|
Cardinals Created By Honorius II
Pope Honorius II (r. 1124–1130) created 27 cardinals in six consistories held throughout his pontificate. This included his successors Anastasius IV and Celestine II both in 1127. 1124 * Guido 1125 * Gregorio * Uberto Ratta * Alberico Tomacelli * Rodolfo degli Armanni della Staffa * Stefano * Ugo Geremei * Cosma * Pietro dei Garsendi 1126 * Mathieu O.S.B. Clun. * Giovanni O.S.B. Clun. * Sigizzo Bianchelli ''iuniore'' * Gregorio * Matteo * Anselmo Can. Reg. * Pierre * Gian Roberto Capizucchi 1127 * Bennone de' Cocliti * Guido di Castello * Pierre 1128 * Joselmo * Rustico * Rustico de' Rustici 1129 * Errico * Gerardo * Matteo Notes and references Sources * {{Authority control College of Cardinals Honorius II Pope Honorius II (9 February 1060 – 13 February 1130), born Lamberto Scannabecchi,Levillain, pg. 731 was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 21 December 1124 to his death in 1130. Although from a humble background, ... 12th-ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
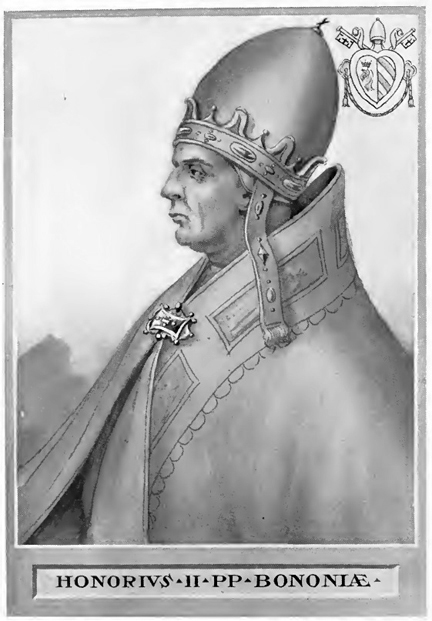
Pope Honorius II
Pope Honorius II (9 February 1060 – 13 February 1130), born Lamberto Scannabecchi,Levillain, pg. 731 was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 21 December 1124 to his death in 1130. Although from a humble background, his obvious intellect and outstanding abilities saw him promoted up through the ecclesiastical hierarchy. Attached to the Frangipani family of Rome, his election as pope was contested by a rival candidate, Celestine II, and force was used to guarantee his election. Honorius's pontificate was concerned with ensuring that the privileges the Roman Catholic Church had obtained through the Concordat of Worms were preserved and, if possible, extended. He was the first pope to confirm the election of the Holy Roman emperor. Distrustful of the traditional Benedictine order, he favoured new monastic orders, such as the Augustinians and the Cistercians, and sought to exercise more control over the larger monastic centres of Monte Cassino and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papal Consistory
In the Roman Catholic Church a consistory is a formal meeting of the College of Cardinals called by the pope. There are two kinds of consistories, extraordinary and ordinary. An "extraordinary" consistory is held to allow the pope to consult with the entire membership of the College of Cardinals. An "ordinary" consistory is ceremonial in nature and attended by cardinals resident in Rome. For example, the pope elevates new cardinals to the College at a consistory; Pope Francis has called consistories for ceremonies of canonization. A meeting of the College of Cardinals to elect a new pope is not a consistory, but a conclave. History The term ''consistory'' comes from the la, con-sistere; "stand together".''Papal Consistory'' by Kevin Knight (Catholic Encyclopedia, 2009) Early popes conferred with their Roman presbytery which include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Anastasius IV
Pope Anastasius IV ( – 3 December 1154), born Corrado Demetri della Suburra, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 July 1153 to his death in 1154. He is the most recent pope to take the name "Anastasius" upon his election. Early life He was a Roman, son of Benedictus de Suburra, probably of the family of Demetri, and became a secular clerk. He was created cardinal-priest of S. Pudenziana by Pope Paschal II no later than in 1114. In 1127 or 1128, Pope Honorius II promoted him to the suburbicarian See of Sabina. He was probably given this position for siding with Honorius II during a dispute over the appointment of a new abbot of Farfa. He had taken part in the double papal election of 1130, had been one of the most determined opponents of Antipope Anacletus II and, when Pope Innocent II fled to France, had been left behind as his vicar in Italy. At the time of his election to the papacy in July 1153, he was Dean of the College of Cardinals and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Celestine II
Pope Celestine II ( la, Caelestinus II; died 8 March 1144), born Guido di Castello,Thomas, pg. 91 was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 26 September 1143 to his death in 1144. Early life Guido di Castello, possibly the son of a local noble, Niccolo di Castello,Mann, pg. 105 was born either in Città di Castello, situated in Paterna Santa Felicità upon the Apennines, or at Macerata in the March of Ancona.Mann, pg. 105 Guido had studied under Pierre Abélard, and eventually became a distinguished master in the schools.Mann, pg. 105 Eventually Guido began his career in Rome as a subdeacon and a ''scriptor apostolicus'' under Pope Callixtus II.Mann, pg. 105 He was created Cardinal-Deacon of Santa Maria in Via Lata by Pope Honorius II in 1127;Mann, pg. 106 as such, he signed the papal bulls issued between 3 April 1130 and 21 December 1133. In the double papal election, 1130, papal election of 1130 he joined the obedience of Pope Innocent II. In December ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uberto Lanfranchi
Uberto Lanfranchi (or Humbert) (died 1137) was the Cardinal-deacon of Santa Maria in Via Lata (appointed by Pope Calixtus II no later than 1123), then the Cardinal-priest of San Clemente (appointed by Honorius II in 1126), and finally the Archbishop of Pisa (appointed by Innocent II in 1132/3). Lanfranchi was from northern Italy, either from Pisa, where he had been a regular canon, or from Bologna. Richard A. Fletcher (1984), ''Saint James's Catapult: The Life and Times of Diego Gelmírez of Santiago de Compostela'' (Oxford: Clarendon Press), 216. Uberto subscribed a Papal bull on 6 April 1123 when he was a cardinal-deacon and as cardinal-priest he undersigned bulls between 28 March 1126 and 2 September 1133. In 1129 Humber was sent as a Papal legate to the Kingdom of León. Upon his arrival (probably late in 1129 or in the early days of 1130) he met with Diego Gelmírez, the Archbishop of Santiago de Compostela and an important intermediary between the Papacy and king Alfonso VI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida International University
Florida International University (FIU) is a public research university with its main campus in Miami-Dade County. Founded in 1965, the school opened its doors to students in 1972. FIU has grown to become the third-largest university in Florida and the fifth-largest public university in the United States by enrollment. FIU is a constituent part of the State University System of Florida. In 2021, it was ranked #1 in the Florida Board of Governors performance funding, and had over $246 million in research expenditures. The university is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". FIU has 11 colleges and more than 40 centers, facilities, labs, and institutes that offer more than 200 programs of study. It has an annual budget of over $1.7 billion and an annual economic impact of over $5 billion. The university is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools (SACS). FIU's intercollegiate sports teams, the FIU Panthers, compete i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
College Of Cardinals
The College of Cardinals, or more formally the Sacred College of Cardinals, is the body of all cardinals of the Catholic Church. its current membership is , of whom are eligible to vote in a conclave to elect a new pope. Cardinals are appointed by the pope for life. Changes in life expectancy partly account for the increases in the size of the college.Broderick, 1987, p. 13. Since the emergence of the College of Cardinals in the early Middle Ages, the size of the body has historically been limited by popes, ecumenical councils, and even the College itself. The total number of cardinals from 1099 to 1986 has been about 2,900 (excluding possible undocumented 12th-century cardinals and pseudocardinals appointed during the Western Schism by pontiffs now considered to be antipopes, and subject to some other sources of uncertainty), nearly half of whom were created after 1655.Broderick, 1987, p. 11. History The word ''cardinal'' is derived from the Latin ''cardō'', meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lists Of Cardinals By Papal Appointment
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union club Other uses * Angle of list, the leaning to either port or starboard of a ship * List (information), an ordered collection of pieces of information ** List (abstract data type), a method to organize data in computer science * List on Sylt, previously called List, the northernmost village in Germany, on the island of Sylt * ''List'', an alternative term for ''roll'' in flight dynamics * To ''list'' a building, etc., in the UK it means to designate it a listed building that may not be altered without permission * Lists (jousting), the barriers used to designate the tournament area where medieval knights jousted * ''The Book of Lists'', an American series of books with unusual lists See also * The List (other) * Listing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th-century Cardinals
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |