|
Centaurus (Chinese Astronomy)
The modern constellation Centaurus lies across two of the quadrants symbolized by the Azure Dragon of the East (жқұж–№йқ’йҫҚ, ''DЕҚng FДҒng QД«ng LГіng''), the Vermillion Bird of the South (еҚ—ж–№жңұйӣҖ, ''NГЎn FДҒng ZhЕ« QuГЁ''),The constellation House of Music Instruments which is lied in this area were unknown yet and the Southern Asterisms (иҝ‘еҚ—жҘөжҳҹеҚҖ, ''JГ¬nnГЎnjГӯxД«ngЕҚu''). According to the quadrant, Centaurus is possibly not fully visible in the Chinese sky. Hadar (Beta Centauri) is a bright star in this constellation that is possibly never seen in Chinese sky. The name of the western constellation in modern Chinese is еҚҠдәәйҰ¬еә§ (''bГ n rГ©n mЗҺ zuГІ''), meaning "the centaur constellation". Stars The map of Chinese constellation in constellation Centaurus area consists of: See also *Traditional Chinese star names *Chinese constellations *List of brightest stars This is a list of stars arranged by their apparent magnitude вҖ“ their brightness as observed fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centaurus (constellation)
Centaurus is a bright constellation in the southern sky. One of the largest constellations, Centaurus was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. In Greek mythology, Centaurus represents a centaur; a creature that is half human, half horse (another constellation named after a centaur is one from the zodiac: Sagittarius). Notable stars include Alpha Centauri, the nearest star system to the Solar System, its neighbour in the sky Beta Centauri, and V766 Centauri, one of the largest stars yet discovered. The constellation also contains Omega Centauri, the brightest globular cluster as visible from Earth and the largest identified in the Milky Way, possibly a remnant of a dwarf galaxy. Notable features Stars Centaurus contains several very bright stars. Its alpha and beta stars are used as "pointer stars" to help observers find the constellation Crux. Centaurus has 281 stars above m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upsilon2 Centauri
Upsilon2 Centauri (П…2 Centauri) is a binary star system in the southern constellation Centaurus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.33. Based upon an annual parallax shift of just 2.57 mas as seen from Earth, this star is located roughly 1,300 light years from the Sun. Relative to its neighbors, the system has a peculiar velocity of and it may form a runaway star system. This is a single-lined spectroscopic binary star system with an orbital period of 207.357 days and an eccentricity of 0.55. The primary component has the spectrum of an evolved F-type giant/bright giant hybrid with a stellar classification of F7 II/III. It is around 46 million years old with 6.9 times the mass of the Sun. The star is radiating 3,919 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Centauri
Alpha Centauri ( Latinized from Оұ Centauri and often abbreviated Alpha Cen or Оұ Cen) is a triple star system in the constellation of Centaurus. It consists of 3 stars: Alpha Centauri A (officially Rigil Kentaurus), Alpha Centauri B (officially Toliman) and Alpha Centauri C (officially Proxima Centauri). Proxima Centauri is also the closest star to the Sun at 4.2465 light-years (1.3020 pc). Alpha Centauri A and B are Sun-like stars ( Class G and K, respectively), and together they form the binary star system Alpha Centauri AB. To the naked eye, the two main components appear to be a single star with an apparent magnitude of вҲ’0.27. It is the brightest star in the constellation and the third-brightest in the night sky, outshone only by Sirius and Canopus. Alpha Centauri A has 1.1 times the mass and 1.5 times the luminosity of the Sun, while Alpha Centauri B is smaller and cooler, at 0.9 times the Sun's mass and less than 0.5 times its luminosity. The pair or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Centauri
Epsilon Centauri (Оө Cen, Оө Centauri) is a star in the southern constellation of Centaurus. It is one of the brightest stars in the constellation with a slightly variable apparent visual magnitude of +2.30. Parallax measurements put it at a distance of around from Earth. In Chinese, (), meaning '' Southern Gate'', refers to an asterism consisting of Оө Centauri and Оұ Centauri. Consequently, the Chinese name for Оө Centauri itself is (, en, the First Star of Southern Gate.) Оө Centauri is a massive star with nearly 12 times the mass of the Sun. The spectrum matches a stellar classification of B1 III, indicating this is an evolved giant star. It is radiating more than 15,000 times the luminosity of the Sun from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 24,000 K, giving it the blue-white hue of a B-type star. This is classified as a Beta Cephei type variable star A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chi Centauri
Chi Centauri (ПҮ Cen, ПҮ Centauri) is a star in the constellation Centaurus. ПҮ Centauri is a blue-white B-type main sequence dwarf with a mean apparent magnitude of +4.36. It is approximately 510 light years from Earth. It is classified as a Beta Cephei type variable star and its brightness varies by 0.02 magnitudes with a period of 50.40 minutes. This star is a proper motion member of the Upper CentaurusвҖ“Lupus sub-group in the ScorpiusвҖ“Centaurus OB association In astronomy, stellar kinematics is the observational study or measurement of the kinematics or motions of stars through space. Stellar kinematics encompasses the measurement of stellar velocities in the Milky Way and its satellites as well as t ..., the nearest such co-moving association of massive stars to the Sun. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Chi Centauri Centauri, Chi Beta Cephei variables B-type main-sequence stars Centaurus Upper Centaurus Lupus 5285 068862 122980 CD-40 8405 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phi Centauri
Phi Centauri, Latinized from ПҶ Centauri, is a blue-white hued star in the southern constellation Centaurus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +3.7. The annual parallax shift is 6.21 mas as measured from Earth, which yields a distance estimate of around 530 light years. It is moving further from the Sun with a radial velocity of +5 km/s. This is a B-type subgiant star with a stellar classification of B2 IV. It has no known companions, but does show radial velocity variations and higher order pulsations in the spectrum. The star is just 18 million years old with 8.5 times the mass of the Sun and has 4.2 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating around 4,000 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of about 21,638 K. This star is a proper motion member of the Upper CentaurusвҖ“Lupus sub-group in the ScorpiusвҖ“Centaurus OB association In astronomy, stellar kinematics is the obse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
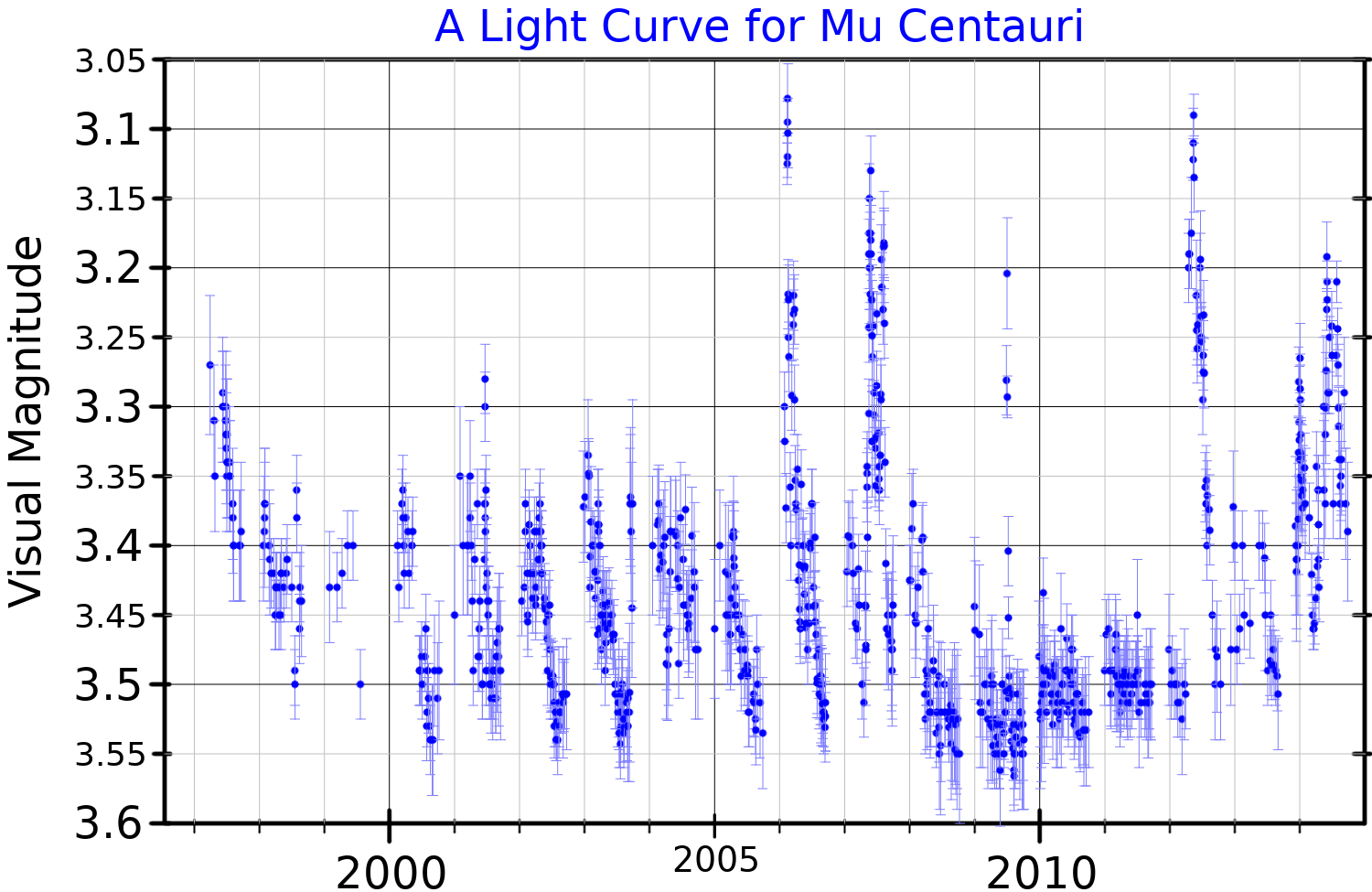
Mu Centauri
Mu Centauri, Latinized from Ој Centauri, is a third-magnitude star in the southern constellation of Centaurus. With the stars ОҪ and ПҶ Centauri, it marks what has been traditionally portrayed as "''dextro Latere''" (the right side) of the CentauThe apparent visual magnitude of this star is 3.42, making it one of the brighter members of the constellation. The distance to this star can be estimated directly using parallax measurements, which yield a value of roughly 510 light years (155 parsecs) from Earth. The spectrum of Mu Centauri is considered to be a standard for a B2 Be star with the stellar classification of B2V:e. The 'e' suffix is used to mark the presence of emission lines, caused by a circumstellar disk of hot gas that was formed from material ejected from the star. Mu Centauri is a pulsating variable star that has multiple non-radial cycles with a primary period of 0.503 days. Three other pulsation cycles have a similar period, while two hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nu Centauri
Nu Centauri, Latinized from ОҪ Centauri, is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Centaurus. The combined apparent visual magnitude of the pair is +3.41, making this one of the brightest members of the constellation. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, this star system is located at a distance of roughly from Earth. The margin of error for this distance is about 2%, which is enough to give an error in distance of Вұ10 light years. This is a single-lined spectroscopic binary system, which means that the two stellar components have not been individually resolved with a telescope. Instead, their orbital motion can be tracked through periodic shifts in the spectrum of the primary. The gravitational perturbation of the hidden secondary component upon the primary is causing the latter to first move toward and then away from the Earth, creating Doppler shift changes in the spectrum. From these subtle shifts, the orbital ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iota Centauri
Iota Centauri, Latinized from О№ Centauri, is a star in the southern constellation of Centaurus. Based upon parallax measurements, it lies at a distance of approximately from Earth. Iota Centauri has an apparent visual magnitude of +2.73, making it easily visible to the naked eye. In Chinese, (), meaning ''Pillars'', refers to an asterism consisting of О№ Centauri, П…2 Centauri, П…1 Centauri, a Centauri, ПҲ Centauri, 4 Centauri, 3 Centauri and 1 Centauri. Consequently, the Chinese name for О№ Centauri itself is (, en, the Eleventh Star of Pillars.) The spectrum of О№ Centauri matches a stellar classification of A2 V. It is an A-type main sequence star that is generating energy by the nuclear fusion of hydrogen in its core region. This energy is being radiated from the outer envelope of the star at an effective temperature of 8,600 K, giving the star a white hue. It has about 2.5 times the Sun's mass and is roughly 350 million years old. The abundance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1 Centauri
1 Centauri, or i Centauri, is a yellow-white-hued binary star system in the southern constellation Centaurus. It can be seen with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of +4.23. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 51.54 mas as seen from Earth's orbit, it is located 51.5 light-years from the Sun. The system is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of вҲ’21.5 km/s. Spectrographic images taken at the Cape Observatory between 1921 and 1923 showed this star has a variable radial velocity, which indicated this is a single-lined spectroscopic binary star system. The pair have an orbital period of 9.94 days and an eccentricity of about 0.2. The primary component has received a number of different stellar classifications. For example, Jaschek et al. (1964) lists F0V, F2III, F4III and F4IV, thus ranging in evolutionary state from an ordinary F-type main-sequence star to a giant star. More recently, Houk (1982) listed a class of F3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3 Centauri
3 Centauri is a triple star system in the southern constellation of Centaurus, located approximately 300 light years from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, blue-white hued star with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.32. As of 2017, the two visible components had an angular separation of along a position angle of 106В°. The system has the Bayer designation k Centauri; ''3 Centauri'' is the Flamsteed designation. It is a suspected eclipsing binary with a variable star designation V983 Centauri. The brighter member, designated component A, is a magnitude 4.52 chemically peculiar star of the helium-weak (CP4) variety, and has a stellar classification of B5 III-IVp. The spectrum of the star displays overabundances of elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, manganese, iron, and nickel, while carbon, oxygen, magnesium, aluminium, sulfur, and chlorine appear underabundant relative to the Sun. Weak emission line features are also visible. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4 Centauri
4 Centauri is a star in the constellation Centaurus. It is a blue-white B-type subgiant with an apparent magnitude of +4.75 and is approximately 640 light years from Earth. 4 Centauri is a hierarchical quadruple star system. The primary component of the system, 4 Centauri A, is a spectroscopic binary, meaning that its components cannot be resolved but periodic Doppler shifts in its spectrum show that it must be orbiting. 4 Centauri A has an orbital period of 6.927 days and an eccentricity of 0.23. Because light from only one of the stars can be detected (i.e. it is a single-lined spectroscopic binary), some parameters such as its inclination are unknown. The secondary component, is also a single-lined spectroscopic binary. It has an orbital period of 4.839 days and an eccentricity of 0.05. The secondary component is a metallic-lined A-type star An A-type main-sequence star (A V) or A dwarf star is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type A and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)