|
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
Cardiac resynchronisation therapy (CRT or CRT-P) is the insertion of electrodes in the left and right ventricles of the heart, as well as on occasion the right atrium, to treat heart failure by coordinating the function of the left and right ventricles via a pacemaker, a small device inserted into the anterior chest wall. CRT is indicated in patients with a low ejection fraction (typically 120 ms. The insertion of electrodes into the ventricles is done under local anesthetic, with access to the ventricles most commonly via the subclavian vein, although access may be conferred from the axillary or cephalic veins. Right ventricular access is direct, while left ventricular access is conferred via the coronary sinus (CS). CRT defibrillators (CRT-D) also incorporate the additional function of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), to quickly terminate an abnormally fast, life-threatening heart rhythm. CRT and CRT-D have become increasingly important therapeutic options ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials depending on the type of battery. The electrophore, invented by Johan Wilcke, was an early version of an electrode used to study static electricity. Anode and cathode in electrochemical cells Electrodes are an essential part of any battery. The first electrochemical battery made was devised by Alessandro Volta and was aptly named the Voltaic cell. This battery consisted of a stack of copper and zinc electrodes separated by brine-soaked paper disks. Due to fluctuation in the voltage provided by the voltaic cell it wasn't very practical. The first practical battery was invented in 1839 and named the Daniell cell after John Frederic Daniell. Still making use of the zinc–copper electrode combination. Since then many more batteries have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute For Health And Care Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care in England that publishes guidelines in four areas: * the use of health technologies within England's National Health Service (NHS) and NHS Wales (such as the use of new and existing medicines, treatments and procedures) * clinical practice (guidance on the appropriate treatment and care of people with specific diseases and conditions) * guidance for public sector workers on health promotion and ill-health avoidance * guidance for social care services and users. These appraisals are based primarily on evidence-based evaluations of efficacy, safety and cost-effectiveness in various circumstances. It serves both the English NHS and the Welsh NHS. It was set up as the National Institute for Clinical Excellence in 1999, and on 1 April 2005 joined with the Health Development Agency to become the new National Institute for Health a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericardial Effusion
A pericardial effusion is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardial cavity. The pericardium is a two-part membrane surrounding the heart: the outer fibrous connective membrane and an inner two-layered serous membrane. The two layers of the serous membrane enclose the pericardial cavity (the potential space) between them.Phelan, D., Collier, P., Grimm, R. Pericardial Disease'. Cleveland Clinic. July 2015. Retrieved Nov 2020. This pericardial space contains a small amount of pericardial fluid. The fluid is normally 15-50 mL in volume. The pericardium, specifically the pericardial fluid provides lubrication, maintains the anatomic position of the heart in the chest, and also serves as a barrier to protect the heart from infection and inflammation in adjacent tissues and organs.Vogiatzidis, Konstantinos et al.Physiology of pericardial fluid production and drainage" ''Frontiers in physiology'' vol. 6 62. 18 Mar. 2015, doi:10.3389/fphys.2015.00062 By definition, a pericardial e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
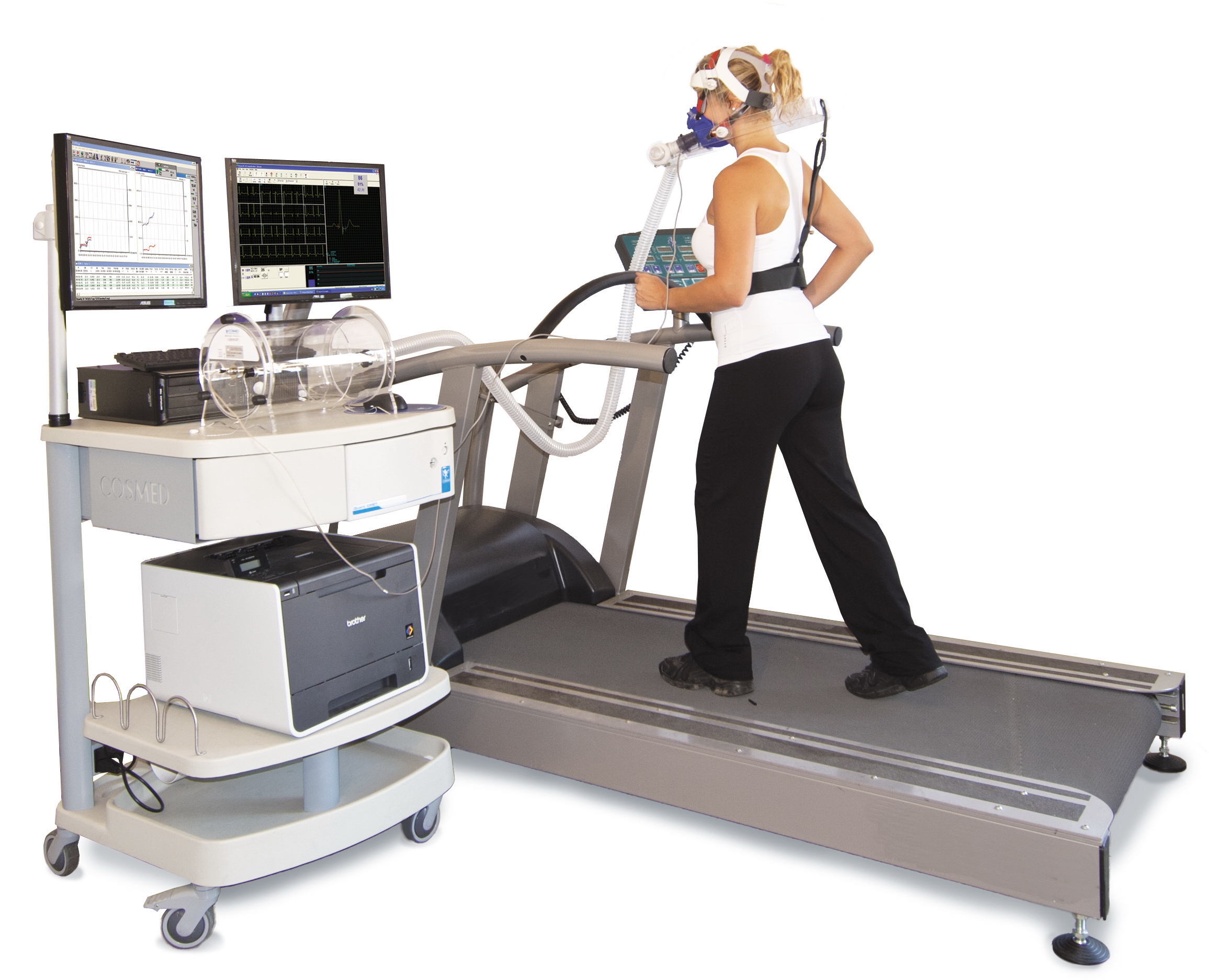
Vo2 Max
VO2 max (also maximal oxygen consumption, maximal oxygen uptake or maximal aerobic capacity) is the maximum rate of oxygen consumption attainable during physical exertion. The name is derived from three abbreviations: "V̇" for volume (the dot appears over the V to indicate "per unit of time"), "O2" for oxygen, and "max" for maximum. A similar measure is VO2 peak (peak oxygen consumption), which is the measurable value from a session of physical exercise, be it incremental or otherwise. It could match or underestimate the actual VO2 max. Confusion between the values in older and popular fitness literature is common. The measurement of V̇O2 max in the laboratory provides a quantitative value of endurance fitness for comparison of individual training effects and between people in endurance training. Maximal oxygen consumption reflects cardiorespiratory fitness and endurance capacity in exercise performance. Elite athletes, such as competitive distance runners, racing cyclists or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular Remodeling
In cardiology, ventricular remodeling (or cardiac remodeling) refers to changes in the size, shape, structure, and function of the heart. This can happen as a result of exercise (physiological remodeling) or after injury to the heart muscle (pathological remodeling). The injury is typically due to acute myocardial infarction (usually transmural or ST segment elevation infarction), but may be from a number of causes that result in increased pressure or volume, causing pressure overload or volume overload (forms of strain) on the heart. Chronic hypertension, congenital heart disease with intracardiac shunting, and valvular heart disease may also lead to remodeling. After the insult occurs, a series of histopathological and structural changes occur in the left ventricular myocardium that lead to progressive decline in left ventricular performance. Ultimately, ventricular remodeling may result in diminished contractile (systolic) function and reduced stroke volume. Physiological remodeli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Cardiac Pacemaker
An artificial cardiac pacemaker (or artificial pacemaker, so as not to be confused with the natural cardiac pacemaker) or pacemaker is a medical device that generates electrical impulses delivered by electrodes to the chambers of the heart either the upper atria, or lower ventricles to cause the targeted chambers to contract and pump blood. By doing so, the pacemaker regulates the function of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The primary purpose of a pacemaker is to maintain an adequate heart rate, either because the heart's natural pacemaker is not fast enough, or because there is a block in the heart's electrical conduction system. Modern pacemakers are externally programmable and allow a cardiologist, particularly a cardiac electrophysiologist, to select the optimal pacing modes for individual patients. Most pacemakers are on demand, in which the stimulation of the heart is based on the dynamic demand of the circulatory system. Others send out a fixed rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronary Circulation
Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle (myocardium). Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Cardiac veins then drain away the blood after it has been deoxygenated. Because the rest of the body, and most especially the brain, needs a steady supply of oxygenated blood that is free of all but the slightest interruptions, the heart is required to function continuously. Therefore its circulation is of major importance not only to its own tissues but to the entire body and even the level of consciousness of the brain from moment to moment. Interruptions of coronary circulation quickly cause heart attacks (myocardial infarctions), in which the heart muscle is damaged by oxygen starvation. Such interruptions are usually caused by coronary ischemia linked to coronary artery disease, and sometimes to embolism from other causes like obstruction in blood flow through vessels. Structure Coronary arteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venography
Venography (also called phlebography or ascending phlebography) is a procedure in which an x-ray of the veins, a venogram, is taken after a special dye is injected into the bone marrow or veins. The dye has to be injected constantly via a catheter, making it an invasive procedure. Normally the catheter is inserted by the groin and moved to the appropriate site by navigating through the vascular system. Contrast venography is the gold standard for judging diagnostic imaging methods for deep venous thrombosis; although, because of its cost, invasiveness, and other limitations this test is rarely performed. Venography can also be used to distinguish blood clots from obstructions in the veins, to evaluate congenital vein problems, to see how the deep leg vein valves are working, or to identify a vein for arterial bypass grafting. Areas of the venous system that can be investigated include the lower extremities, the inferior vena cava, and the upper extremities. The United States Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrast Agent
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radiopharmaceuticals, which emit radiation themselves. In x-rays, contrast agents enhance the radiodensity in a target tissue or structure. In MRIs, contrast agents shorten (or in some instances increase) the relaxation times of nuclei within body tissues in order to alter the contrast in the image. Contrast agents are commonly used to improve the visibility of blood vessels and the gastrointestinal tract. Several types of contrast agent are in use in medical imaging and they can roughly be classified based on the imaging modalities where they are used. Most common contrast agents work based on X-ray attenuation and magnetic resonance signal enhancement. Radiocontrast media For radiography, which is based on X-rays, iodine and barium are the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Catheters are manufactured for specific applications, such as cardiovascular, urological, gastrointestinal, neurovascular and ophthalmic procedures. The process of inserting a catheter is ''catheterization''. In most uses, a catheter is a thin, flexible tube (''soft'' catheter) though catheters are available in varying levels of stiffness depending on the application. A catheter left inside the body, either temporarily or permanently, may be referred to as an "indwelling catheter" (for example, a peripherally inserted central catheter). A permanently inserted catheter may be referred to as a "permcath" (originally a trademark). Catheters can be inserted into a body cavity, duct, or vessel, brain, skin or adipose tissue. Functionally, they all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asystole
Asystole (New Latin, from Greek privative a "not, without" + ''systolē'' "contraction") is the absence of ventricular contractions in the context of a lethal heart arrhythmia (in contrast to an induced asystole on a cooled patient on a heart-lung machine and general anesthesia during surgery necessitating stopping the heart). Asystole is the most serious form of cardiac arrest and is usually irreversible. Also referred to as cardiac flatline, asystole is the state of total cessation of electrical activity from the heart, which means no tissue contraction from the heart muscle and therefore no blood flow to the rest of the body. Asystole should not be confused with very brief pauses in the heart's electrical activity—even those that produce a temporary flatline—that can occur in certain less severe abnormal rhythms. Asystole is different from very fine occurrences of ventricular fibrillation, though both have a poor prognosis, and untreated fine VF will lead to asystole. Fault ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Conduction System Of The Heart
The cardiac conduction system (CCS) (also called the electrical conduction system of the heart) transmits the signals generated by the sinoatrial node – the heart's pacemaker, to cause the heart muscle to contract, and pump blood through the body's circulatory system. The pacemaking signal travels through the right atrium to the atrioventricular node, along the bundle of His, and through the bundle branches to Purkinje fibers in the walls of the ventricles. The Purkinje fibers transmit the signals more rapidly to stimulate contraction of the ventricles. The conduction system consists of specialized heart muscle cells, situated within the myocardium. There is a skeleton of fibrous tissue that surrounds the conduction system which can be seen on an ECG. Dysfunction of the conduction system can cause irregular heart rhythms including rhythms that are too fast or too slow. Structure Electrical signals arising in the SA node (located in the right atrium) stimulate the atr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |