|
Casco Class Cutter
The ''Casco'' class was a large class of United States Coast Guard cutters in commission from the late 1940s through the late 1980s. They saw service as weather reporting ships in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans until the early 1970s, and some saw combat service during the Vietnam War. Design Between 1941 and 1946, the United States Navy acquired 35 ''Barnegat''-class small seaplane tenders, designated "AVP" in the Navys alphanumeric hull numbering system and designed to logistically and administratively support a squadron of flying boats operating from undeveloped areas and, with a substantial anti-air, antisurface, and antisubmarine capability, to escort larger seaplane tenders. Most of them served during World War II, although even during the war the Navy determined the number of ''Barnegat''s to be surplus to requirements; as a result, one was completed as a catapult training ship for Navy floatplane pilots (retaining its "AVP" designation) and four were converted duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puget Sound Navy Yard
Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, officially Puget Sound Naval Shipyard and Intermediate Maintenance Facility (PSNS & IMF), is a United States Navy shipyard covering 179 acres (0.7 km2) on Puget Sound at Bremerton, Washington in uninterrupted use since its establishment in 1891; it has also been known as Navy Yard Puget Sound, Bremerton Navy Yard, and the Bremerton Naval Complex. It is bordered on the south by Sinclair Inlet, on the west by the Bremerton Annex of Naval Base Kitsap, and on the north and east by the city of Bremerton, Washington. It is the Pacific Northwest's largest naval shore facility and one of Washington state's largest industrial installations. PSNS & IMF provides the Navy with maintenance, modernization, and technical and logistics support, and employs 14,000 people. History Puget Sound Naval Shipyard was established in 1891 as a Naval Station and was designated Navy Yard Puget Sound in 1901. During World War I, the Navy Yard constructed ships, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedgehog (weapon)
The Hedgehog (also known as an ''Anti-Submarine Projector'') was a forward-throwing anti-submarine weapon that was used primarily during the Second World War. The device, which was developed by the Royal Navy, fired up to 24 spigot mortars ahead of a ship when attacking a U-boat. It was deployed on convoy escort warships such as destroyers and corvettes to supplement the depth charges. As the mortar projectiles employed contact fuzes rather than time or barometric (depth) fuzes, detonation occurred directly against a hard surface such as the hull of a submarine making it more deadly than depth charges, which relied on damage caused by hydrostatic shockwaves. During WWII out of 5,174 British depth charge attacks there were 85.5 kills, a ratio of 60.5 to 1. In comparison, the Hedgehog made 268 attacks for 47 kills, a ratio of 5.7 to 1. Development The "Hedgehog", so named because the empty rows of its launcher spigots resembled the spines on the back of a hedgehog, was a repla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying Boat
A flying boat is a type of fixed-winged seaplane with a hull, allowing it to land on water. It differs from a floatplane in that a flying boat's fuselage is purpose-designed for floatation and contains a hull, while floatplanes rely on fuselage-mounted floats for buoyancy. Though the fuselage provides buoyancy, flying boats may also utilize under-wing floats or wing-like projections (called sponsons) extending from the fuselage for additional stability. Flying boats often lack landing gear which would allow them to land on the ground, though many modern designs are convertible amphibious aircraft which may switch between landing gear and flotation mode for water or ground takeoff and landing. Ascending into common use during the First World War, flying boats rapidly grew in both scale and capability during the interwar period, during which time numerous operators found commercial success with the type. Flying boats were some of the largest aircraft of the first half of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squadron (aviation)
A squadron in air force, army aviation, or naval aviation is a unit comprising a number of military aircraft and their aircrews, usually of the same type, typically with 12 to 24 aircraft, sometimes divided into three or four flights, depending on aircraft type and air force. Land-based squadrons equipped with heavier type aircraft such as long-range bombers, cargo aircraft, or air refueling tankers have around 12 aircraft as a typical authorization, while most land-based fighter equipped units have an authorized number of 18 to 24 aircraft. In naval aviation, sea-based and land-based squadrons will typically have smaller numbers of aircraft, ranging from as low as four for early warning to as high as 12 for fighter/attack. In most armed forces, two or more squadrons will form a group or a wing. Some military forces (including the United States Air Force, United States Space Force, Royal Air Force, Royal Netherlands Air Force, Belgian Air Component, German Air Force, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hull Code
The United States Navy, United States Coast Guard, and United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) use a hull classification symbol (sometimes called hull code or hull number) to identify their ships by type and by individual ship within a type. The system is analogous to the pennant number system that the Royal Navy and other European and Commonwealth navies use. History United States Navy The U.S. Navy began to assign unique Naval Registry Identification Numbers to its ships in the 1890s. The system was a simple one in which each ship received a number which was appended to its ship type, fully spelled out, and added parenthetically after the ship's name when deemed necessary to avoid confusion between ships. Under this system, for example, the battleship ''Indiana'' was USS ''Indiana'' (Battleship No. 1), the cruiser ''Olympia'' was USS ''Olympia'' (Cruiser No. 6), and so on. Beginning in 1907, some ships also were referred to alternati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnegat Class Small Seaplane Tender
The ''Barnegat'' class was a large class of United States Navy small seaplane tenders (AVP) built during World War II. Thirty were completed as seaplane tenders, four as motor torpedo boat tenders, and one as a catapult training ship.''Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1922–1946'', p. 157 Design Before World War II, the United States Navy foresaw a need for a large force of seaplane tenders in the event of a war in the Pacific, to allow air operations from undeveloped islands and atolls. Full-size seaplane tenders (AVs) were designed to support two squadrons of flying boats each, but they were more expensive to build and had a deep draft, precluding their use in shallow harbors. The U.S. Navy therefore also planned for "small seaplane tenders" (AVPs), with a shallower draft, capable of supporting only one squadron each, but cheaper to build and able to operate in shallow waters. The AVPs were not the descendants of the "seaplane tenders (destroyer)" (AVDs); those had b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage (4,635,628 tonnes as of 2019) and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft . The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during the American Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was United States in the Vietnam War, supported by the United States and other anti-communism, anti-communist Free World Military Forces, allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975. After the French 1954 Geneva Conference, military withdrawal from Indochina in 1954 – following their defeat in the First Indochina War – the Viet Minh to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of Earth, the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North America, North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8th paralle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
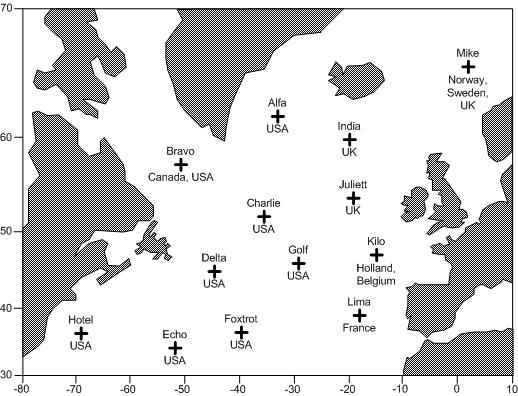
Weather Ship
A weather ship, or ocean station vessel, was a ship stationed in the ocean for surface and upper air meteorological observations for use in weather forecasting. They were primarily located in the north Atlantic and north Pacific oceans, reporting via radio. The vessels aided in search and rescue operations, supported transatlantic flights, acted as research platforms for oceanographers, monitored marine pollution, and aided weather forecasting by weather forecasters and in computerized atmospheric models. Research vessels remain heavily used in oceanography, including physical oceanography and the integration of meteorological and climatological data in Earth system science. The idea of a stationary weather ship was proposed as early as 1921 by Météo-France to help support shipping and the coming of transatlantic aviation. They were used during World War II but had no means of defense, which led to the loss of several ships and many lives. On the whole, the establishment of wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Coast Guard
The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is the maritime security, search and rescue, and law enforcement service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the country's eight uniformed services. The service is a maritime, military, multi-mission service unique among the United States military branches for having a maritime law enforcement mission with jurisdiction in both domestic and international waters and a federal regulatory agency mission as part of its duties. It is the largest and most powerful coast guard in the world, rivaling the capabilities and size of most navies. The U.S. Coast Guard is a humanitarian and security service. It protects the United States' borders and economic and security interests abroad; and defends its sovereignty by safeguarding sea lines of communication and commerce across vast territorial waters spanning 95,000 miles of coastline and its Exclusive Economic Zone. With national and economic security depending upon open global t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)