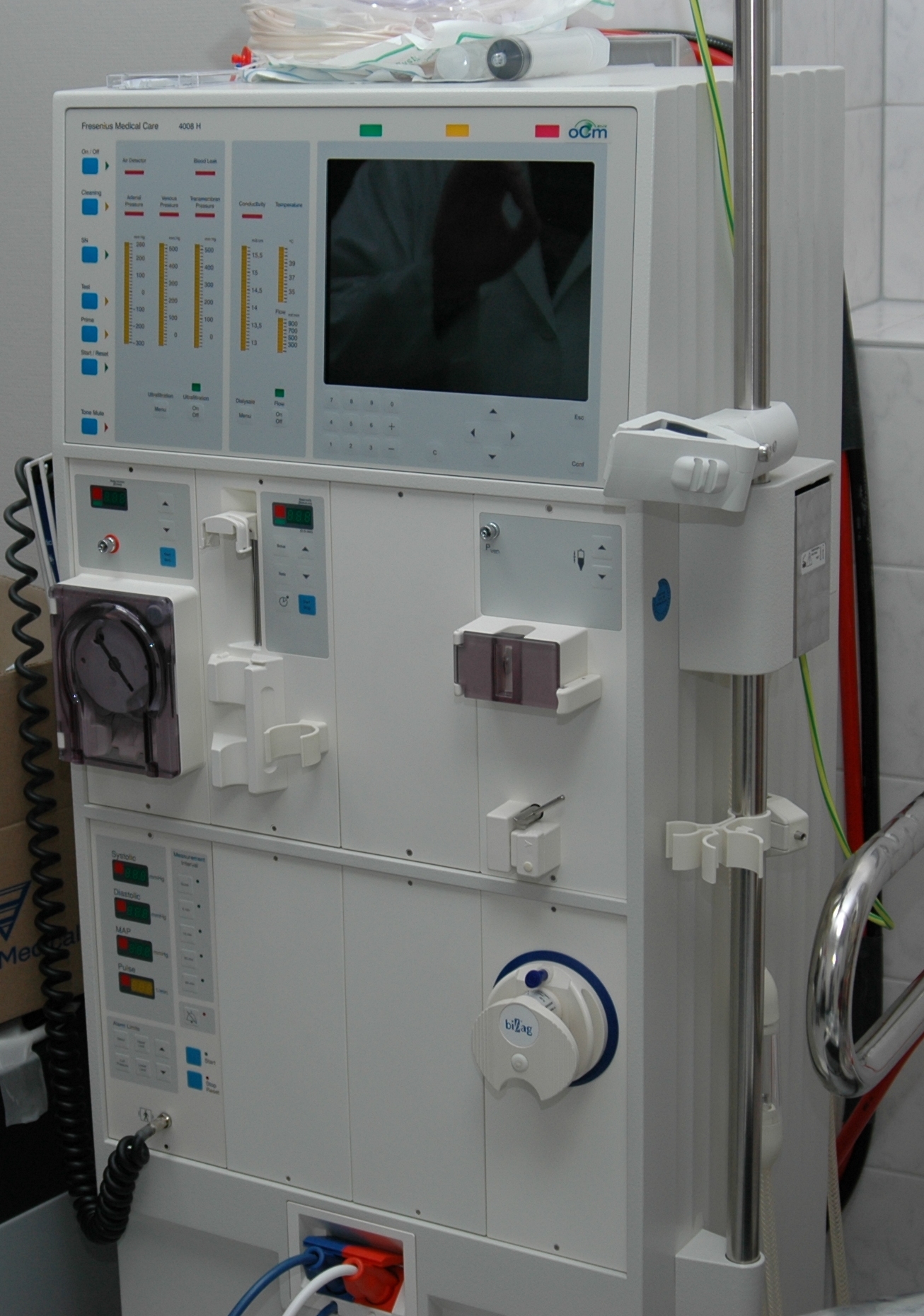
Kidney Dialysis
Kidney dialysis (from Greek , , 'dissolution'; from , , 'through', and , , 'loosening or splitting') is the process of removing excess water, solutes, and toxins from the blood in people whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions naturally. This is referred to as renal replacement therapy. The first successful dialysis was performed in 1943. Dialysis may need to be initiated when there is a sudden rapid loss of kidney function, known as acute kidney injury (previously called acute renal failure), or when a gradual decline in kidney function, chronic kidney disease, reaches stage 5. Stage 5 chronic renal failure is reached when the glomerular filtration rate is 10–15% of normal, creatinine clearance is less than 10 mL per minute and uremia is present. Dialysis is used as a temporary measure in either acute kidney injury or in those awaiting kidney transplant and as a permanent measure in those for whom a transplant is not indicated or not possible.Pendse S, Singh A, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), also known as extracorporeal life support (ECLS), is an extracorporeal technique of providing prolonged cardiac and respiratory support to persons whose heart and lungs are unable to provide an adequate amount of gas exchange or perfusion to sustain life. The technology for ECMO is largely derived from cardiopulmonary bypass, which provides shorter-term support with arrested native circulation. The device used is a membrane oxygenator, also known as an artificial lung. ECMO works by temporarily drawing blood from the body to allow artificial oxygenation of the red blood cells and removal of carbon dioxide. Generally, it is used either post-cardiopulmonary bypass or in late-stage treatment of a person with profound heart and/or lung failure, although it is now seeing use as a treatment for cardiac arrest in certain centers, allowing treatment of the underlying cause of arrest while circulation and oxygenation are supported. ECMO is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetal Surgery
Fetal surgery also known as antenatal surgery, prenatal surgery, is a growing branch of maternal-fetal medicine that covers any of a broad range of surgical techniques that are used to treat congenital abnormalities in fetuses who are still in the pregnant uterus. There are three main types: open fetal surgery, which involves completely opening the uterus to operate on the fetus; minimally invasive fetoscopic surgery, which uses small incisions and is guided by fetoscopy and sonography; and percutaneous fetal therapy, which involves placing a catheter under continuous ultrasound guidance. Fetal intervention is relatively new. Advancing technologies allow earlier and more accurate diagnosis of diseases and congenital problems in a fetus. Fetal surgery draws principally from the fields of surgery, obstetrics and gynecology, and pediatrics- especially the subspecialties of neonatology (care of newborns, especially high-risk ones), maternal-fetal medicine (care of high-risk preg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centre Hospitalier De L'Université De Montréal
The Centre hospitalier de l'Université de Montréal (CHUM, translated as University of Montreal Health Centre) is one of two major healthcare networks in the city of Montreal, Quebec. It is a teaching institution affiliated with the French-language Université de Montréal. The CHUM is one of the largest hospitals in Canada; a public not-for-profit corporation, it receives most of its funding from Quebec taxpayers through the Ministry of Health and Social Services as mandated by the Canada Health Act. The CHUM's primary mission is to provide inpatient and ambulatory care to its immediate urban clientele and specialized and ultraspecialized services to the broader metropolitan and provincial population. Its mandate also includes pure and applied research, teaching, and the evaluation of medical technology and best healthcare practices. Every year, more than 500,000 patients are admitted for care at the CHUM. As of October 2017, the CHUM's hospital operations are being concentrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish General Hospital
The Jewish General Hospital (JGH; french: Hôpital général juif), known officially as the Sir Mortimer B. Davis Jewish General Hospital (french: Hôpital général juif Sir Mortimer B. Davis) since 1978, is an acute-care teaching hospital in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The hospital is affiliated with McGill University and has 637 beds, one of the most of a hospital site in Canada. In 2019, Newsweek ranked the hospital 4th in Canada and 1st in Quebec. History The Jewish General Hospital, which opened its doors in 1934, was founded as a general hospital, open to all patients regardless of race, religion, language or ethnic background. It was founded by the Jewish community of Montreal in part as a response to the anti-Semitic "Days of Shame" doctor's strike at the Hôpital Notre-Dame in Montreal, Quebec, Canada where all interns at the hospital walked off the job for four days to protest the hiring of a Jewish senior intern, Dr. Samuel Rabinovitch and then only returned to work a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hôpital Maisonneuve-Rosemont
Hôpital Maisonneuve-Rosemont is a hospital in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, located in the boroughs of Rosemont–La Petite-Patrie and Mercier-Hochelaga-Maisonneuve. It serves the eastern part of the city and offers 800 beds. It employs 5,000 people and 3,000 students annually. History Hôpital Maisonneuve-Rosemont was founded in 1971 as a result of a merger of two previous hospitals: Hôpital Maisonneuve and Hôpital Saint-Joseph de Rosemont. Hôpital Maisonneuve was founded by the Grey Nuns in 1954 and housed a nursing school and the Montreal Heart Institute. Hôpital Saint-Joseph de Rosemont was founded in 1950 by the Misericordia Sisters. It specialized in treating tuberculosis. Specialization Hôpital Maisonneuve-Rosemont offers general medical care, but it is known for specializing in a few particular areas: ophthalmology, stem cell treatments of various cancers, and nephrology Nephrology (from Greek'' nephros'' "kidney", combined with the suffix ''-logy'', "the study of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_ECMO_for_cardiac_or_respiratory_failure.jpg)

