|
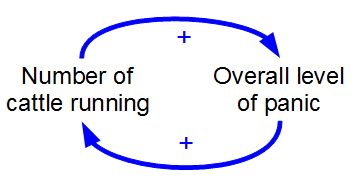
Causal Loop Diagram
A causal loop diagram (CLD) is a causal diagram that aids in visualizing how different variables in a system are causally interrelated. The diagram consists of a set of words and arrows. Causal loop diagrams are accompanied by a narrative which describes the causally closed situation the CLD describes. Closed loops, or causal feedback loops, in the diagram are very important features of CLDs. The words with arrows coming in and out represent variables, or quantities whose value changes over time and the links represent a causal relationship between the two variables (i.e., they do not represent a material flow). A link marked + indicates a positive relation where an increase in the causal variable leads, all else equal, to an increase in the effect variable, or a decrease in the causal variable leads, all else equal, to a decrease in the effect variable. A link marked - indicates a negative relation where an increase in the causal variable leads, all else equal, to a decrease in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CLD Positive ANI
CLD may refer to: Medicine * Cholesterol-lowering drug * Chronic liver disease *Chronic lung disease Transport *Chelsfield railway station in Orpington, London (National Rail station code: CLD) * ChairLift Detachable, a classification of a Detachable chairlift * McClellan–Palomar Airport in CarLsbaD, California (IATA Code: CLD) Science and technology * Causal loop diagram for modeling dynamic systems * The Center for Life Detection, a NASA-supported collaboration of researchers in the science of detecting life beyond the Earth * Chaldean Neo-Aramaic (language), in ISO 639-3 code (list of all codes beginning with "c") * , the clear direction flag instruction on x86 compatible CPUs, opposite of * CLD chromophore in organic chemistry and polymeric nonlinear optics * CLD player, a series of Laserdisc players with CD playback from Pioneer * Color layout descriptor, a summary used in digital image processing to capture the spatial distribution of color in an image * Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adoption CLD
Adoption is a process whereby a person assumes the parenting of another, usually a child, from that person's biological or legal parent or parents. Legal adoptions permanently transfer all rights and responsibilities, along with filiation, from the biological parents to the adoptive parents. Unlike guardianship or other systems designed for the care of the young, adoption is intended to effect a permanent change in status and as such requires societal recognition, either through legal or religious sanction. Historically, some societies have enacted specific laws governing adoption, while others used less formal means (notably contracts that specified inheritance rights and parental responsibility (access and custody), parental responsibilities without an accompanying transfer of filiation). Modern systems of adoption, arising in the 20th century, tend to be governed by comprehensive statutes and regulations. History Antiquity ;Adoption for the well-born While the modern form o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Dynamics
System dynamics (SD) is an approach to understanding the nonlinear behaviour of complex systems over time using stocks, flows, internal feedback loops, table functions and time delays. Overview System dynamics is a methodology and mathematical modeling technique to frame, understand, and discuss complex issues and problems. Originally developed in the 1950s to help corporate managers improve their understanding of industrial processes, SD is currently being used throughout the public and private sector for policy analysis and design. Convenient graphical user interface (GUI) system dynamics software developed into user friendly versions by the 1990s and have been applied to diverse systems. SD models solve the problem of simultaneity (mutual causation) by updating all variables in small time increments with positive and negative feedbacks and time delays structuring the interactions and control. The best known SD model is probably the 1972 '' The Limits to Growth''. This mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, ''A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A''.Keesing, R.M. (1981). Cultural anthropology: A contemporary perspective (2nd ed.) p.149. Sydney: Holt, Rinehard & Winston, Inc. In contrast, a system in which the results of a change act to reduce or counteract it has negative feedback. Both concepts play an important role in science and engineering, including biology, chemistry, and cybernetics. Mathematically, positive feedback is defined as a positive loop gain around a closed loop of cause and effect. That is, positive feedback is in phase with the input, in the sense that it adds to make the input larger. Positive feedback tends to cause system instability. When the loop gain is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances. Whereas positive feedback tends to lead to instability via exponential growth, oscillation or chaotic behavior, negative feedback generally promotes stability. Negative feedback tends to promote a settling to equilibrium, and reduces the effects of perturbations. Negative feedback loops in which just the right amount of correction is applied with optimum timing can be very stable, accurate, and responsive. Negative feedback is widely used in mechanical and electronic engineering, and also within living organisms, and can be seen in many other fields from chemistry and economics to physical systems such as the climate. General negative feedback systems are studied in control systems engineering. Negative feedback l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directed Acyclic Graph
In mathematics, particularly graph theory, and computer science, a directed acyclic graph (DAG) is a directed graph with no directed cycles. That is, it consists of vertices and edges (also called ''arcs''), with each edge directed from one vertex to another, such that following those directions will never form a closed loop. A directed graph is a DAG if and only if it can be topologically ordered, by arranging the vertices as a linear ordering that is consistent with all edge directions. DAGs have numerous scientific and computational applications, ranging from biology (evolution, family trees, epidemiology) to information science (citation networks) to computation (scheduling). Directed acyclic graphs are sometimes instead called acyclic directed graphs or acyclic digraphs. Definitions A graph is formed by vertices and by edges connecting pairs of vertices, where the vertices can be any kind of object that is connected in pairs by edges. In the case of a directed graph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Network
A Bayesian network (also known as a Bayes network, Bayes net, belief network, or decision network) is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph (DAG). Bayesian networks are ideal for taking an event that occurred and predicting the likelihood that any one of several possible known causes was the contributing factor. For example, a Bayesian network could represent the probabilistic relationships between diseases and symptoms. Given symptoms, the network can be used to compute the probabilities of the presence of various diseases. Efficient algorithms can perform inference and learning in Bayesian networks. Bayesian networks that model sequences of variables (''e.g.'' speech signals or protein sequences) are called dynamic Bayesian networks. Generalizations of Bayesian networks that can represent and solve decision problems under uncertainty are called influence diagrams. Graphical m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causal Loop Diagram Of A Model
Causality (also referred to as causation, or cause and effect) is influence by which one event, process, state, or object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the cause is partly responsible for the effect, and the effect is partly dependent on the cause. In general, a process has many causes, which are also said to be ''causal factors'' for it, and all lie in its past. An effect can in turn be a cause of, or causal factor for, many other effects, which all lie in its future. Some writers have held that causality is metaphysically prior to notions of time and space. Causality is an abstraction that indicates how the world progresses. As such a basic concept, it is more apt as an explanation of other concepts of progression than as something to be explained by others more basic. The concept is like those of agency and efficacy. For this reason, a leap of intuition may be needed to grasp it. Accordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balancing Loop
Balance or balancing may refer to: Common meanings * Balance (ability) in biomechanics * Balance (accounting) * Balance or weighing scale * Balance as in equality or equilibrium Arts and entertainment Film * ''Balance'' (1983 film), a Bulgarian film * ''Balance'' (1989 film), a short animated film * '' La Balance'', a 1982 French film Television * '' Balance: Television for Living Well'', a Canadian television talk show * "The Balance" (Roswell), an episode of the television series ''Roswell'' * "The Balance", an episode of the animated series ''Justice League'' * "Balancing" (''Brooklyn Nine-Nine''), an episode of the eighth season of ''Brooklyn Nine-Nine'' *"Balancing", an episode of the television series ''Teletubbies'' Music Performers * Balance (band), a 1980s pop-rock group Albums * ''Balance'' (Akrobatik album), 2003 * ''Balance'' (Kim-Lian album), 2004 * ''Balance'' (Leo Kottke album), 1978 * ''Balance'' (Joe Morris album), 2014 * ''Balance'' (Swollen Members ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causal Diagram
In the philosophy of science, a causal model (or structural causal model) is a conceptual model that describes the causal mechanisms of a system. Causal models can improve study designs by providing clear rules for deciding which independent variables need to be included/controlled for. They can allow some questions to be answered from existing observational data without the need for an interventional study such as a randomized controlled trial. Some interventional studies are inappropriate for ethical or practical reasons, meaning that without a causal model, some hypotheses cannot be tested. Causal models can help with the question of ''external validity'' (whether results from one study apply to unstudied populations). Causal models can allow data from multiple studies to be merged (in certain circumstances) to answer questions that cannot be answered by any individual data set. Causal models have found applications in signal processing, epidemiology and machine learn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CLD Links ANI
CLD may refer to: Medicine * Cholesterol-lowering drug * Chronic liver disease *Chronic lung disease Transport *Chelsfield railway station in Orpington, London (National Rail station code: CLD) * ChairLift Detachable, a classification of a Detachable chairlift * McClellan–Palomar Airport in CarLsbaD, California (IATA Code: CLD) Science and technology * Causal loop diagram for modeling dynamic systems * The Center for Life Detection, a NASA-supported collaboration of researchers in the science of detecting life beyond the Earth * Chaldean Neo-Aramaic (language), in ISO 639-3 code (list of all codes beginning with "c") * , the clear direction flag instruction on x86 compatible CPUs, opposite of * CLD chromophore in organic chemistry and polymeric nonlinear optics * CLD player, a series of Laserdisc players with CD playback from Pioneer * Color layout descriptor, a summary used in digital image processing to capture the spatial distribution of color in an image * Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magoroh Maruyama
Magoroh Maruyama (April 29, 1929 – March 16, 2018) was a Japanese/American business educator, consultant and researcher, best known for his contributions to cybernetics.Holloman, R. E., & Arutiunov, S. A. (Eds.). (1978). ''Perspectives on ethnicity''. Walter de Gruyter. Biography Maruyama was born in 1929 in Tokyo, Japan, son of Shinsaku Maruyama and Toyoko (Takashima) Maruyama, and moved to the United States in 1950. He received his B.A. from the University of California at Berkeley in 1951. After postgraduate studies at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich and the University of Heidelberg, he obtained his Ph.D. from the University of Lund in Sweden. Maruyama started his academic career as assistant professor in human development at the University of California at Berkeley in 1960. Among his many academic appointments he was professor for Systems Science at Portland State University from 1973 to 1976. He was also Professor in the School of International Politics, Economic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |