|
Carbonyl Olefin Metathesis
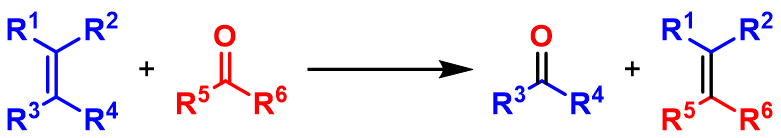
Carbonyl olefin metathesis is a type of Olefin metathesis, metathesis reaction that entails, formally, the redistribution of fragments of an alkene and a Carbonyl group, carbonyl by the scission and regeneration of carbon-carbon and carbon-oxygen double bonds respectively. It is a powerful method in organic synthesis using simple carbonyls and olefins and converting them into less accessible products with higher structural complexity. Photochemical conditions The carbonyl–olefin metathesis reaction can proceed stepwise under Photochemistry, photochemical conditions, where in the first step irradiation by a light source induces a [2+2] cycloaddition between a carbonyl and olefin, known as the Paternò–Büchi reaction. The isolated oxetane intermediate can subsequently be fragmented into a new carbonyl and olefin product under thermal or acidic conditions. Metal-mediated process The metal-mediated processes include a carbonyl-olefination and an Olefin metathesis, olefin–ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olefin Metathesis
Olefin metathesis is an organic reaction that entails the redistribution of fragments of alkenes (olefins) by the scission and regeneration of carbon-carbon double bonds. Because of the relative simplicity of olefin metathesis, it often creates fewer undesired by-products and hazardous wastes than alternative organic reactions. For their elucidation of the reaction mechanism and their discovery of a variety of highly active catalysts, Yves Chauvin, Robert H. Grubbs, and Richard R. Schrock were collectively awarded the 2005 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Catalysts The reaction requires metal catalysts. Most commercially important processes employ heterogeneous catalysts. The heterogeneous catalysts are often prepared by in-situ activation of a metal halides (MClx) using organoaluminium or organotin compounds, e.g. combining MClx–EtAlCl2. A typical catalyst support is alumina. Commercial catalysts are often based on molybdenum and ruthenium. Well-defined organometallic co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |