|
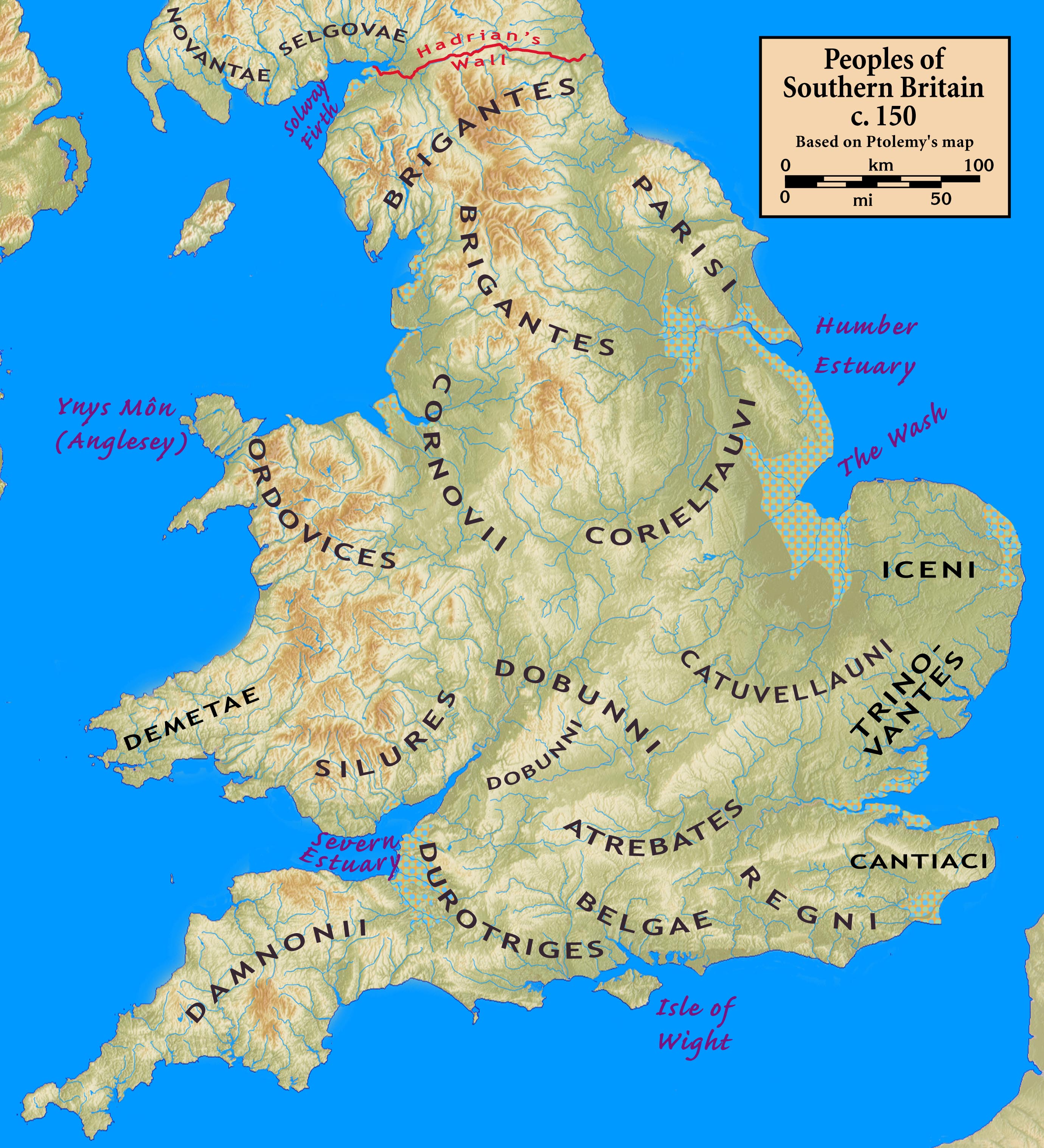
Celtic Tribes Of Britain
The names of the Celtic Iron Age tribes in Britain were recorded by Roman and Greek historians and geographers, especially Ptolemy. Information from the distribution of Celtic coins has also shed light on the extents of the territories of the various groups that occupied the island. Historiography The following ethnic names were recorded in the 2nd century CE at the earliest. Technically, the Iron Age had ended by this date, having transitioned into the Roman period. These tribes were not necessarily the same tribes that had been living in the same area during the Iron Age. Available evidence seems to indicate that the tribes of the Middle Iron Age tended to group together into larger tribal kingdoms during the Late Iron Age. The Belgae and Atrebates share their names with tribes in France and Belgium, which, together with Caesar's note that Diviciacus of the Suessiones had ruled territory in Britain, suggests that this part of the country might have been conquered and ruled f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century bc, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . " e Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe."; in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantiaci
The Cantiaci or Cantii were an Iron Age Celtic people living in Britain before the Roman conquest, and gave their name to a '' civitas'' of Roman Britain. They lived in the area now called Kent, in south-eastern England. Their capital was ''Durovernum Cantiacorum'', now Canterbury. They were bordered by the Regni to the west, and the Catuvellauni to the north. Julius Caesar landed in Cantium in 55 and 54 BCE, the first Roman expeditions to Britain. He recounts in his ''De Bello Gallico'' v. 14: Rulers Pre-Roman Iron Age Julius Caesar named five Celtic tribes inhabiting the land that would become the "heartland of the Catuvellauni": the Ancalites, the Bibroci, the Cassi, the Cenimagni, and the Segontiaci, each with their own "king" or chieftain. He found their way of life to be very similar to their cousins in Gaul with whom they were close – the invasion of Britain may have been triggered by the Britons' supply of arms to the Gauls, who were being subjug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigantes
The Brigantes were Ancient Britons who in pre-Roman times controlled the largest section of what would become Northern England. Their territory, often referred to as Brigantia, was centred in what was later known as Yorkshire. The Greek geographer Ptolemy named the Brigantes as a people in Ireland also, where they could be found around what is now Wexford, Kilkenny and Waterford, while another people named ''Brigantii'' is mentioned by Strabo as a sub-tribe of the Vindelici in the region of the Alps. Within Britain, the territory which the Brigantes inhabited was bordered by that of four other peoples: the Carvetii in the northwest, the Parisii to the east and, to the south, the Corieltauvi and the Cornovii. To the north was the territory of the Votadini, which straddled the present day border between England and Scotland. Etymology The name ''Brigantes'' (Βρίγαντες in Ancient Greek) shares the same Proto-Celtic root as the goddess Brigantia, ''*brigant-'' meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parisi (Yorkshire)
The Parisi were a British Celtic tribe located somewhere within the present-day East Riding of Yorkshire, in England, known from a single brief reference by Ptolemy in his ''Geographica'' of about AD 150. Many writers have connected them with the archaeological Arras culture and some with the more widely known Parisii of Gaul. Historical sources and archaeology The Parisi are known from a description in Ptolemy's ''Geographica'' (''Geographica'' II, 3, 10) which locates them to near ''Opportunum Sinus'' ("Good harbour"). Ptolemy is presumed never to have visited Roman Britain, compiling his work from existing sources, probably in Alexandria. The tribe is inferred to have been surrounded by the Brigantes, and with the Coritani south of them across the Humber. Ptolemy mentions the Parisi in association with '' Petvaria'', a town thought to be located close to Brough, East Riding of Yorkshire. Ptolemy also mentions a promontory ''Promontarium Ocellum'', which may be either Spu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corieltauvi
The Corieltauvi (also the Coritani, and the Corieltavi) were a tribe of people living in Britain prior to the Roman conquest, and thereafter a ''civitas'' of Roman Britain. Their territory was in what is now the English East Midlands. They were bordered by the Brigantes to the north, the Cornovii to the west, the Dobunni and Catuvellauni to the south, and the Iceni to the east. Their capital was called ''Ratae Corieltauvorum'', known today as Leicester. Late Iron Age The Corieltauvi were a largely agricultural people who had few strongly defended sites or signs of centralised government. They appear to have been a federation of smaller, self-governing tribal groups. From the beginning of the 1st century, they began to produce inscribed coins: almost all featured two names, and one series had three, suggesting they had multiple rulers. The names on the earliest coins are so abbreviated as to be unidentifiable. Later coins feature the name of Volisios, apparently the paramount king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornovii (Midlands)
The Cornovīī (Common Brittonic: *''Cornowī'') were a Celtic people of the Iron Age and Roman Britain, who lived principally in the modern English counties of Cheshire, Shropshire, north Staffordshire, north Herefordshire and eastern parts of the Welsh counties of Flintshire, Powys and Wrexham. Their capital in pre-Roman times was probably a hillfort on the Wrekin. Ptolemy's 2nd-century ''Geography'' names two of their towns: Deva Victrix (Chester) and Viroconium Cornoviorum (Wroxeter), which became their capital under Roman rule. Their territory was bordered by the Brigantes to the North, the Corieltauvi to the East, the Dobunni to the South, and the Deceangli, and Ordovices to the West. The people who inhabited the very north of the British mainland (modern Caithness), and Cornwall were also known by the same name, but according to mainstream or academic opinion were quite separate and unrelated peoples. (see list of ancient Celtic peoples and tribes). The problem of trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carvetii
The Carvetii (Common Brittonic: *''Carwetī'') were a Brittonic Celtic tribe living in what is now Cumbria, in North-West England during the Iron Age, and were subsequently identified as a ''civitas'' (canton) of Roman Britain. Etymology The suffix ''carv-'' is related to Welsh ''carw'', Breton ''karv'' and Irish ''carow'' ('deer'). Richard von Kienle has proposed the translation 'those who belong to the deer'.' Location Historical speculation has the Carvetii occupying the Solway Plain, the area immediately south of Hadrian's Wall, the Eden Valley, and possibly the Lune Valley. The Setantii may have occupied North Lancashire and south Cumbria. Evidence of existence The Carvetii are not mentioned in Ptolemy's ''Geography'', nor in any other classical text, and are known only from three Roman (third and fourth century AD) inscriptions, one of which is now lost. One was in Old Penrith, (the Voreda Roman fort) north of the present Penrith, on a tombstone. The others were on tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceni
The Iceni ( , ) or Eceni were a Brittonic tribe of eastern Britain during the Iron Age and early Roman era. Their territory included present-day Norfolk and parts of Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, and bordered the area of the Corieltauvi to the west, and the Catuvellauni and Trinovantes to the south. In the Roman period, their capital was Venta Icenorum at modern-day Caistor St Edmund. Julius Caesar does not mention the Iceni in his account of his invasions of Britain in 55 and 54 BC, though they may be related to the Cenimagni, whom Caesar notes as living north of the River Thames at that time. The Iceni were a significant power in eastern Britain during Claudius' conquest of Britain in AD 43, in which they allied with Rome. Increasing Roman influence on their affairs led to revolt in AD 47, though they remained nominally independent under king Prasutagus until his death around AD 60. Roman encroachment after Prasutagus' death led his wife Boudica to launch a major revolt from 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinovantes
The Trinovantēs (Common Brittonic: *''Trinowantī'') or Trinobantes were one of the Celtic tribes of Pre-Roman Britain. Their territory was on the north side of the Thames estuary in current Essex, Hertfordshire and Suffolk, and included lands now located in Greater London. They were bordered to the north by the Iceni, and to the west by the Catuvellauni. Their name possibly derives from the Celtic intensive prefix "tri-" and a second element which was either "nowio" – new, so meaning "very new" in the sense of "newcomers", but possibly with an applied sense of vigorous or lively ultimately meaning "the very vigorous people". Their capital was Camulodunum (modern Colchester), one proposed site of the legendary Camelot. Shortly before Julius Caesar's invasion of Britain in 55 and 54 BC, the Trinobantes were considered the most powerful tribe in Britain. At this time their capital was probably at Braughing (in modern-day Hertfordshire). In some manuscripts of Caesar's ''Galli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regni
The Regni, Regini, or Regnenses were a Tribe which occupied modern West Sussex, East Sussex, south-west Kent, eastern Surrey, and the eastern edges of Hampshire. Their Tribal centre was at Noviomagus_Reginorum (Chichester in West_Sussex), close to Trisantona Fluvius (the River_Arun) which joined the English_Channel at Littlehampton, a little way to the east of Noviomagus_Reginorum. The tribe was bordered to the west by the Belgae, to the north by the Atrebates, and to the east by the Cantiaci, while much of their northern border was filled by the vast and near-impenetrable Weald Forest. Nevertheless, they were thinly scattered on either side of the Weald, and there were safe paths through the forest. The people of King Cogidubnus Before the Roman conquest, their land and capital appear to have been part of the territory of the Atrebates, possibly as part of a confederation of tribes. It has been suggested that, after the first phase of the conquest, the Romans maintained the At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durotriges
The Durotriges were one of the Celtic tribes living in Britain prior to the Roman invasion. The tribe lived in modern Dorset, south Wiltshire, south Somerset and Devon east of the River Axe and the discovery of an Iron Age hoard in 2009 at Shalfleet, Isle of Wight gives evidence that they may also have lived in the western half of the island. After the Roman conquest, their main ''civitates'', or settlement-centred administrative units, were Durnovaria (modern Dorchester, "the probable original capital") and Lindinis (modern Ilchester, "whose former, unknown status was thereby enhanced"). Their territory was bordered to the west by the Dumnonii; and to the east by the Belgae.__NOTOC__ Name The tribe's name is known from Ptolemy's ''Geography'' and from two inscriptions on Hadrian's Wall, both dating from after the Roman conquest of Britain. It is not known if anyone referred to them as the Durotriges before they arrived in the area now known as Dorset. The name can probably be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornovii (Cornwall)
The Cornovii is a hypothetical name for a tribe presumed to have been part of the Dumnonii, a Celtic tribe inhabiting the south-west peninsula of Great Britain, during some part of the Iron Age, Roman and post-Roman periods. The Cornovii are supposed to have lived at the western end of the peninsula, in the area now known as Cornwall, and if the tribal name were correct it would be the ultimate source of the name of that present-day county. Morris, John (1973) ''The Age of Arthur'' The existence of this sub-tribe, clan or sept, is not mentioned in Ptolemy's 2nd-century ''Geography'', as are many of the other Iron Age tribes in Britain. It has been inferred solely on the basis of a place-name listed in the ''Ravenna Cosmography'' of c. 700 CE as ''purocoronavis'', which is considered to be a scribal error for ''durocornavis'' (or ''durocornovium''Todd (1987), p. 203.), interpreted as meaning "the fortress of the Cornovii".Webster, Graham (1991). ''The Cornovii''; rev. ed. (Peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |