|
Cao E
Cao E (Chinese: 曹娥, pinyin: Cáo É) (130–143), was a young girl from Shangyu District, Shaoxing, Zhejiang Province in China. She was the daughter of the shaman Cao Xu. The girl died in the year 143 while trying to save her father from drowning. In the year 151 a temple was built for her and the river in which she and her father drowned, was named after her. Life Cao Xu (曹盱) was the father of Cao E. He was a shaman who led local ceremonies at Shangyu. At the ceremony of the Dragon Boat Festival in the year 143, Cao Xu fell into the Shun river. A large-scale search was launched that lasted 17 days, but yielded nothing. Cao E, his daughter of 13 years old, decided in the course of filial piety (孝, ''xiao'') to search for her father in the river. After five days, she appeared above water with her father in her arms, both dead from drowning. This act made Cao E a very famous girl, a textbook example of filial piety. The veneration of the girl started right away ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao'e Stele
During the Eastern Han Dynasty in the year 143, Cao E drowned at the age of 13 in the Shun River while trying to save her father from drowning. In the year 151, a temple and a stele was made for her to honor Cao E. The original stele was lost over time but in the year 1093 (Northern Song Dynasty), Cai Bian (蔡卞) made a replacement stele. This stele is 2.1 metres high and 1 metre wide and is entitled: "The stele of Cao E, the filial piety daughter" and has become a historical monument. The stele is placed in the Cao'e Temple in the Shangyu District, Shaoxing in the northeast of Zhejiang Province in China. The stele's text was commissioned by . It was written by Handan Chun Handan Chun (), courtesy name Zishu () or Zili (), also known as Handan Zhu (), was a writer, calligrapher, and official from Yingchuan Commandery (modern day Yuzhou, Henan) who served the state of Cao Wei during the early 3rd century. As a cal ... after failed complete it. References {{Subject bar, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Shuang Pu
''Wu Shuang Pu'' () is a book of woodcut prints, first printed in 1694, early on in the Qing dynasty. This book contains the biographies and imagined portraits of 40 notable heroes and heroines from the Han Dynasty to the Song Dynasty, all accompanied by a brief introduction and guided by a related poem in yuefu style. The illustrations from the book were widely distributed and re-used, often as motifs on Chinese porcelain. The original book has a seal what says Nanling, that's why the book is also known as Nanling Wu Shuang Pu. A re-edition of this book from the year 1699 is kept in the National Museum of China. In January 2006, an original hand-painted book of Wu Shuang Pu was sold at the Chongyuan auction house in Shanghai for 2.86 million CNY, some 440,000 Dollar (GBP 320,000). The scholar and philologist Mao Qiling praised the book in the preface, he felt that the prose in this book formed a trinity with the poems and prints. The painter of Wu Shuang Pu is Jin Shi (金� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hangzhou Bay
Hangzhou Bay, or the Bay of Hangzhou (), is a funnel-shaped inlet of the East China Sea, bordered by the province of Zhejiang and the municipality of Shanghai, which lies north of the Bay. The Bay extends from the East China Sea to its head at the city of Hangzhou, from which its name is derived. At Hangzhou, the Qiantang River flows into this Bay, providing freshwater from the West while seawater comes in from the East. Thus, Hangzhou Bay, especially its western end, is sometimes called in the scientific literature as the Qiantang River Estuary. At the southeast end of Hangzhou Bay, off Ningbo, are many small islands that are collectively called the Zhoushan Islands. This archipelago of islands is urbanized with the administrative status of a prefecture-level city in Zhejiang Province. At less than 15 meters in depth, the entire Bay is relatively shallow. Consequently, the main port in the Bay area is the one in Ningbo and Zhoushan, at the southeast end of the Bay on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Language
Chinese (, especially when referring to written Chinese) is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and many minority ethnic groups in Greater China. About 1.3 billion people (or approximately 16% of the world's population) speak a variety of Chinese as their first language. Chinese languages form the Sinitic branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages family. The spoken varieties of Chinese are usually considered by native speakers to be variants of a single language. However, their lack of mutual intelligibility means they are sometimes considered separate languages in a family. Investigation of the historical relationships among the varieties of Chinese is ongoing. Currently, most classifications posit 7 to 13 main regional groups based on phonetic developments from Middle Chinese, of which the most spoken by far is Mandarin (with about 800 million speakers, or 66%), followed by Min (75 million, e.g. Southern Min), Wu (74 million, e.g. Shangh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic (Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in the 8th and 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiaocao'ezhen
Xiaocao'e () (pinyin: xiǎo Cáo É) is a town located in the administrative territorial entity of Yuyao, Ningbo, Zhejiang province, China, established in 1949 and named after Cao E (130-143), the filial piety daughter who drowns when she tries to save her father. Xiaocao'e has a densely populated area of 33.4 square kilometres with a population of 40400 (2017) and the town contains eight administrative territorial entities, one of them is Cao'ecun (Cao E village). The town is situated approx 50 km from the harbour of Ningbo and is known for her industry, fruit, honey, mustard, pepper and cotton. In October 2021 this town was chosen to one of the 1000 top towns in China at place 553. Climate The region around Xiaocao'e has a warm and temperate climate without a dry season but with a lot of rain in the hot summers, a climate classification Cfa according to Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filial Piety
In Confucianism, Chinese Buddhism, and Daoist ethics, filial piety (, ''xiào'') (Latin: pietas) is a virtue of respect for one's parents, elders, and ancestors. The Confucian ''Classic of Filial Piety'', thought to be written around the late Warring States-Qin-Han period, has historically been the authoritative source on the Confucian tenet of filial piety. The book—a purported dialogue between Confucius and his student Zengzi—is about how to set up a good society using the principle of filial piety. Filial piety is central to Confucian role ethics. In more general terms, filial piety means to be good to one's parents; to take care of one's parents; to engage in good conduct, not just towards parents but also outside the home so as to bring a good name to one's parents and ancestors; to show love, respect, and support; to display courtesy; to ensure male heirs; to uphold fraternity among brothers; to wisely advise one's parents, including dissuading them from moral unrighte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb
A tomb ( grc-gre, τύμβος ''tumbos'') is a :wikt:repository, repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be called ''immurement'', and is a method of Disposal of human corpses, final disposition, as an alternative to cremation or burial. Overview The word is used in a broad sense to encompass a number of such types of places of interment or, occasionally, grave (burial), burial, including: * Shrine, Architectural shrines – in Christianity, an architectural shrine above a saint's first grave (burial), place of burial, as opposed to a similar shrine on which stands a reliquary or feretory into which the saint's remains have been transferred * Burial vault (tomb), Burial vault – a stone or brick-lined underground space for multiple burials, originally vault (architecture), vaulted, often privately owned for specific family groups; usually benea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
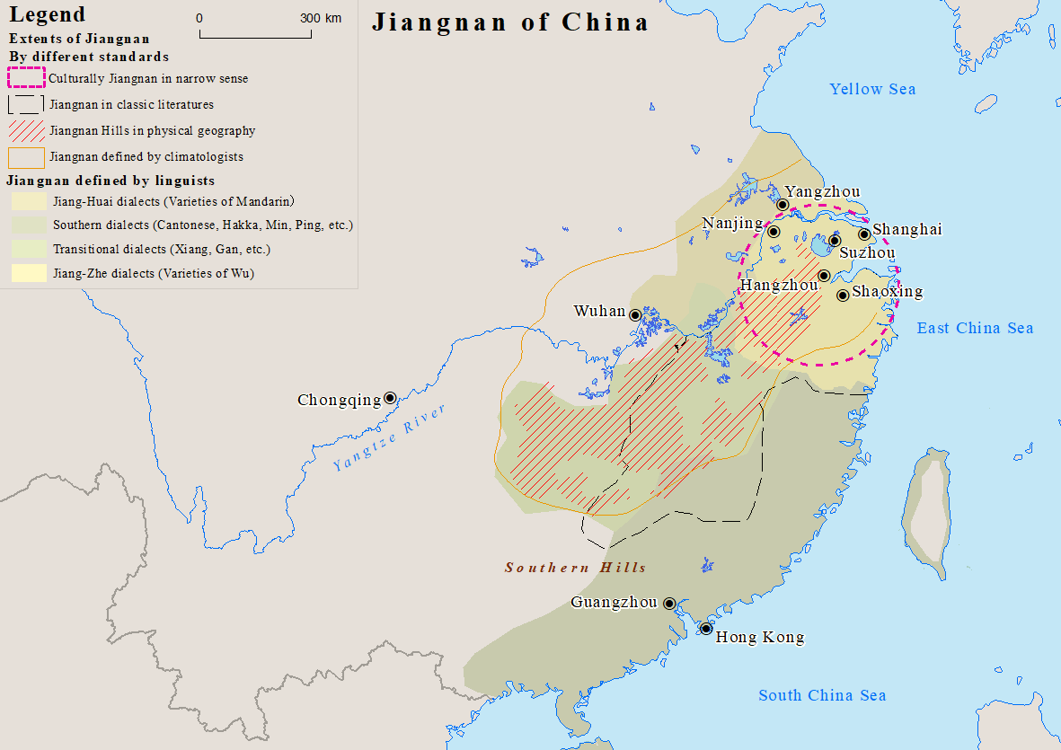
Jiangnan
Jiangnan or Jiang Nan (; formerly romanized Kiang-nan, literally "South of the River" meaning "South of the Yangtze") is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, including the southern part of its delta. The region encompasses the city of Shanghai, the southern part of Jiangsu Province, the southeastern part of Anhui Province, the northern part of Jiangxi Province and the northern part of Zhejiang Province. The most important cities in the area include Anqing, Changzhou, Hangzhou, Nanjing, Ningbo, Shaoxing, Suzhou, Wuxi, Wenzhou, and Zhenjiang. Jiangnan has long been regarded as one of the most prosperous regions in China due to its wealth in trade and very high human development. Most people of the region speak Wu Chinese dialects as their native languages. Etymology The word Jiangnan is based on the Chinese name for the Yangtze, ''Cháng Jiāng'', and ''nán'' meaning "south." In the 19th century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memorial Service
A funeral is a ceremony connected with the final disposition of a corpse, such as a burial or cremation, with the attendant observances. Funerary customs comprise the complex of beliefs and practices used by a culture to remember and respect the dead, from interment, to various monuments, prayers, and rituals undertaken in their honor. Customs vary between cultures and religious groups. Funerals have both normative and legal components. Common secular motivations for funerals include mourning the deceased, celebrating their life, and offering support and sympathy to the bereaved; additionally, funerals may have religious aspects that are intended to help the soul of the deceased reach the afterlife, resurrection or reincarnation. The funeral usually includes a ritual through which the corpse receives a final disposition. Depending on culture and religion, these can involve either the destruction of the body (for example, by cremation or sky burial) or its preservation (for examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Façade
A façade () (also written facade) is generally the front part or exterior of a building. It is a Loanword, loan word from the French language, French (), which means 'frontage' or 'face'. In architecture, the façade of a building is often the most important aspect from a design standpoint, as it sets the tone for the rest of the building. From the engineering perspective, the façade is also of great importance due to its impact on Efficient energy use, energy efficiency. For historical façades, many local zoning regulations or other laws greatly restrict or even forbid their alteration. Etymology The word is a loanword from the French , which in turn comes from the Italian language, Italian , from meaning 'face', ultimately from post-classical Latin . The earliest usage recorded by the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' is 1656. Façades added to earlier buildings It was quite common in the Georgian architecture, Georgian period for existing houses in English towns to be give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Carving
Stone carving is an activity where pieces of rough natural stone are shaped by the controlled removal of stone. Owing to the permanence of the material, stone work has survived which was created during our prehistory or past time. Work carried out by paleolithic societies to create stone tools is more often referred to as knapping. Stone carving that is done to produce lettering is more often referred to as lettering. The process of removing stone from the earth is called mining or quarrying. Stone carving is one of the processes which may be used by an artist when creating a sculpture. The term also refers to the activity of masons in dressing stone blocks for use in architecture, building or civil engineering. It is also a phrase used by archaeologists, historians, and anthropologists to describe the activity involved in making some types of petroglyphs. History The earliest known works of representational art are stone carvings. Often marks carved into rock or petrog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
