|
Canine Vector-borne Disease
A canine vector-borne disease (CVBD) is one of "a group of globally distributed and rapidly spreading illnesses that are caused by a range of pathogens transmitted by arthropods including ticks, fleas, mosquitoes and phlebotomine sandflies."Domenico Otranto, Filipe Dantas-Torres & Edward B. BreitschwerdtManaging canine vector-borne diseases of zoonotic concern: part one ''Trends in Parasitology'' Vol. 25, Issue 4, pp. 157–163 (April 2009). CVBDs are important in the fields of veterinary medicine, animal welfare, and public health. Some CVBDs are of zoonotic concern. Many CVBD are transmissible to humans as well as companion animals. Some CVBD are fatal; most can only be controlled, not cured. Therefore, infection should be avoided by preventing arthropod vectors from feeding on the blood of their preferred hosts. While it is well known that arthropods transmit bacteria and protozoa during blood feeds, viruses are also becoming recognized as another group of transmitted pathoge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time frames, but soil has the longest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leishmania Infantum
''Leishmania infantum'' is the causative agent of infantile visceral leishmaniasis in the Mediterranean region and in Latin America, where it has been called ''Leishmania chagasi''. It is also an unusual cause of cutaneous leishmaniasis, which is normally caused by specific lineages (or zymodemes). Wild canids and domestic dogs are the natural reservoir of this organism. The sandfly species ''Lutzomyia longipalpis'' serves as the primary vector for the transmission of the disease. ''Leishmania infantum'' is closely related to ''Leishmania donovani'', and some authors believe that these two species are so close as to actually be subspecies of each other; however, phylogenetic analyses can easily distinguish between the two groups despite no difference in morphology in the species complex. Some isolates formerly labelled ''L. donovani'' may be actually ''L. infantum''. Model system for studies of DNA repair Comparative bioinformatic analyses showed that the size of the ''L. infant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ixodidae
The Ixodidae are the family of hard ticks or scale ticks, one of the three families of ticks, consisting of over 700 species. They are known as 'hard ticks' because they have a scutum or hard shield, which the other major family of ticks, the 'soft ticks' (Argasidae), lack. They are ectoparasites of a wide range of host species, and some are vectors of pathogens that can cause human disease. Description They are distinguished from the Argasidae by the presence of a scutum. In both the nymph and the adult, a prominent gnathosoma (or capitulum, mouth and feeding parts) projects forward from the animal's body; in the Argasidae, conversely, the gnathosoma is concealed beneath the body. They differ, too, in their lifecycle; Ixodidae that attach to a host bite painlessly and are generally unnoticed, and they remain in place until they engorge and are ready to change their skin; this process may take days or weeks. Some species drop off the host to moult in a safe place, whereas others r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chagas Disease
Chagas disease, also known as American trypanosomiasis, is a tropical parasitic disease caused by ''Trypanosoma cruzi''. It is spread mostly by insects in the subfamily ''Triatominae'', known as "kissing bugs". The symptoms change over the course of the infection. In the early stage, symptoms are typically either not present or mild, and may include fever, swollen lymph nodes, headaches, or swelling at the site of the bite. After four to eight weeks, untreated individuals enter the chronic phase of disease, which in most cases does not result in further symptoms. Up to 45% of people with chronic infections develop heart disease 10–30 years after the initial illness, which can lead to heart failure. Digestive complications, including an enlarged esophagus or an enlarged colon, may also occur in up to 21% of people, and up to 10% of people may experience nerve damage. is commonly spread to humans and other mammals by the bite of a kissing bug. The disease may also be spr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypanosomiasis
Trypanosomiasis or trypanosomosis is the name of several diseases in vertebrates caused by parasitic protozoan trypanosomes of the genus ''Trypanosoma''. In humans this includes African trypanosomiasis and Chagas disease. A number of other diseases occur in other animals. African trypanosomiasis, which is caused by either ''Trypanosoma brucei gambiense'' or ''Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense'', threatens some 65 million people in sub-Saharan Africa, especially in rural areas and populations disrupted by war or poverty. The number of cases has been going down due to systematic eradication efforts: in 1998 almost 40,000 cases were reported but almost 300,000 cases were suspected to have occurred; in 2009, the number dropped below 10,000; and in 2018 it dropped below 1000. Chagas disease causes 21,000 deaths per year mainly in Latin America. Signs and symptoms The tsetse fly bite erupts into a red chancre sore and within a few weeks, the person can experience fever, swollen lymph gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypanosoma Cruzi
''Trypanosoma cruzi'' is a species of parasitic euglenoids. Among the protozoa, the trypanosomes characteristically bore tissue in another organism and feed on blood (primarily) and also lymph. This behaviour causes disease or the likelihood of disease that varies with the organism: Chagas disease in humans, dourine and surra in horses, and a brucellosis-like disease in cattle. Parasites need a host body and the haematophagous insect triatomine (descriptions "assassin bug", "cone-nose bug", and "kissing bug") is the major vector in accord with a mechanism of infection. The triatomine likes the nests of vertebrate animals for shelter, where it bites and sucks blood for food. Individual triatomines infected with protozoa from other contact with animals transmit trypanosomes when the triatomine deposits its faeces on the host's skin surface and then bites. Penetration of the infected faeces is further facilitated by the scratching of the bite area by the human or animal host. Life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reduviidae
The Reduviidae are a large cosmopolitan family of the order Hemiptera (true bugs). Among the Hemiptera and together with the Nabidae almost all species are terrestrial ambush predators: most other predatory Hemiptera are aquatic. The main examples of nonpredatory Reduviidae are some blood-sucking ectoparasites in the subfamily Triatominae. Though spectacular exceptions are known, most members of the family are fairly easily recognizable; they have a relatively narrow neck, sturdy build, and a formidable curved proboscis (sometimes called a rostrum). Large specimens should be handled with caution, if at all, because they sometimes defend themselves with a very painful stab from the proboscis. Taxonomy The Reduviidae are members of the suborder Heteroptera of the order Hemiptera. The family members are almost all predatory, except for a few blood-sucking species, some of which are important as disease vectors. About 7000 species have been described, in more than 20 recognized subfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leishmania Major
''Leishmania major'' is a species of parasite found in the genus ''Leishmania'', and is associated with the disease zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis (also known as Aleppo boil, Baghdad boil, Bay sore, Biskra button, Chiclero ulcer, Delhi boil, Kandahar sore, Lahore sore, Oriental sore, Pian bois, and Uta). ''L. major'' is an intracellular pathogen which infects the macrophages and dendritic cells of the immune system. Though ''Leishmania'' species are found on every continent aside from Antarctica, ''Leishmania major'' is found only in the Eastern Hemisphere, specifically in Northern Africa, the Middle East, Northwestern China, and Northwestern India. Biology Life cycle As a trypanosomatid, ''L. major'' begins its lifecycle in amastigote form in the midgut of the main vector, female sand flies ('' Phlebotomus spp.''). Once in the gut of the sand fly, the parasites change from aflagelated amastigotes into flagellated promastigotes for 1–2 weeks until they are fully develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leishmania Peruviana
''Leishmania'' is a parasitic protozoan, a single-celled organism of the genus ''Leishmania'' that are responsible for the disease leishmaniasis. They are spread by sandflies of the genus ''Phlebotomus'' in the Old World, and of the genus ''Lutzomyia'' in the New World. At least 93 sandfly species are proven or probable vectors worldwide.WHO (2010) Annual report. Geneva Their primary hosts are vertebrates; ''Leishmania'' commonly infects hyraxes, canids, rodents, and humans. History Members of an ancient genus of the ''Leishmania'' parasite, ''Paleoleishmania'', have been detected in fossilized sand flies dating back to the early Cretaceous period. The first written reference to the conspicuous symptoms of cutaneous leishmaniasis surfaced in the Paleotropics within oriental texts dating back to the 7th century BC (allegedly transcribed from sources several hundred years older, between 1500 and 2000 BC). Due to its broad and persistent prevalence throughout antiquity as a myster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
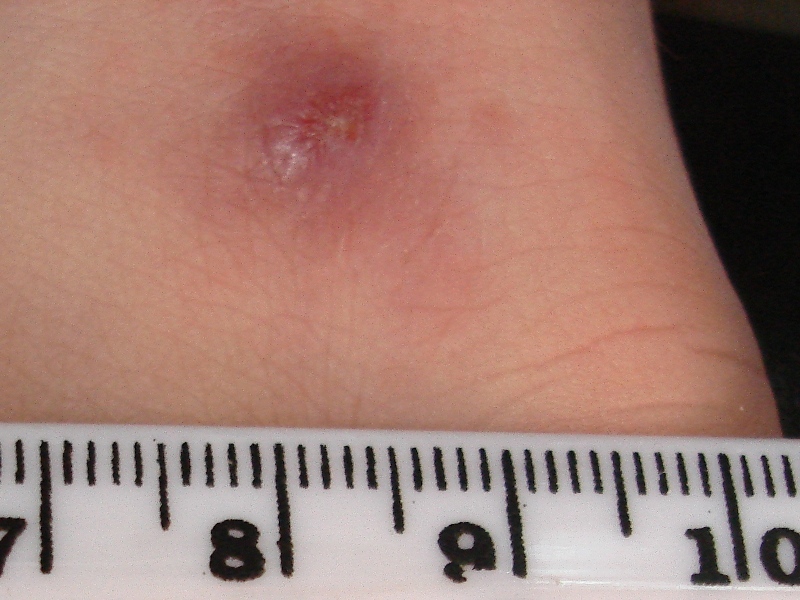
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is the most common form of leishmaniasis affecting humans. It is a skin infection caused by a single-celled parasite that is transmitted by the bite of a phlebotomine sand fly. There are about thirty species of ''Leishmania'' that may cause cutaneous leishmaniasis. This disease is considered to be a zoonosis (an infectious disease that is naturally transmissible from animals to humans), with the exception of ''Leishmania tropica'' — which is often an anthroponotic disease (an infectious disease that is naturally transmissible from humans to vertebrate animals). Signs and symptoms Post kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis Post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis (PKDL) is a recurrence of kala-azar that may appear on the skin of affected individuals months and up to 20 years after being partially treated, untreated or even in those considered adequately treated. In Sudan, they can be demonstrated in up to 60% of treated cases. They manifest as hypopigmented ski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leishmania Tropica
''Leishmania tropica'' is a flagellate parasite and the cause of anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in humans. This parasite is restricted to Afro-Eurasia and is a common cause of infection in Afghanistan, Iran, Syria, Yemen, Algeria, Morocco, and northern India. History The first description of ''Leishmania tropica'' was done in 1903 by James Homer Wright, an American pathologist. In 1914, it was suggested that ''L. tropica'' should be divided into two subspecies, namely ''L. tropica minor'' and ''L. tropica major'', based on the size of the parasites found in skin lesions. Later, these two subspecies turned out to be epidemiologically different and were correlated to different types of lesions. ''L. tropica minor'' causes dry nodular lesions in urban environments, while ''L. tropica major'' causes wet ulcerating lesions in rural regions. Bray et al. therefore proposed in 1973 that the subspecies should be considered as two separate species, ''L. tropica major'' became '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by parasites of the Trypanosoma, trypanosome genus ''Leishmania''. It is generally spread through the bite of Phlebotominae, phlebotomine Sandfly, sandflies, ''Phlebotomus'' and ''Lutzomyia'', and occurs most frequently in the tropics and sub-tropics of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and southern Europe. The disease can present in three main ways: Cutaneous leishmaniasis, cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral leishmaniasis, visceral. The cutaneous form presents with skin ulcers, while the mucocutaneous form presents with ulcers of the skin, mouth, and nose. The visceral form starts with skin ulcers and later presents with fever, low red blood cell count, and enlarged spleen and liver. Infections in humans are caused by more than 20 species of ''Leishmania''. Risk factors include poverty, malnutrition, deforestation, and urbanization. All three types can be diagnosed by seeing the parasites under microscopy. Addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |