|
Canis Etruscus
''Canis etruscus'', the Etruscan wolf, is an extinct species of canine that was endemic to Mediterranean Europe during the Early Pleistocene. The Etruscan wolf has been described as a small wolf-like dog. The Etruscan wolf has been accepted as the ancestor of '' C. mosbachensis'', that is the ancestor of the grey wolf (''C. lupus''), for a long time. Recent research has suggested that ''C. borjgali'' from Dmanisi has to be considered the ancestor of '' C. mosbachensis''. Taxonomy The fossil record for ancient vertebrates is composed of rarely occurring fragments, from which it is often impossible to obtain genetic material. Researchers are limited to morphologic analysis but it is difficult to estimate the intra-species and inter-species variations and relationships that existed between specimens across time and place. Some observations are debated by researchers who do not always agree, and hypotheses that are supported by some authors are challenged by others. Several specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Pleistocene
The Early Pleistocene is an unofficial sub-epoch in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, being the earliest division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently estimated to span the time between 2.580 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago) and 0.773 ± 0.005 Ma. The term Early Pleistocene applies to both the Gelasian Age (to 1.800 ± 0.005 Ma) and the Calabrian Age. While the Gelasian and the Calabrian have officially been defined by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) to effectively constitute the Early Pleistocene, the succeeding Chibanian and Tarantian ages have yet to be ratified. These proposed ages are unofficially termed the Middle Pleistocene and Late Pleistocene respectively. The Chibanian provisionally spans time from 773 ka to 126 ka, and the Tarantian from then until the definitive end of the whole Pleistocene, c. 9700 BC in the 10th millennium BC The 10th millennium BC spanned the ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valdarno
The Valdarno is the valley of the river Arno, although this name does not apply to the entire river basin. Usage of the term generally excludes Casentino and the valleys formed by major tributaries. Some towns in the area: *Rignano sull'Arno * Figline e Incisa Valdarno *San Giovanni Valdarno *Montevarchi * Terranuova Bracciolini *Reggello Reggello is a '' comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Florence in the Italian region of Tuscany, located about southeast of Florence, between the north-western side of Pratomagno and the Upper Valdarno. The municipality bor ... * Castelfranco Piandiscò Valleys of Tuscany {{Tuscany-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nea Apollonia
Nea Apollonia ( el, Νέα Απολλωνία) is a village and a community of the Volvi municipality. Before the 2011 local government reform it was part of the municipality of Apollonia, of which it was a municipal district. The 2011 census recorded 1,851 inhabitants in the village and 1,922 inhabitants in the community. The community of Nea Apollonia covers an area of 70.855 km2. Administrative division The community of Volvi consists of four separate settlements: *Loutra Volvis (population 54) * Mesopotamo (population 17) *Nea Apollonia (population 1,851) The aforementioned population figures are as of 2011. See also * List of settlements in the Thessaloniki regional unit This is a list of settlements in the Thessaloniki regional unit, Greece: * Adam * Adendro * Agia Paraskevi * Agia Triada * Agios Antonios * Agios Athanasios * Agios Charalambos * Agios Pavlos * Agios Vasileios * Akropotamos * Ampelokipo ... References {{Volvi div Populated places in T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set (mathematics), set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canis Etruscus Restoration
''Canis'' is a genus of the Caninae which includes multiple extant species, such as wolves, dogs, coyotes, and golden jackals. Species of this genus are distinguished by their moderate to large size, their massive, well-developed skulls and dentition, long legs, and comparatively short ears and tails.Heptner, V. G.; Naumov, N. P. (1998). ''Mammals of the Soviet Union'' Vol.II Part 1a, SIRENIA AND CARNIVORA (Sea Cows, Wolves and Bears). Science Publishers, Inc. USA. pp. 124–129. . Taxonomy The genus ''Canis'' (Carl Linnaeus, 1758) was published in the 10th edition of Systema Naturae and included the dog-like carnivores: the domestic dog, wolves, coyotes and jackals. All species within ''Canis'' are phylogenetically closely related with 78 chromosomes and can potentially interbreed. In 1926, the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) in Opinion 91 included Genus ''Canis'' on its ''Official Lists and Indexes of Names in Zoology''. In 1955, the ICZN's Direction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canis Arnensis
''Canis arnensis'', the Arno River dog, is an extinct species of canine that was endemic to Mediterranean Europe during the Early Pleistocene. The Arno River dog has been described as a small jackal-like dog. Its anatomy and morphology relate it more to the modern golden jackal (''Canis aureus'') than to the larger Etruscan wolf of that time. It is probably the ancestor of modern jackals. Taxonomy The fossil record for ancient vertebrates is composed of rarely occurring fragments from which it is often impossible to obtain genetic material. Researchers are limited to morphologic analysis, but it is difficult to estimate the intraspecies and interspecies variations and relationships that existed between specimens across time and place. Some observations are debated by researchers who do not always agree and hypotheses that are supported by some authors are challenged by others. Several species of Caninae from the Pleistocene of Europe have been described. Most of their syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jackal
Jackals are medium-sized canids native to Africa and Eurasia. While the word "jackal" has historically been used for many canines of the subtribe canina, in modern use it most commonly refers to three species: the closely related black-backed jackal (''Lupulella mesomelas'') and side-striped jackal (''Lupulella adusta'') of sub-Saharan-Africa, and the golden jackal (''Canis aureus'') of south-central Europe and Asia. The African golden wolf (''Canis lupaster'') was also formerly considered as a jackal. While they do not form a monophyletic clade, all jackals are opportunistic omnivores, predators of small to medium-sized animals and proficient scavengers. Their long legs and curved canine teeth are adapted for hunting small mammals, birds, and reptiles, and their large feet and fused leg bones give them a physique well-suited for long-distance running, capable of maintaining speeds of for extended periods of time. Jackals are crepuscular, most active at dawn and dusk. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canis Falconeri
''Xenocyon'' ("strange dog") is an extinct subgenus of ''Canis''. The group includes ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ''africanus'', ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ''antonii'' and ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ''falconeri'' that gave rise to ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ''lycanoides''. The hypercarnivorous ''Xenocyon'' gave rise to the modern dhole and the African wild dog. Taxonomy ''Xenocyon'' is proposed as a subgenus of ''Canis'' named ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon''). One taxonomic authority proposes that as part of this subgenus, the group named ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ex gr. ''falconeri'' (ex gr. meaning "of the group including") would include all of the large hypercarnivorous canids that inhabited the Old World during the Late Pliocene–Early Pleistocene: ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ''africanus'' in Africa, ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ''antonii'' in Asia and ''Canis'' (''Xenocyon'') ''falconeri'' in Europe. Further, these three could be regarded as extreme geographical variations within the one taxon. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faunal Turnover
An evolutionary radiation is an increase in taxonomic diversity that is caused by elevated rates of speciation, that may or may not be associated with an increase in morphological disparity. Radiations may affect one clade or many, and be rapid or gradual; where they are rapid, and driven by a single lineage's adaptation to their environment, they are termed adaptive radiations. Examples Perhaps the most familiar example of an evolutionary radiation is that of placental mammals immediately after the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs at the end of the Cretaceous, about 66 million years ago. At that time, the placental mammals were mostly small, insect-eating animals similar in size and shape to modern shrews. By the Eocene (58–37 million years ago), they had evolved into such diverse forms as bats, whales, and horses. Other familiar radiations include the Avalon Explosion, the Cambrian Explosion, the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event, the Carboniferous-Earliest Perm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villafranchian
Villafranchian age ( ) is a period of geologic time (3.5–1.0 Ma) spanning the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene used more specifically with European Land Mammal Ages. Named by Italian geologist Lorenzo Pareto for a sequence of terrestrial sediments studied near Villafranca d'Asti, a town near Turin,http://archaeologywordsmith.com/lookup.php?category=&where=headword&terms=Villafranchian it succeeds the Ruscinian age, and is followed by the Galerian. The Villafranchian is sub-divided into six faunal units based on the localities of Triversa, Montopoli, Saint-Vallier, Olivola, Tasso and Farnetta.The Pleistocene Boundary and the Beginning of the Quaternary edited by John A. Van Couvering. Cambridge University Press 1997 A major division of both geological deposits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
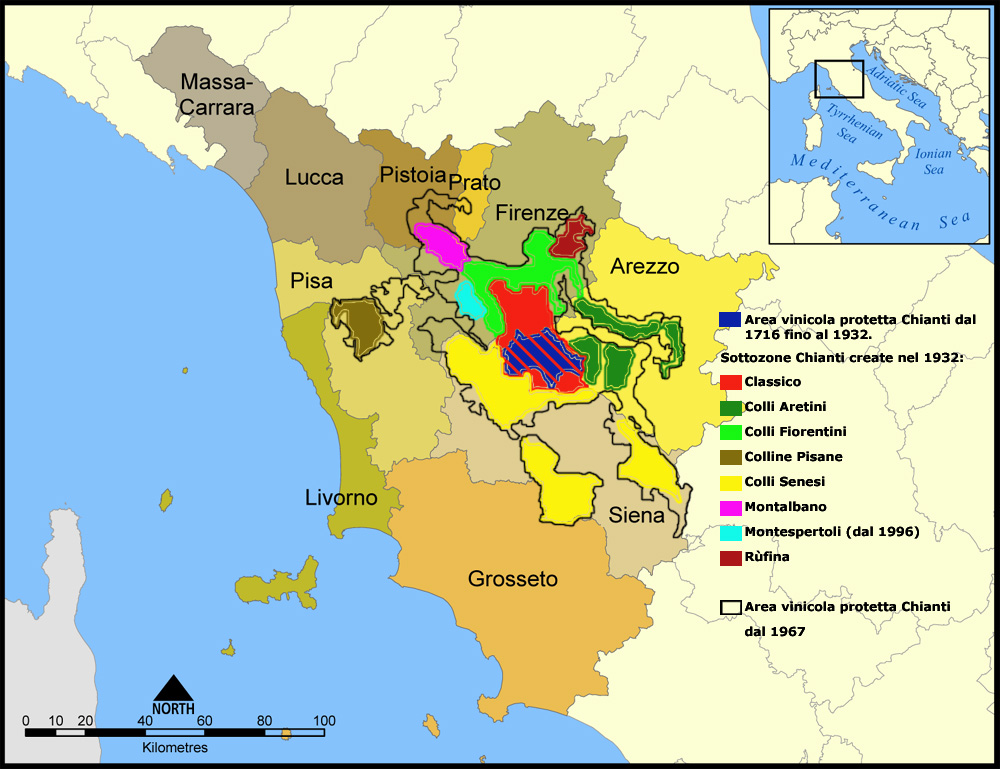
Chianti (region)
Chianti (), in Italy also referred to as Monti del Chianti ("Chianti Mountains") or Colline del Chianti ("Chianti Hills"), is a mountainous area of Tuscany in the provinces of Florence, Siena and Arezzo, composed mainly of hills and mountains. It is known for the wine produced in and named for the region, Chianti. History The territory of Chianti was initially limited, in the thirteenth century, by the municipalities of Gaiole in Chianti, Radda in Chianti and Castellina in Chianti and thus defined the "Chianti League" (Lega di Chianti). Cosimo III de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany, even decided in 1716 to issue an edict in which he officially recognized the boundaries of the Chianti district, which was the first legal document in the world to define a wine production area. The villages of Chianti are often characterized by Romanesque churches and fortified medieval castles, signs of the ancient wars between Siena and Florence or as Monteriggioni, a fortified village north of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratomagno
The Pratomagno is a mountain range, which has the Arno River on both sides: to the west is the upper Valdarno and to the east is the Casentino. It lies north-west of the city of Arezzo, in Tuscany, Italy Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical .... Its highest peak has an elevation of 1,592 m. References {{Coord, 43, 39, N, 11, 39, E, display=title, region:IT_type:mountain_source:GNS-enwiki Mountain ranges of Italy Apennine Mountains Mountains of Tuscany Metropolitan City of Florence Province of Arezzo Geographical, historical and cultural regions of Italy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)